The Climate of
Japan
 Temple in Okazaki, Aichi
Temple in Okazaki, Aichi
Climate Map
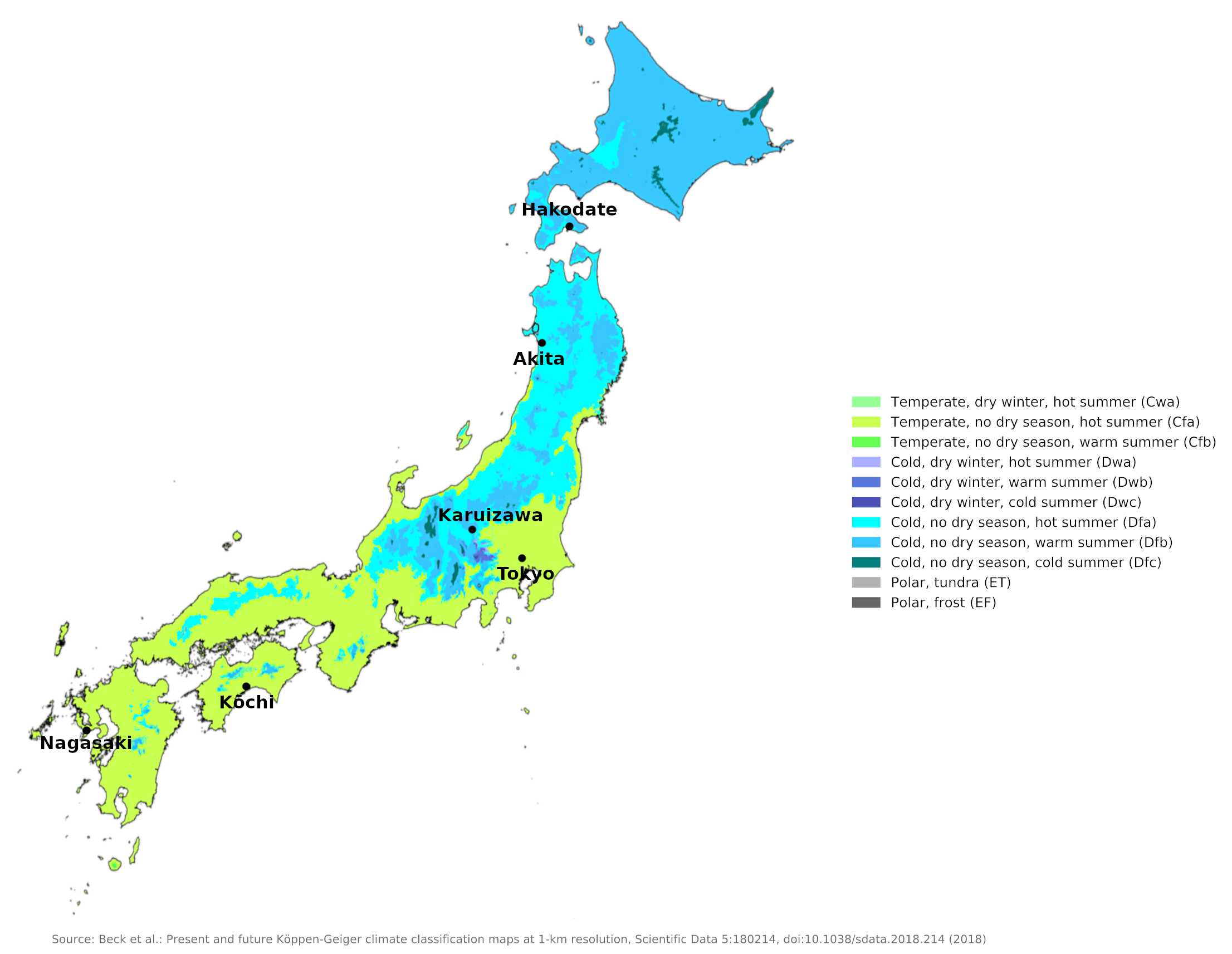 Climate map of Japan
Climate map of Japan
What is the climate of Japan like?
Japan comprises a group of islands between 45° and 32°N off the east coast of Asia. The total area of the country is about one and a half times the size of the United Kingdom. From north to south, the main islands are Hokkaido, Honshu (the largest island), Shikoku and Kyushu. All islands are hilly or even mountainous, especially Honshu where the highest peaks like Fujiyama reach over 3,600 meters (12,000 feet). There are numerous other peaks that rise above 2,000 meters (6,500 feet), many of which are extinct or even active volcanoes. The higher mountains in Hokkaido and Honshu are snow-capped all year round.
Most of Japan is in the temperate zone, with the exception of the subtropical southern island chains. The climate is heavily influenced by the major seasonal wind reversal of the Asian monsoon, but there are important differences between Japan and Korea or northern China. Japan has a climate modified and tempered by the surrounding sea; Winters are less cold than at the same latitude on the continent, and rainfall is much heavier.
The weather is under the dual influence of the Siberian weather system and Southern Pacific patterns. The climate from June to September is marked by hot, wet weather brought by tropical airflows from the Pacific Ocean and Southeast Asia. These airflows are full of moisture and deposit substantial amounts of rain when they reach land. In winter, a high-pressure area develops over Siberia, and a low-pressure area over the northern Pacific Ocean. The result is a flow of cold air eastward across Japan that brings freezing temperatures and heavy snowfalls to the central mountain ranges facing the Sea of Japan, but clear skies to areas fronting on the Pacific.
Two major ocean currents affect this climatic pattern. The warm Japan Current ("Kuroshio") and the cold Kuril Current ("Oyashio"). The Kuroshio Current flows northward on the Pacific side of Japan and warms areas as far north as Tokyo; a small branch, the Tsushima Current, flows up the Sea of Japan side. It creates a milder and more temperate climate than found at comparable latitudes elsewhere. The Oyashio Current affects Northern Japan. It is a cold current that flows along the east coast of Hokkaido and northern Honshu. It which abounds in plankton beneficial to cold-water fish, flows southward along the northern Pacific, cooling adjacent coastal areas. The meeting point of these currents at latitude 36° north is a bountiful fishing ground.
There are four different seasons: winter (December to February), spring (March to May), summer (June to August) and autumn (September to November). There is a marked rainy season, which typically begins in early June. It is followed by hot, sticky weather. Five or six typhoons pass over or near Japan every year from early August to early September, sometimes resulting in significant damage. Annual precipitation, which averages between 1,000 and 2,500 millimeters (40 to 100 inches), is concentrated in the period between June and September. In fact, 70 to 80 percent of the annual precipitation falls during this period.
In summer and early fall, much of the heavy rain is brought by typhoons, or tropical cyclones, moving north from the South China Sea or the region east of the Philippines. Some parts of central and southern Japan experience a double rainfall maximum; one in early summer, the so-called Baiu or Plum Rain, and a second in late summer or early autumn brought by typhoons.
The main rainy season is from May to October, with some regional variations. The southern island of Shikoku is particularly prone to typhoons, which are violent hurricanes from the Pacific Ocean. The typhoon season lasts from May to October, and several storms typically sweep the islands each year, often accompanied by high winds and heavy rains. In regions bordering the Sea of Japan, the snow-laden winter monsoon can be devastating. Flooding is common, particularly in the Pacific coastal areas. In many places great dams and dikes were built against rivers that can flow above the surrounding plains.
Winter rainfall is particularly heavy on the west coast of northern Honshu and Hokkaido. Snowfall is heavy here as the cold, outflowing winter monsoons from Siberia and Manchuria warm and absorb moisture over the sea. In parts of this area, there is more precipitation in winter than in summer. Elsewhere in Japan, winter is a relatively dry season. Much of the cloud and precipitation is associated with depressions that develop where warm, moist Pacific polar air meets cold continental air along the North Pacific polar front. Winter weather varies and is changeable throughout Japan, but especially in the north and west.
In most places in Japan, the daily hours of sunshine are moderate due to the humid atmosphere and copious rainfall. They are lowest in Hokkaido and northern Honshu, where they average two to three hours a day in winter and five or six hours a day in summer. Further south there is more sunshine averaging six to seven hours a day year-round. Summer sun is often less than spring, which is a drier season. Spring is perhaps the most pleasant season in Japan; the weather is usually warm and sunny, but fresher and drier than in summer or autumn.
Northern Japan
Northern Japan has warm summers but long, cold winters. Winters in northern Japan, especially in Hokkaido, are severe with heavy snowfall. At sea level, the climate is very similar to that of Newfoundland or northern New England (see Hakodate in southern Hokkaido and Akita in northern Honshu). Summers are short but fairly warm, and on the east coast, summers are wetter than winters.
| Climate data for Hakodate (1991−2020) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 0.9 (33.6) | 1.8 (35.2) | 5.8 (42.4) | 12.0 (53.6) | 17.0 (62.6) | 20.4 (68.7) | 24.1 (75.4) | 25.9 (78.6) | 23.2 (73.8) | 17.1 (62.8) | 10.0 (50.0) | 3.2 (37.8) | 13.5 (56.3) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −2.4 (27.7) | −1.8 (28.8) | 1.9 (35.4) | 7.3 (45.1) | 12.3 (54.1) | 16.2 (61.2) | 20.3 (68.5) | 22.1 (71.8) | 18.8 (65.8) | 12.5 (54.5) | 6.0 (42.8) | −0.1 (31.8) | 9.4 (48.9) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −6.0 (21.2) | −5.7 (21.7) | −2.2 (28.0) | 2.8 (37.0) | 8.0 (46.4) | 12.6 (54.7) | 17.3 (63.1) | 18.9 (66.0) | 14.6 (58.3) | 7.8 (46.0) | 1.8 (35.2) | −3.6 (25.5) | 5.5 (41.9) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 77.4 (3.05) | 64.5 (2.54) | 64.1 (2.52) | 71.9 (2.83) | 88.9 (3.50) | 79.8 (3.14) | 123.6 (4.87) | 156.5 (6.16) | 150.5 (5.93) | 105.6 (4.16) | 110.8 (4.36) | 94.6 (3.72) | 1,188 (46.77) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 91 (36) | 74 (29) | 41 (16) | 2 (0.8) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 18 (7.1) | 79 (31) | 306 (120) |
| Source: Japan Meteorological Agency | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Akita (1991−2020) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 3.1 (37.6) | 4.0 (39.2) | 7.9 (46.2) | 14.0 (57.2) | 19.6 (67.3) | 23.7 (74.7) | 27.1 (80.8) | 29.2 (84.6) | 25.4 (77.7) | 19.0 (66.2) | 12.2 (54.0) | 5.9 (42.6) | 15.9 (60.6) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 0.4 (32.7) | 0.8 (33.4) | 4.0 (39.2) | 9.6 (49.3) | 15.2 (59.4) | 19.6 (67.3) | 23.4 (74.1) | 25.0 (77.0) | 21.0 (69.8) | 14.5 (58.1) | 8.3 (46.9) | 2.8 (37.0) | 12.1 (53.8) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −2.1 (28.2) | −2.1 (28.2) | 0.4 (32.7) | 5.2 (41.4) | 11.1 (52.0) | 16.0 (60.8) | 20.4 (68.7) | 21.6 (70.9) | 17.1 (62.8) | 10.4 (50.7) | 4.5 (40.1) | 0.0 (32.0) | 8.5 (47.3) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 118.9 (4.68) | 98.5 (3.88) | 99.5 (3.92) | 109.9 (4.33) | 125.0 (4.92) | 122.9 (4.84) | 197.0 (7.76) | 184.6 (7.27) | 161.0 (6.34) | 175.5 (6.91) | 189.1 (7.44) | 159.8 (6.29) | 1,741.6 (68.57) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 100 (39) | 79 (31) | 30 (12) | 1 (0.4) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 6 (2.4) | 58 (23) | 273 (107) |
| Source: Japan Meteorological Agency | |||||||||||||
Central Japan
In central and southern Japan, summers are very warm, and winters are short. Since the country is dominated by humid sea air with frequent cold temperatures, the summer heat is often muggy and oppressive, especially in Japan's big cities. But very hot days are rare.
In the mountains, temperatures are reduced enough by the altitude to be quite comfortable in summer. Conditions here can be very pleasant on sunny days in spring and summer. Compare the climate table for Karuizawa, a hilltop resort at 1,000 meters (3,300 feet), with that for Tokyo, which is on the central Honshu coast, and representative of some of the major cities of Japan.
| Climate data for Karuizawa (1991−2020) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 2.3 (36.1) | 3.5 (38.3) | 7.8 (46.0) | 14.3 (57.7) | 19.2 (66.6) | 21.5 (70.7) | 25.3 (77.5) | 26.3 (79.3) | 21.7 (71.1) | 16.2 (61.2) | 11.2 (52.2) | 5.3 (41.5) | 14.5 (58.2) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −3.3 (26.1) | −2.6 (27.3) | 1.1 (34.0) | 7.0 (44.6) | 12.3 (54.1) | 16.0 (60.8) | 20.1 (68.2) | 20.8 (69.4) | 16.7 (62.1) | 10.5 (50.9) | 4.8 (40.6) | −0.5 (31.1) | 8.6 (47.4) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −8.2 (17.2) | −8.0 (17.6) | −4.5 (23.9) | 0.6 (33.1) | 6.3 (43.3) | 11.8 (53.2) | 16.4 (61.5) | 17.1 (62.8) | 13.0 (55.4) | 6.3 (43.3) | −0.2 (31.6) | −5.3 (22.5) | 3.8 (38.8) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 36.8 (1.45) | 36.8 (1.45) | 68.3 (2.69) | 81.0 (3.19) | 108.8 (4.28) | 154.6 (6.09) | 191.8 (7.55) | 141.6 (5.57) | 193.5 (7.62) | 151.1 (5.95) | 52.5 (2.07) | 29.6 (1.17) | 1,246.2 (49.06) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 44 (17) | 38 (15) | 33 (13) | 5 (2.0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (0.4) | 19 (7.5) | 141 (56) |
| Source: Japan Meteorological Agency | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Tokyo (1991–2020) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 9.8 (49.6) | 10.9 (51.6) | 14.2 (57.6) | 19.4 (66.9) | 23.6 (74.5) | 26.1 (79.0) | 29.9 (85.8) | 31.3 (88.3) | 27.5 (81.5) | 22.0 (71.6) | 16.7 (62.1) | 12.0 (53.6) | 20.3 (68.5) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 5.4 (41.7) | 6.1 (43.0) | 9.4 (48.9) | 14.3 (57.7) | 18.8 (65.8) | 21.9 (71.4) | 25.7 (78.3) | 26.9 (80.4) | 23.3 (73.9) | 18.0 (64.4) | 12.5 (54.5) | 7.7 (45.9) | 15.8 (60.4) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 1.2 (34.2) | 2.1 (35.8) | 5.0 (41.0) | 9.8 (49.6) | 14.6 (58.3) | 18.5 (65.3) | 22.4 (72.3) | 23.5 (74.3) | 20.3 (68.5) | 14.8 (58.6) | 8.8 (47.8) | 3.8 (38.8) | 12.1 (53.8) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 59.7 (2.35) | 56.5 (2.22) | 116.0 (4.57) | 133.7 (5.26) | 139.7 (5.50) | 167.8 (6.61) | 156.2 (6.15) | 154.7 (6.09) | 224.9 (8.85) | 234.8 (9.24) | 96.3 (3.79) | 57.9 (2.28) | 1,598.2 (62.92) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 4 (1.6) | 4 (1.6) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 8 (3.1) |
| Source: Japan Meteorological Agency | |||||||||||||
Southern Japan
In southern Honshu and in Kyushu and Shikoku, winters are mild and almost subtropical. This is especially true on the shores of the Inland Sea, the narrow strip of water that separates these islands. Winter precipitation is light here and snow and frost are very rare (see Kōchi and Nagasaki).
| Climate data for Kōchi (1991−2020) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 12.2 (54.0) | 13.2 (55.8) | 16.3 (61.3) | 20.9 (69.6) | 24.8 (76.6) | 27.1 (80.8) | 30.8 (87.4) | 32.1 (89.8) | 29.5 (85.1) | 25.0 (77.0) | 19.6 (67.3) | 14.4 (57.9) | 22.2 (72.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 6.7 (44.1) | 7.8 (46.0) | 11.2 (52.2) | 15.8 (60.4) | 20.0 (68.0) | 23.1 (73.6) | 27.0 (80.6) | 27.9 (82.2) | 25.0 (77.0) | 19.9 (67.8) | 14.2 (57.6) | 8.8 (47.8) | 17.3 (63.1) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 2.1 (35.8) | 3.1 (37.6) | 6.4 (43.5) | 10.9 (51.6) | 15.5 (59.9) | 19.7 (67.5) | 23.9 (75.0) | 24.5 (76.1) | 21.4 (70.5) | 15.6 (60.1) | 9.7 (49.5) | 4.2 (39.6) | 13.1 (55.6) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 59.1 (2.33) | 107.8 (4.24) | 174.8 (6.88) | 225.3 (8.87) | 280.4 (11.04) | 359.5 (14.15) | 357.3 (14.07) | 284.1 (11.19) | 398.1 (15.67) | 207.5 (8.17) | 129.6 (5.10) | 83.1 (3.27) | 2,666.4 (104.98) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (0.4) |
| Source: Japan Meteorological Agency | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Nagasaki (1991−2020) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 10.7 (51.3) | 12.0 (53.6) | 15.3 (59.5) | 19.9 (67.8) | 23.9 (75.0) | 26.5 (79.7) | 30.3 (86.5) | 31.9 (89.4) | 28.9 (84.0) | 24.1 (75.4) | 18.5 (65.3) | 13.1 (55.6) | 21.2 (70.2) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 7.2 (45.0) | 8.1 (46.6) | 11.2 (52.2) | 15.6 (60.1) | 19.7 (67.5) | 23.0 (73.4) | 26.9 (80.4) | 28.1 (82.6) | 24.9 (76.8) | 20.0 (68.0) | 14.5 (58.1) | 9.4 (48.9) | 17.4 (63.3) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 4.0 (39.2) | 4.5 (40.1) | 7.5 (45.5) | 11.7 (53.1) | 16.1 (61.0) | 20.2 (68.4) | 24.5 (76.1) | 25.3 (77.5) | 21.9 (71.4) | 16.5 (61.7) | 11.0 (51.8) | 6.0 (42.8) | 14.1 (57.4) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 63.1 (2.48) | 84.0 (3.31) | 123.2 (4.85) | 153.0 (6.02) | 160.7 (6.33) | 335.9 (13.22) | 292.7 (11.52) | 217.9 (8.58) | 186.6 (7.35) | 102.1 (4.02) | 100.7 (3.96) | 74.8 (2.94) | 1,894.7 (74.59) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 3 (1.2) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 4 (1.6) |
| Source: Japan Meteorological Agency | |||||||||||||
References
- E. A. Pearce, Charles Gordon Smith, (1990) The Hutchinson World Weather Guide, John Murray Press. ISBN 1859863426
- Timothy L. Gall, (ed.), (2003), Worldmark Encyclopedia of the Nations, Eleventh Edition, Thomson Gale
- Federal Research Division, Library of Congress, (1992), Japan: a country study. Claitor's Pub. Division. ISBN 0844407313
- Hugh Chisholm, (ed.), (1911), Encyclopædia Britannica, Eleventh edition, Cambridge University Press
The Climate of
Japan
In summary:
Most of Japan is in the temperate zone, with the exception of the southern regions, which are almost subtropical. Average temperature ranges from 17°C (63°F) in the southern portions to 9°C (48°F) in the extreme north. There is a winter range of -9°C to 16° C (15°F to 61°F) and a summer range of 20°C to 30°C (68°F to 86°F). Winters tend to be warmer than in similar latitudes except in the north and west, where snowfalls are frequent and heavy. Spring is usually pleasant, and the summer hot and humid. Autumn weather is usually clear and bright.
There is a rainy season that moves from south to north during June and July. The peak rainy season is from May to October, with some regional variations. Yearly rainfall averages 1000 to 2500 mm (40 to 100 in). Winter snowfall is generally heavy along the western coast and in the north.