The Climate of the
United Arab Emirates
 Dubai Creek, a natural tidal creek in Dubai
Dubai Creek, a natural tidal creek in Dubai
Climate Map
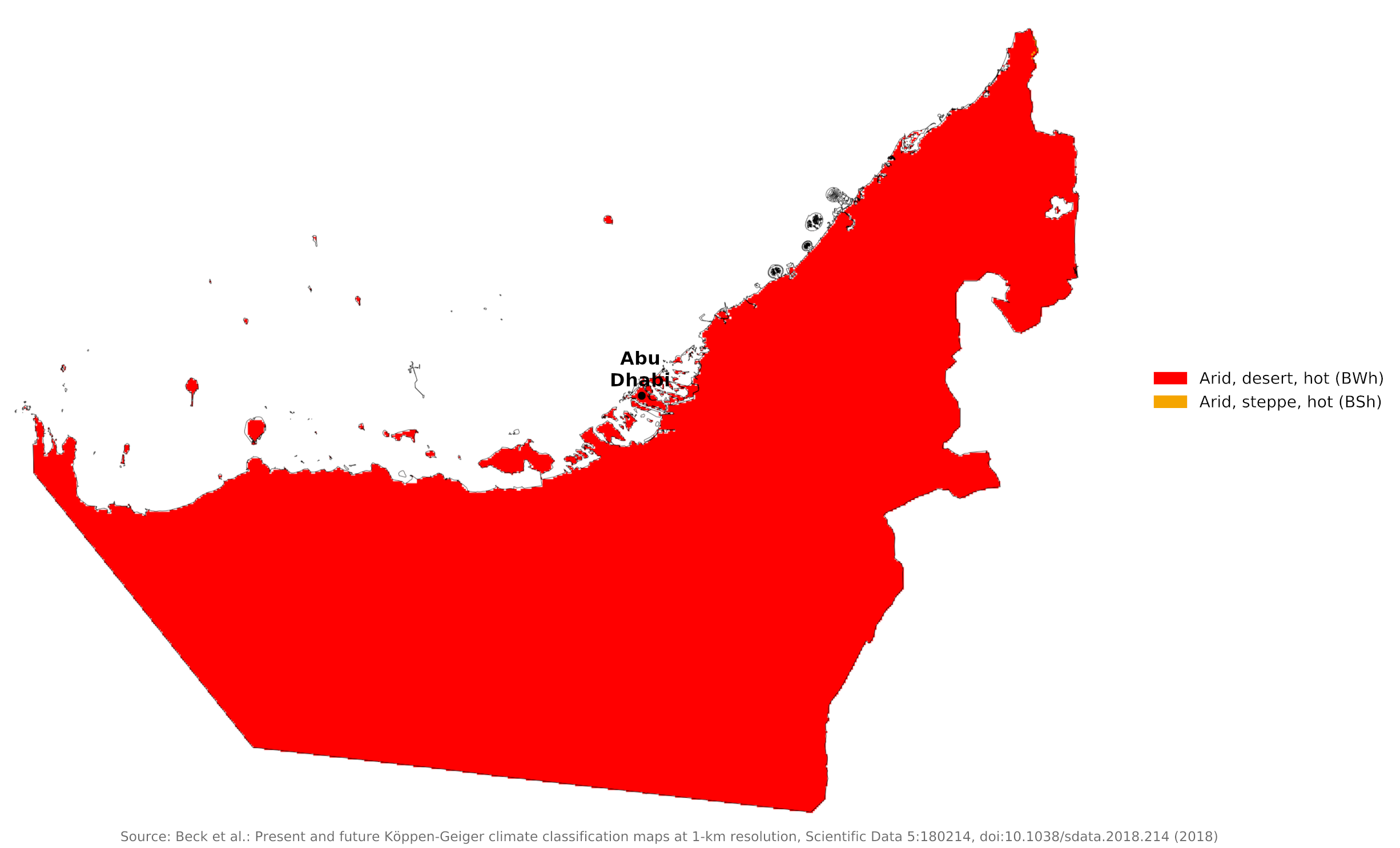 Climate map of the United Arab Emirates
Climate map of the United Arab Emirates
What is the climate of the United Arab Emirates like?
The United Arab Emirates consists of a union of seven small Arab states. They lie on the southern shore of the Persian Gulf between Qatar on the west and Oman on the east. They have a land boundary with Saudi Arabia on the northern fringes of the Rub' al Khali (the "Empty Quarter"). Most of the country is flat and consists of a sandy or rocky desert.
The climate is arid and subtropical, and is generally is hot and dry. Temperatures are very high between May and October and warm to mild for the rest of the year.
The hottest months are July and August, when average maximum temperatures reach 43°C (109°F) on the coastal plain. Summer conditions are most unpleasant on the coast where humidity is high. In the Hajar Mountains in the east, temperatures are cooler, a result of increased altitude. Both inland and on the coast there is some danger of heat exhaustion and heatstroke during the hottest weather. Humidity on the coast can exceed 85 percent. During the late summer months, a humid southeastern wind known as the Sharqi makes the coastal region especially unpleasant.
Winters are warmer than the interior of Saudi Arabia. Average minimum temperatures in January and February are around 13°C (56°F), but average temperatures are around 20°C (68°F).
Annual rainfall is very low and mostly occurs between November and April, with the wettest months being February and March. Normal annual rainfall is from 50 to 100 millimeters (2 to 4 inches), with considerably more in certain regions; the mountains receive an average of 140 to 200 millimeters (5 to 8 inches) and the eastern coast receives an average of 100 to 140 millimeters (4 to 5 inches). Rain in the coastal region falls in short, torrential bursts during the summer months, sometimes resulting in floods in ordinarily dry wadi beds.
The region is prone to occasional, violent dust storms, which can severely reduce visibility. Prevailing winds, including the cool Shamal from the northeast and the Khamsin from the south, produce sandstorms. Influenced by monsoons, they vary by season and location.
| Climate data for Abu Dhabi | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 24.1 (75.4) | 26.0 (78.8) | 29.5 (85.1) | 34.5 (94.1) | 39.3 (102.7) | 40.8 (105.4) | 42.1 (107.8) | 42.7 (108.9) | 40.4 (104.7) | 36.5 (97.7) | 31.1 (88.0) | 26.3 (79.3) | 34.4 (94.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 18.8 (65.8) | 19.6 (67.3) | 22.6 (72.7) | 26.4 (79.5) | 31.2 (88.2) | 33.0 (91.4) | 34.9 (94.8) | 35.3 (95.5) | 32.7 (90.9) | 29.1 (84.4) | 24.5 (76.1) | 20.8 (69.4) | 27.4 (81.3) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 13.2 (55.8) | 14.6 (58.3) | 17.5 (63.5) | 20.8 (69.4) | 23.8 (74.8) | 26.1 (79.0) | 28.8 (83.8) | 29.5 (85.1) | 26.6 (79.9) | 23.2 (73.8) | 18.7 (65.7) | 15.8 (60.4) | 21.5 (70.8) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 7.0 (0.28) | 21.2 (0.83) | 14.5 (0.57) | 6.1 (0.24) | 1.3 (0.05) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1.5 (0.06) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0.3 (0.01) | 5.2 (0.20) | 57.1 (2.24) |
| Source: NOAA | |||||||||||||
References
- E. A. Pearce, Charles Gordon Smith, (1990) The Hutchinson World Weather Guide, John Murray Press. ISBN 1859863426
- Timothy L. Gall, (ed.), (2003), Worldmark Encyclopedia of the Nations, Eleventh Edition, Thomson Gale
- Federal Research Division, Library of Congress, (1994), Persian Gulf states: country studies. Claitor's Pub. Division. ISBN 0844407933
- Hugh Chisholm, (ed.), (1911), Encyclopædia Britannica, Eleventh edition, Cambridge University Press
The Climate of the
United Arab Emirates
In summary:
The climate of the United Arab Emirates is arid and subtropical. The months between May and October are extremely hot, with temperatures exceeding 40°C (104°F) and high humidity near the coast. Winter temperatures average around 20°C (68°F).
Normal annual rainfall is from 50 to 100 mm (2 to 4 in), with rather more in the mountains; most rainfall occurs between November and April.