The Climate of
Alaska
.jpg) Klondike Gold Rush National Historical Park, Skagway
Klondike Gold Rush National Historical Park, Skagway
Climate Map
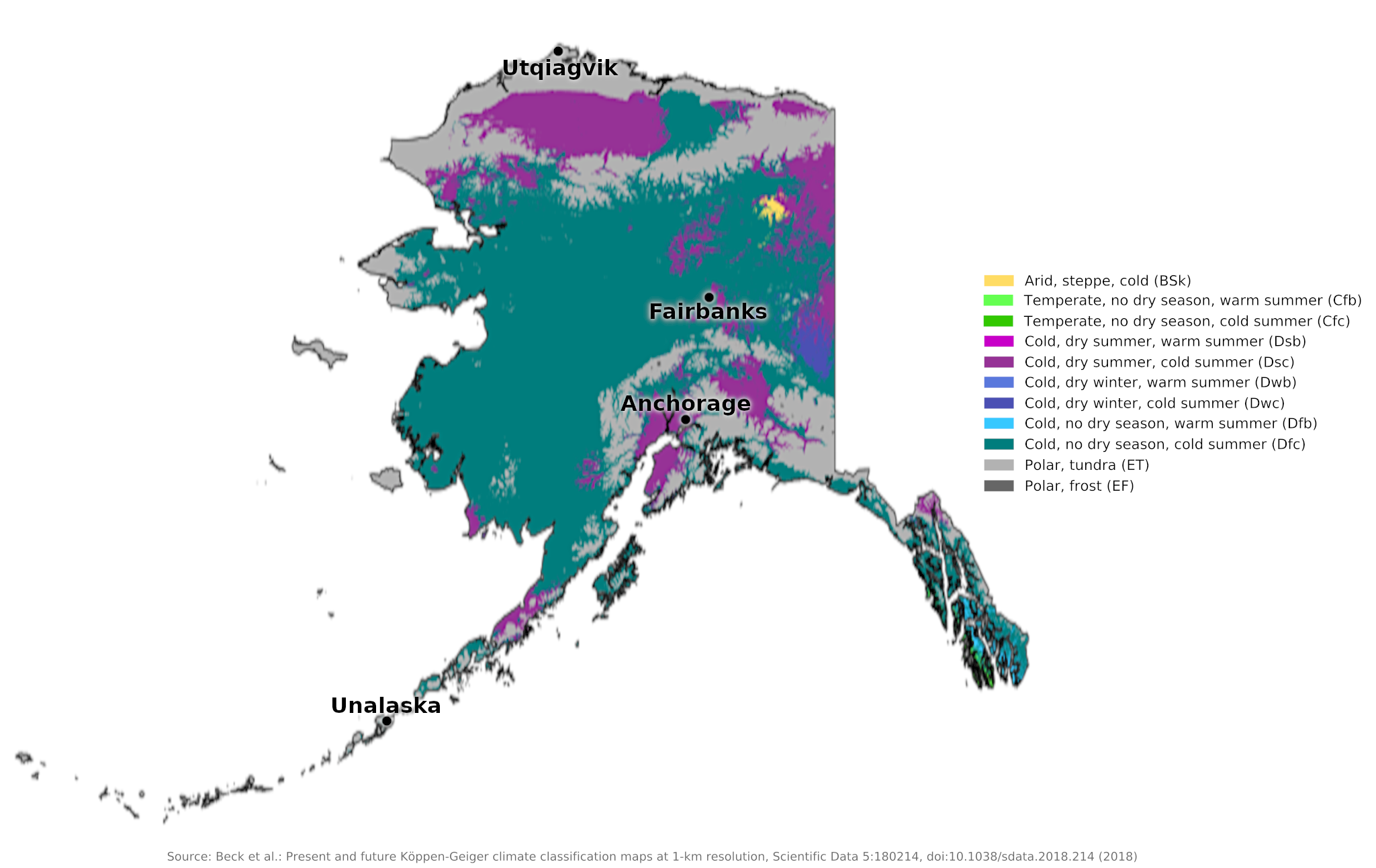 Climate map of Alaska
Climate map of Alaska
What is the climate of Alaska like?
Alaska is one of the states of the USA but separate from the rest of the continental United States. To the east runs a long border with Canada. Alaska is the largest state in the United States, twice the size of Texas. It includes the northwestern parts of the North American continent between 60° and 72°N with separate and distinct appendages. There is a narrow mountainous coastal strip with numerous offshore islands extending south to 55°N to give Alaska a long land border in the North Pacific between 50° and 55°N towards the coast of Siberia.
Much of Alaska is mountainous as it includes the northern mountain ranges of the Rocky Mountains with some of the tallest mountains in North America. Large and impressive glaciers descend from these mountains almost to sea level. Inland are extensive lowlands, including the valleys of the Yukon and Porcupine Rivers.
The interior and north coast of Alaska has a cold arctic or subarctic climate similar to that of northern Canada. The mountains have permanent snow and ice and the lowlands suffer from permafrost. The rivers remain frozen from September to the end of May. Fairbanks is representative of much of interior Alaska. The short summer can be surprisingly warm for the latitude, helped by the long hours of daylight and, weather permitting, sustained sunshine. The winters are long and very severe. Wind chill is a serious hazard when low temperatures are accompanied by strong winds. The low annual rainfall is mostly snow, but summer is the wettest season.
| Climate data for Fairbanks (1991–2020) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °F (°C) | 0.6 (−17.4) | 11.6 (−11.3) | 24.9 (−3.9) | 45.6 (7.6) | 62.1 (16.7) | 71.8 (22.1) | 72.7 (22.6) | 66.4 (19.1) | 55.3 (12.9) | 34.1 (1.2) | 12.3 (−10.9) | 4.3 (−15.4) | 38.5 (3.6) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | −8.3 (−22.4) | 0.2 (−17.7) | 10.7 (−11.8) | 33.7 (0.9) | 50.3 (10.2) | 61.0 (16.1) | 62.9 (17.2) | 57.0 (13.9) | 45.8 (7.7) | 26.2 (−3.2) | 4.1 (−15.5) | −4.3 (−20.2) | 28.3 (−2.1) |
| Average low °F (°C) | −17.2 (−27.3) | −11.2 (−24.0) | −3.4 (−19.7) | 21.7 (−5.7) | 38.6 (3.7) | 50.2 (10.1) | 53.1 (11.7) | 47.6 (8.7) | 36.2 (2.3) | 18.4 (−7.6) | −4.1 (−20.1) | −13 (−25) | 18.1 (−7.7) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 0.61 (15) | 0.52 (13) | 0.40 (10) | 0.34 (8.6) | 0.54 (14) | 1.48 (38) | 2.26 (57) | 2.10 (53) | 1.35 (34) | 0.76 (19) | 0.74 (19) | 0.57 (14) | 11.67 (296) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 10.2 (26) | 10.0 (25) | 6.5 (17) | 3.1 (7.9) | 0.9 (2.3) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 2.3 (5.8) | 8.2 (21) | 12.5 (32) | 10.9 (28) | 64.6 (164) |
| Source: NOAA | |||||||||||||
Summers are colder and shorter here on the Arctic Ocean coast (see the climate of Utqiagvik). The sea is frozen most of the year or partially blocked by drift ice in summer.
| Climate data for Utqiagvik (1991-2020) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °F (°C) | −5.2 (−20.7) | −5.5 (−20.8) | −3.8 (−19.9) | 10.6 (−11.9) | 26.9 (−2.8) | 40.9 (4.9) | 47.7 (8.7) | 44.5 (6.9) | 37.1 (2.8) | 25.6 (−3.6) | 11.5 (−11.4) | −0.4 (−18.0) | 19.2 (−7.1) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | −11.5 (−24.2) | −11.9 (−24.4) | −10.5 (−23.6) | 4.0 (−15.6) | 22.7 (−5.2) | 36.0 (2.2) | 41.7 (5.4) | 39.8 (4.3) | 33.7 (0.9) | 21.2 (−6.0) | 5.7 (−14.6) | −6.3 (−21.3) | 13.7 (−10.2) |
| Average low °F (°C) | −17.8 (−27.7) | −18.3 (−27.9) | −17.2 (−27.3) | −2.5 (−19.2) | 18.5 (−7.5) | 31.1 (−0.5) | 35.6 (2.0) | 35.1 (1.7) | 30.3 (−0.9) | 16.8 (−8.4) | −0.1 (−17.8) | −12.2 (−24.6) | 8.3 (−13.2) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 0.14 (3.6) | 0.21 (5.3) | 0.18 (4.6) | 0.18 (4.6) | 0.28 (7.1) | 0.43 (11) | 0.98 (25) | 1.09 (28) | 0.77 (20) | 0.54 (14) | 0.37 (9.4) | 0.22 (5.6) | 5.39 (138.2) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 3.5 (8.9) | 3.5 (8.9) | 2.9 (7.4) | 3.6 (9.1) | 3.4 (8.6) | 0.7 (1.8) | 0.2 (0.51) | 0.8 (2.0) | 4.1 (10) | 10.3 (26) | 7.8 (20) | 5.0 (13) | 45.8 (116.21) |
| Source: NOAA | |||||||||||||
The weather and climate are slightly different on the Pacific Coast. This is a much heavier rainfall region with more changeable and unsettled weather throughout the year. Summer temperatures are cool and can be less warm than inland. Winters are cool but mild compared to the very low temperatures found inland. The weather and climate here are heavily influenced by the frequent frontal lows that develop in the North Pacific between Japan and the Aleutian Islands. Clouds and fog are common in all seasons. Anchorage sits in a deeply sheltered bay on the west coast and experiences warmer winter temperatures than inland.
| Climate data for Anchorage (1991−2020) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °F (°C) | 22.7 (−5.2) | 27.3 (−2.6) | 33.0 (0.6) | 45.1 (7.3) | 56.3 (13.5) | 63.4 (17.4) | 66.2 (19.0) | 64.0 (17.8) | 55.7 (13.2) | 42.0 (5.6) | 28.9 (−1.7) | 25.0 (−3.9) | 44.1 (6.7) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 16.9 (−8.4) | 21.3 (−5.9) | 25.8 (−3.4) | 37.5 (3.1) | 48.1 (8.9) | 55.9 (13.3) | 59.6 (15.3) | 57.5 (14.2) | 49.3 (9.6) | 36.3 (2.4) | 23.6 (−4.7) | 19.4 (−7.0) | 37.6 (3.1) |
| Average low °F (°C) | 11.0 (−11.7) | 15.2 (−9.3) | 18.6 (−7.4) | 29.9 (−1.2) | 40.0 (4.4) | 48.4 (9.1) | 52.9 (11.6) | 50.9 (10.5) | 42.9 (6.1) | 30.7 (−0.7) | 18.3 (−7.6) | 13.8 (−10.1) | 31.0 (−0.6) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 0.75 (19) | 0.86 (22) | 0.69 (18) | 0.43 (11) | 0.65 (17) | 1.02 (26) | 1.82 (46) | 2.93 (74) | 3.10 (79) | 1.82 (46) | 1.19 (30) | 1.16 (29) | 16.42 (417) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 12.4 (31) | 13.4 (34) | 11.0 (28) | 4.0 (10) | 0.3 (0.76) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.4 (1.0) | 5.6 (14) | 12.6 (32) | 18.2 (46) | 77.9 (198) |
| Source: NOAA | |||||||||||||
Anchorage, however, is much colder than the offshore islands and Aleutian Islands, which benefit from the relatively warm Pacific ocean temperatures. The coastal region and islands have a weather and climate very similar to that of the coasts of Norway. Unalaska is representative of the weather and climate of the Aleutian Islands.
| Climate data for Unalaska (1991–2020) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °F (°C) | 37.3 (2.9) | 38.6 (3.7) | 38.9 (3.8) | 41.8 (5.4) | 46.7 (8.2) | 52.3 (11.3) | 57.4 (14.1) | 59.3 (15.2) | 54.6 (12.6) | 48.1 (8.9) | 43.3 (6.3) | 39.3 (4.1) | 46.5 (8.1) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 33.0 (0.6) | 34.0 (1.1) | 34.1 (1.2) | 37.1 (2.8) | 42.0 (5.6) | 47.3 (8.5) | 52.0 (11.1) | 53.7 (12.1) | 49.4 (9.7) | 43.2 (6.2) | 38.2 (3.4) | 35.0 (1.7) | 41.6 (5.3) |
| Average low °F (°C) | 28.7 (−1.8) | 29.4 (−1.4) | 29.2 (−1.6) | 32.5 (0.3) | 37.4 (3.0) | 42.4 (5.8) | 46.6 (8.1) | 48.1 (8.9) | 44.2 (6.8) | 38.4 (3.6) | 33.2 (0.7) | 30.6 (−0.8) | 36.7 (2.6) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 6.79 (172) | 5.18 (132) | 4.65 (118) | 3.47 (88) | 4.20 (107) | 2.52 (64) | 2.30 (58) | 2.86 (73) | 5.73 (146) | 7.89 (200) | 6.66 (169) | 7.88 (200) | 60.13 (1,527) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 25.6 (65) | 17.3 (44) | 17.2 (44) | 6.4 (16) | 0.4 (1.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 1.1 (2.8) | 6.7 (17) | 18.5 (47) | 93.2 (237) |
| Source: NOAA | |||||||||||||
References
- E. A. Pearce, Charles Gordon Smith, (1990) The Hutchinson World Weather Guide, John Murray Press. ISBN 1859863426
- Timothy L. Gall, (ed.), (2003), Worldmark Encyclopedia of the Nations, Eleventh Edition, Thomson Gale
- Hugh Chisholm, (ed.), (1911), Encyclopædia Britannica, Eleventh edition, Cambridge University Press
The Climate of
Alaska
In summary:
The climate of Alaska varies from maritime-temperate in the south to arctic conditions in the north. The Alaskan summer is relatively dry, the autumn and winter wetter. Snow flurries begin around the middle of September and snow is heavy all winter long, but the air is dry. In May the rivers open, the land thaws out, and in summer the sun shines from eighteen hours or more. Western Alaska is rainy and cool; while in the north the winters are longer and more severe.