The Climate of the
Czech Republic
 The market square in Cheb
The market square in Cheb
Climate Map
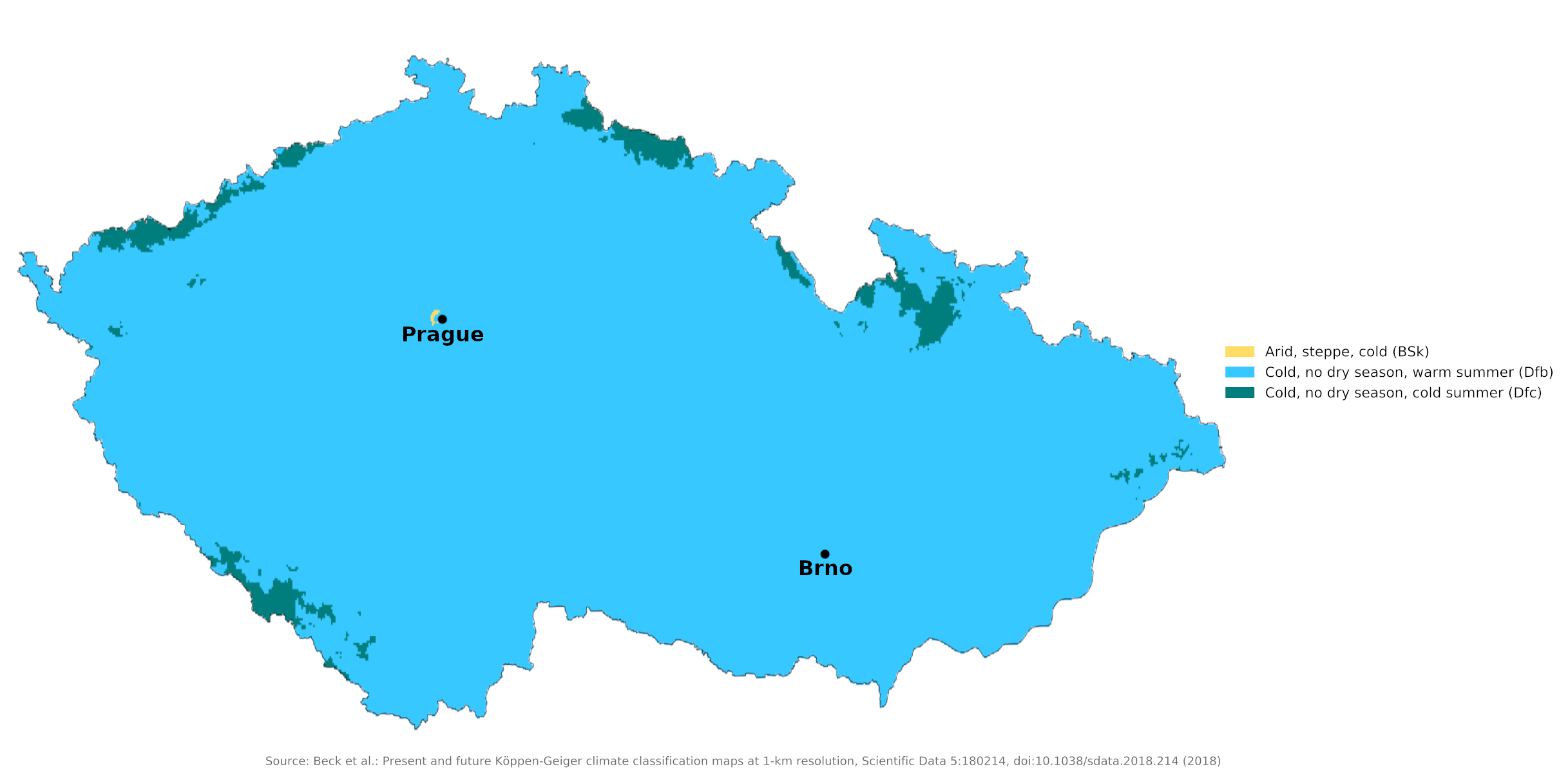 Climate map of the Czech Republic
Climate map of the Czech Republic
What is the climate of the Czech Republic like?
The Czech Republic consists of the ancient provinces of Bohemia and Moravia. The country is hilly with much of its area rising over 1,000 meters (3,250 feet), and with a mountainous rim on the German border. The country shares borders with Poland (north), Slovakia (east), Austria (south), and Germany (west).
The Czech Republic is completely landlocked within Central Europe, with a climate that is transitional between the milder and wetter conditions of Atlantic Europe and the more extreme conditions (severe winters and warm summers) found further east. The country is frequently influenced by the maritime weather prevalent in Western Europe. There is little difference of weather from one area to another and everywhere it can be changeable at all times of the year. However, when the systems to the north are weak, Mediterranean weather may occasionally brush southern parts of the country.
The longest spells of settled weather occur during calm but cold days in winter. The most unpleasant weather occurs in winter, when easterly winds from Russia may bring very low temperatures for several days on end. Both the Moravian lowlands and the Bohemian highlands can experience bitter cold, with temperatures below -18°C (0°F). The mountains are covered with snow from early November through April, and accumulations are deep in some places. The lowlands rarely have more than fifteen centimeters (6 inches) of snow cover at a time.
Summers are moderately warm, with frequent thunderstorms and average temperatures between 13°C to 26°C (55°F and 78°F). Spells of disturbed summer weather are often brought by disturbances originating over the northern Mediterranean. Rainfall comes in sporadic showers, making for many warm, dry days with scattered cumulus clouds. Prevailing winds are westerly; they are usually light in summer (except during thunderstorms) and somewhat stronger in winter. Summer temperatures above 30°C (86°F) are common in Moravia.
Rainfall is heaviest in the spring and summer, with the greatest rainfall occurring in July. Average annual rainfall ranges from 500 to 750 millimeters (20 to 30 inches) in low-lying areas to over 1,250 millimeters (50 inches) in the Krkonoše Mountains. Annual rainfall varies considerably though, and droughts and floods sometimes occur. The number of wet days is rather less than in western Europe and the number of hours of sunshine rather more. Summer sunshine averages as much as eight hours per day.
Prague is illustrative of conditions in Bohemia, whereas Brno is illustrative of conditions in Moravia.
| Climate data for Prague (1981–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 2.6 (36.7) | 4.4 (39.9) | 9.1 (48.4) | 15.1 (59.2) | 20.3 (68.5) | 22.8 (73.0) | 25.3 (77.5) | 25.1 (77.2) | 19.9 (67.8) | 14.2 (57.6) | 7.2 (45.0) | 3.4 (38.1) | 14.1 (57.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 0.1 (32.2) | 1.3 (34.3) | 5.3 (41.5) | 10.1 (50.2) | 15.0 (59.0) | 17.8 (64.0) | 19.9 (67.8) | 19.6 (67.3) | 15.2 (59.4) | 10.3 (50.5) | 4.6 (40.3) | 1.1 (34.0) | 10.0 (50.0) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −2.4 (27.7) | −1.8 (28.8) | 1.5 (34.7) | 5.1 (41.2) | 9.7 (49.5) | 12.7 (54.9) | 14.5 (58.1) | 14.2 (57.6) | 10.5 (50.9) | 6.4 (43.5) | 2.1 (35.8) | −1.1 (30.0) | 6.0 (42.7) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 34 (1.3) | 30 (1.2) | 40 (1.6) | 34 (1.3) | 63 (2.5) | 70 (2.8) | 82 (3.2) | 75 (3.0) | 47 (1.9) | 34 (1.3) | 40 (1.6) | 38 (1.5) | 587 (23.1) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 17.9 (7.0) | 15.9 (6.3) | 10.3 (4.1) | 2.9 (1.1) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.1 (0.0) | 8.4 (3.3) | 15.9 (6.3) | 71.4 (28.1) |
| Source: World Meteorological Organization and Weather Atlas | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Brno (1981–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 1.1 (34.0) | 3.6 (38.5) | 8.7 (47.7) | 15.1 (59.2) | 20.1 (68.2) | 23.0 (73.4) | 25.6 (78.1) | 25.4 (77.7) | 20.0 (68.0) | 13.8 (56.8) | 6.9 (44.4) | 2.0 (35.6) | 13.8 (56.8) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −2.5 (27.5) | −0.3 (31.5) | 3.8 (38.8) | 9.0 (48.2) | 13.9 (57.0) | 17.0 (62.6) | 18.5 (65.3) | 18.1 (64.6) | 14.3 (57.7) | 9.1 (48.4) | 3.5 (38.3) | −0.6 (30.9) | 8.7 (47.7) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −4.3 (24.3) | −3.3 (26.1) | 0.2 (32.4) | 4.5 (40.1) | 9.3 (48.7) | 12.1 (53.8) | 14.0 (57.2) | 13.8 (56.8) | 10.0 (50.0) | 5.7 (42.3) | 1.1 (34.0) | −2.9 (26.8) | 5.0 (41.0) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 23.1 (0.91) | 23.4 (0.92) | 29.7 (1.17) | 28.9 (1.14) | 61.2 (2.41) | 72.2 (2.84) | 69.0 (2.72) | 55.7 (2.19) | 47.9 (1.89) | 31.1 (1.22) | 34.0 (1.34) | 31.9 (1.26) | 508.1 (20.00) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 17.4 (6.9) | 12.4 (4.9) | 5.2 (2.0) | 0.6 (0.2) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 4.5 (1.8) | 12.5 (4.9) | 52.6 (20.7) |
| Source: World Meteorological Organization | |||||||||||||
References
- E. A. Pearce, Charles Gordon Smith, (1990) The Hutchinson World Weather Guide, John Murray Press. ISBN 1859863426
- Timothy L. Gall, (ed.), (2003), Worldmark Encyclopedia of the Nations, Eleventh Edition, Thomson Gale
- Federal Research Division, Library of Congress, (1989), Czechoslovakia: a country study. Claitor's Pub. Division.
- Hugh Chisholm, (ed.), (1911), Encyclopædia Britannica, Eleventh edition, Cambridge University Press
The Climate of
Czechia
In summary:
The Czech Republic has a Central European moderate and transitional climate. The climate is temperate with warm summers, and cold, cloudy, and humid winters. The country as a whole is known for its changeable weather. Rainfall is heaviest in the spring and summer.