The Climate of
Jordan
 Wishes tree in Ajloun
Wishes tree in Ajloun
Climate Map
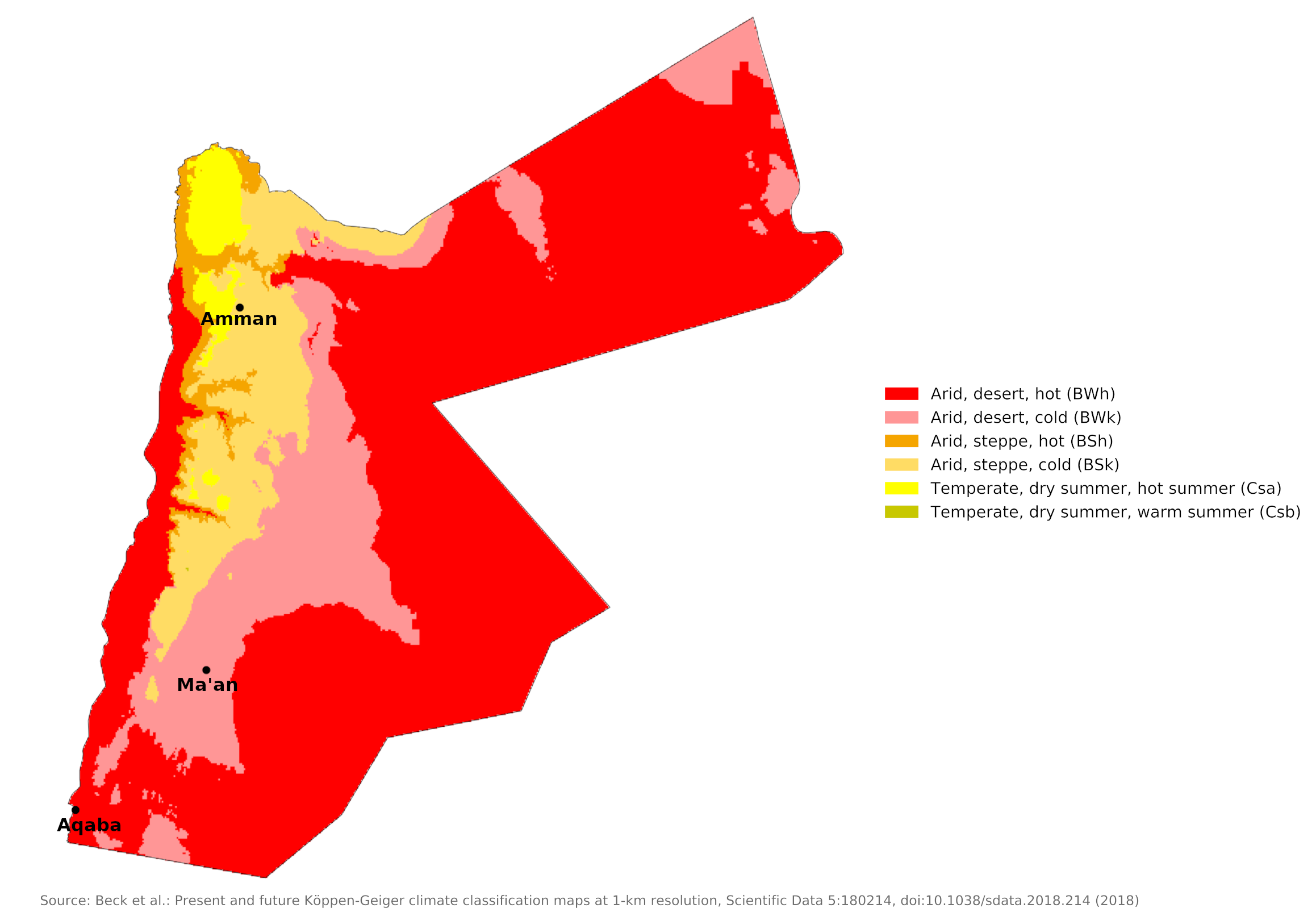 Climate map of Jordan
Climate map of Jordan
What is the climate of Jordan like?
Jordan is a small, almost landlocked, country. It is bordered by Syria on the north, Iraq and Saudi Arabia on the east and south, and Israel on the west. In the extreme south at Aqaba it has a short shoreline on the Gulf of Aqaba branch of the Red Sea.
The main feature of the climate is the contrast between a relatively rainy season from November to April and very dry weather for the rest of the year. The country has a Mediterranean climate, with hot, dry, even summers and cool, changeable winters, during which virtually all precipitation falls. In general, the further away you are from the Mediterranean Sea, the greater the seasonal temperature differences and the less precipitation. Winter months bring with them a series of pronounced low-pressure systems and accompanying cold fronts. These cyclones generally move eastward over the Mediterranean Sea several times a month and result in sporadic rainfall.
For about a month before and after the summer dry season, hot, dry air from the desert, drawn by low pressure, produces strong southerly or south-easterly winds, sometimes reaching gale force. Known as the Khamsin, this dry Scirocco-style wind is usually accompanied by large clouds of dust. Temperatures can rise by 10°C to 15°C (18–27°F) within a few hours. These storms usually last a day or so and cause a lot of discomfort.
The Shammal, another wind of some importance, comes from the north or north-west, generally at intervals between June and September. Remarkably constant during the day but becoming a breeze at night, the Shammal can blow up to nine days out of ten and then repeat the process. It forms as a dry continental mass of polar air that is heated as it moves across the Eurasian landmass. The aridity allows for strong solar heating of the Earth's surface, resulting in high daytime temperatures that moderate after sunset.
Jordan is a very sunny country with average daily hours of sunshine ranging from six to seven in winter and twelve to thirteen in summer. Although summer temperatures are high in the desert, the heat is usually tempered by low humidity and a stiff daytime breeze, while nights are cool and comfortable. The worst weather is brought by the hot, dry winds (especially the Khamsin). Heat stress can occur under these conditions.
The Highlands
The northwestern part of the country is hilly, with some areas rising to over 1,000 meters (3,300 feet). The altitude and proximity to the Mediterranean make this the wettest and most fertile part of Jordan. Here annual rainfall increases from 300 millimeters (12 inches) in the south to 500 or more millimeters (20 inches) in the north.
The country's long summer reaches a peak during August. January is usually the coolest month. Rain falls mainly between November and March. Average temperatures in Amman are 4°C to 12°C (39°F to 54°F) in January and 20°C to 32°C (68°F to 90°F) in August.
| Climate data for Amman | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 12.7 (54.9) | 13.9 (57.0) | 17.6 (63.7) | 23.3 (73.9) | 27.9 (82.2) | 30.9 (87.6) | 32.5 (90.5) | 32.7 (90.9) | 30.8 (87.4) | 26.8 (80.2) | 20.1 (68.2) | 14.6 (58.3) | 23.7 (74.66) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 8.5 (47.3) | 9.4 (48.9) | 12.4 (54.3) | 17.1 (62.8) | 21.4 (70.5) | 24.6 (76.3) | 26.5 (79.7) | 26.6 (79.9) | 24.6 (76.3) | 21.0 (69.8) | 15.0 (59.0) | 10.2 (50.4) | 18.1 (64.6) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 4.2 (39.6) | 4.8 (40.6) | 7.2 (45.0) | 10.9 (51.6) | 14.8 (58.6) | 18.3 (64.9) | 20.5 (68.9) | 20.4 (68.7) | 18.3 (64.9) | 15.1 (59.2) | 9.8 (49.6) | 5.8 (42.4) | 12.5 (54.5) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 60.6 (2.39) | 62.8 (2.47) | 34.1 (1.34) | 7.1 (0.28) | 3.2 (0.13) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.1 (0.00) | 7.1 (0.28) | 23.7 (0.93) | 46.3 (1.82) | 245.0 (9.65) |
| Source: Jordan Meteorological Department | |||||||||||||
Jordan Valley
On the west side of these mountains is the long north-south Jordan Valley which forms a narrow climatic zone. Much of this region lies well below sea level. In this valley, the Jordan flows south to the Dead Sea, the lowest point on earth. Here the winters are very mild and the summers particularly hot; Summer highs of around 38°C (100°F) are common in the Dead Sea region. Rainfall is very light from around 300 millimeters (12 inches) in the northern reaches to less than 100 millimeters (4 inches) in the south.
The climate of Aqaba illustrates the desert conditions in the far south.
| Climate data for Aqaba | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 20.5 (68.9) | 22.3 (72.1) | 25.9 (78.6) | 31.0 (87.8) | 35.3 (95.5) | 38.5 (101.3) | 40.0 (104.0) | 39.6 (103.3) | 36.7 (98.1) | 32.5 (90.5) | 27.0 (80.6) | 22.0 (71.6) | 30.9 (87.6) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 14.9 (58.8) | 16.4 (61.5) | 19.7 (67.5) | 24.3 (75.7) | 28.3 (82.9) | 31.3 (88.3) | 33.1 (91.6) | 33.0 (91.4) | 30.5 (86.9) | 26.6 (79.9) | 21.2 (70.2) | 16.4 (61.5) | 24.6 (76.3) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 9.3 (48.7) | 10.5 (50.9) | 13.4 (56.1) | 17.6 (63.7) | 21.3 (70.3) | 24.0 (75.2) | 26.1 (79.0) | 26.3 (79.3) | 24.2 (75.6) | 20.6 (69.1) | 15.3 (59.5) | 10.8 (51.4) | 18.3 (64.9) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 4.5 (0.18) | 3.7 (0.15) | 3.4 (0.13) | 1.8 (0.07) | 1.0 (0.04) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 3.0 (0.12) | 2.4 (0.09) | 4.9 (0.19) | 24.7 (0.97) |
| Source: Jordan Meteorological Department | |||||||||||||
The Desert
About 90% of Jordan is very dry, and may be classified as a dry desert or steppe region. With an annual rainfall of less than 100 millimeters (4 inches), this is part of the great desert of Arabia and Syria. Summers are consistently hot and sunny, but winter weather can be occasionally cold, with occasional frost, or even snow on the higher ground. The sparse rainfall occurs in winter and spring, usually as heavy showers.
The climate of Ma'an in southern Jordan illustrate these cold-arid desert conditions.
| Climate data for Ma'an (1961–1990) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 13.4 (56.1) | 15.4 (59.7) | 19.0 (66.2) | 24.2 (75.6) | 28.7 (83.7) | 32.4 (90.3) | 33.9 (93.0) | 34.1 (93.4) | 32.3 (90.1) | 27.2 (81.0) | 20.3 (68.5) | 15.1 (59.2) | 24.7 (76.5) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 7.5 (45.5) | 9.1 (48.4) | 12.2 (54.0) | 16.9 (62.4) | 20.8 (69.4) | 24.0 (75.2) | 25.5 (77.9) | 25.6 (78.1) | 23.8 (74.8) | 19.5 (67.1) | 13.5 (56.3) | 9.0 (48.2) | 17.3 (63.1) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 1.6 (34.9) | 2.8 (37.0) | 5.3 (41.5) | 9.5 (49.1) | 13.0 (55.4) | 15.6 (60.1) | 17.2 (63.0) | 17.2 (63.0) | 15.4 (59.7) | 11.7 (53.1) | 6.8 (44.2) | 3.0 (37.4) | 9.9 (49.8) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 7.1 (0.28) | 7.3 (0.29) | 6.9 (0.27) | 3.6 (0.14) | 2.0 (0.08) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.2 (0.01) | 3.8 (0.15) | 4.3 (0.17) | 7.5 (0.30) | 42.7 (1.68) |
| Source: NOAA | |||||||||||||
References
- E. A. Pearce, Charles Gordon Smith, (1990) The Hutchinson World Weather Guide, John Murray Press. ISBN 1859863426
- Timothy L. Gall, (ed.), (2003), Worldmark Encyclopedia of the Nations, Eleventh Edition, Thomson Gale
- Federal Research Division, Library of Congress, (1991), Jordan: a country study. Claitor's Pub. Division.
- Hugh Chisholm, (ed.), (1911), Encyclopædia Britannica, Eleventh edition, Cambridge University Press
The Climate of
Jordan
In summary:
The northwest hills of Jordan have a modified Mediterranean climate, with cool winters and hot, dry summers. The Jordan Valley has intense summer heat, mild but pleasant winters, and little rainfall. The desert regions are subject to great extremes of temperature and very little rain.