The Climate of
Lebanon
 Horsh Beirut, an urban park in the heart of Beirut
Horsh Beirut, an urban park in the heart of Beirut
Climate Map
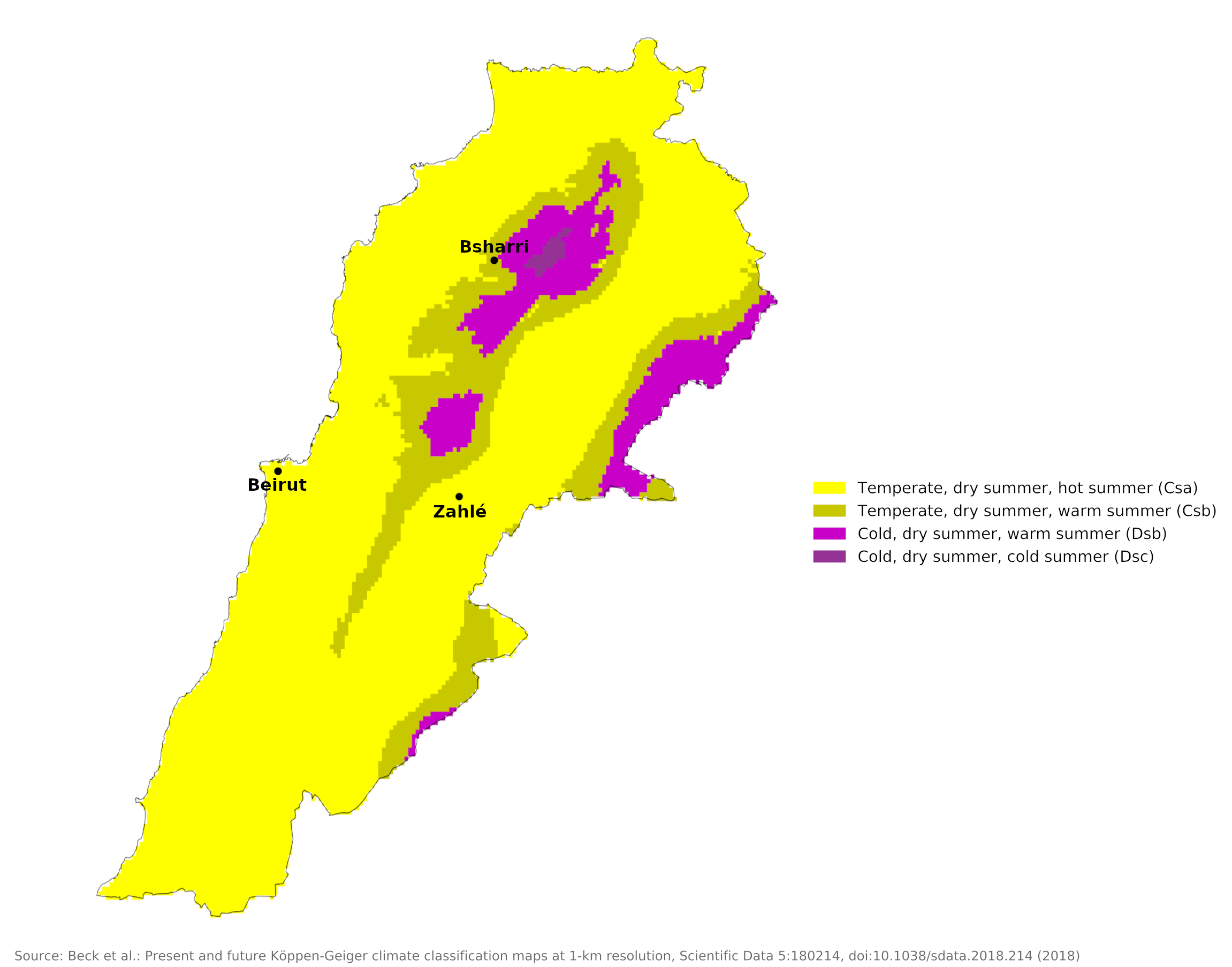 Climate map of Lebanon
Climate map of Lebanon
What is the climate of Lebanon like?
Lebanon is a small, mountainous country lies at the eastern end of the Mediterranean. It is bordered by Syria on the north and east and by Israel on the south. It is about the size of Yorkshire or a little smaller than the state of Connecticut. The country consists of two parallel mountain ranges, running from north to south: the Lebanon Mountains on the west and the Anti-Lebanon range with Mount Hermon on the east. These mountains rise to an average height of over 1,800 meters (6,000 feet) but with summits exceeding 3,000 meters (10,000 feet). These ranges are separated by a narrow north to south valley, the Beqaa, which is everywhere above 1,000 meters (3,300 feet). There is a very narrow plain along the Mediterranean coast.
Lebanon has a Mediterranean climate characterized by a long, hot, and dry summer and cool, rainy winter. But Lebanon has a very varied climate due to the wide range of elevation and the westerly winds that make the Mediterranean coast much wetter than the eastern hills, mountainsides, and valleys. Temperature and precipitation vary greatly from place to place because of the large differences of altitude. Snow lies on the higher mountains until mid-June and some small patches survive throughout the dry, sunny summer.
Average annual rainfall ranges from about 380 millimeters (15 inches) in the Beqaa Valley, to 890 millimeters (35 inches) on the coast, to over 1,250 millimeters (50 inches) in the mountains. Four-fifths of the annual rainfall occurs in the winter months, between November and March. The peaks of the Lebanon Mountains are snow-covered from winter to spring.
The winter rain may be heavy, and disturbed weather brought by Mediterranean depressions may last for several days at a time. In between these unsettled spells of weather there are long periods when it is fine, mild, and sunny. In early and late summer Lebanon is often affected, for a few days at a time, by the hot, dry Khamsin which blows out of Arabia. These winds bring the hottest days and conditions may then be distinctly unpleasant with danger of heat stress.
The Coast
Along the coast, summers are hot and humid, with little or no rain. Humidity is rather high so that the nights may be muggy and a little unpleasant. A sea breeze provides relief during the afternoon and evening; at night the wind direction is reversed, blowing from the land out to sea. Average temperatures in Beirut in the summer are 28°C (82°F).
Winters are very mild along the coast. Winter is the rainy season, but rain is concentrated in just a few days of the rainy season and falls in heavy downpours. The amount of precipitation varies greatly from year to year. There are occasional frosts in winter, and about every fifteen years a light dust of snow falls as far as Beirut. Bitterly cold winds can come from Europe. Proximity to the sea has a moderating effect on the climate, making the temperature range narrower than inland, but temperatures are cooler in the northern parts of the coast, where there is also more rainfall.
Fall is a transitional season with a gradual lowering of temperature and little rain; spring occurs when the winter rains cause the vegetation to revive. The hot Khamsin wind blowing from the Egyptian desert may provide a warming trend during the fall but more often occurs during the spring.
| Climate data for Beirut | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 17.4 (63.3) | 17.5 (63.5) | 19.6 (67.3) | 22.6 (72.7) | 25.4 (77.7) | 27.9 (82.2) | 30.0 (86.0) | 30.7 (87.3) | 29.8 (85.6) | 27.5 (81.5) | 23.2 (73.8) | 19.4 (66.9) | 24.3 (75.7) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 14.0 (57.2) | 14.0 (57.2) | 16.0 (60.8) | 18.7 (65.7) | 21.7 (71.1) | 24.9 (76.8) | 27.1 (80.8) | 27.8 (82.0) | 26.8 (80.2) | 24.1 (75.4) | 19.5 (67.1) | 15.8 (60.4) | 20.9 (69.6) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 11.2 (52.2) | 11.0 (51.8) | 12.6 (54.7) | 15.2 (59.4) | 18.2 (64.8) | 21.6 (70.9) | 24.0 (75.2) | 24.8 (76.6) | 23.7 (74.7) | 21.0 (69.8) | 16.3 (61.3) | 12.9 (55.2) | 17.7 (63.9) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 154 (6.1) | 127 (5.0) | 84 (3.3) | 31 (1.2) | 11 (0.4) | 1 (0.0) | 0.3 (0.01) | 0 (0) | 5 (0.2) | 60 (2.4) | 115 (4.5) | 141 (5.6) | 730 (28.7) |
| Source: www.pogodaiklimat.ru | |||||||||||||
Lebanon Mountains
In the Lebanon Mountains, the gradual increase in altitude results in colder winters with more precipitation and snow. Summers have a wider daily temperature range and less humidity. In winter, frosts are frequent and it snows heavily; In fact, snow covers the highest peaks for most of the year. During the summer, temperatures can soar as high as on the coast during the day, but drop much lower at night. Residents of coastal towns, as well as visitors, seek refuge from the stifling humidity of the coast by spending much of the summer in the mountains, which are home to numerous summer resorts. (See the climate data for Bsharri)
Both the Khamsin and the northern winter wind are felt in the Lebanon mountains. The influence of the Mediterranean is moderated by the high altitude, and although rainfall is still higher than on the coast, temperature ranges are wider and winters are harsher.
| Climate data for Bsharri | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 4 (39) | 4 (39) | 6 (43) | 11 (52) | 16 (61) | 20 (68) | 22 (72) | 23 (73) | 20 (68) | 16 (61) | 11 (52) | 7 (45) | 13 (56) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 0 (32) | 0 (32) | 2 (36) | 7 (45) | 11.5 (52.7) | 15 (59) | 17 (63) | 17.5 (63.5) | 15 (59) | 11.5 (52.7) | 7 (45) | 3.5 (38.3) | 8.9 (48.2) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −4 (25) | −4 (25) | −2 (28) | 3 (37) | 7 (45) | 10 (50) | 12 (54) | 12 (54) | 10 (50) | 7 (45) | 3 (37) | 0 (32) | 5 (40) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 221 (8.7) | 166 (6.5) | 127 (5.0) | 61 (2.4) | 31 (1.2) | 4 (0.2) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 6 (0.2) | 39 (1.5) | 97 (3.8) | 172 (6.8) | 924 (36.3) |
| Source: Climatetemp.info | |||||||||||||
The Beqaa Valley and the eastern Mountains
Inland the Bekaa valley and the eastern mountains are drier, being shielded from the influence of the sea. But no part of Lebanon is a desert such as is found extensively in Syria and Jordan. Summers are delightfully sunny, fresh, and cool in the mountains. Conditions inland and in the Bekaa valley are represented by the climate for Zahlé. Winters are cooler than on the coast, with snow and frost.
There is significantly less precipitation and humidity and a greater variation in daily and annual temperatures. The Khamsin does not occur in the Beqaa Valley, but the north winter wind is so strong that locals say it can "break nails". Despite the relatively low elevation of the Beqaa Valley, more snow falls there than at comparable elevations west of the Lebanon mountains.
Because of the altitude, the eastern or "anti-Lebanon" mountains receive more rainfall than the Beqaa Valley, despite their isolation from maritime influences. Much of this precipitation appears as snow, and the peaks of the Anti-Lebanon Mountains, like those of the Lebanon mountains, are covered in snow for most of the year. Temperatures are cooler than the Beqaa Valley.
| Climate data for Zahlé | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 10.9 (51.6) | 11.8 (53.2) | 15.0 (59.0) | 20.1 (68.2) | 25.0 (77.0) | 29.2 (84.6) | 31.8 (89.2) | 32.5 (90.5) | 29.3 (84.7) | 25.0 (77.0) | 18.5 (65.3) | 12.9 (55.2) | 21.8 (71.3) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 6.2 (43.2) | 6.9 (44.4) | 9.5 (49.1) | 13.7 (56.7) | 17.7 (63.9) | 21.3 (70.3) | 23.5 (74.3) | 24.1 (75.4) | 21.2 (70.2) | 17.7 (63.9) | 12.5 (54.5) | 8.0 (46.4) | 15.2 (59.4) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 1.5 (34.7) | 2.0 (35.6) | 4.0 (39.2) | 7.3 (45.1) | 10.5 (50.9) | 13.4 (56.1) | 15.3 (59.5) | 15.7 (60.3) | 13.2 (55.8) | 10.4 (50.7) | 6.6 (43.9) | 3.1 (37.6) | 8.6 (47.5) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 160 (6.3) | 127 (5.0) | 102 (4.0) | 45 (1.8) | 18 (0.7) | 1 (0.0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (0.1) | 25 (1.0) | 71 (2.8) | 135 (5.3) | 686 (27) |
| Source: Climate-Data.org | |||||||||||||
References
- E. A. Pearce, Charles Gordon Smith, (1990) The Hutchinson World Weather Guide, John Murray Press. ISBN 1859863426
- Timothy L. Gall, (ed.), (2003), Worldmark Encyclopedia of the Nations, Eleventh Edition, Thomson Gale
- Federal Research Division, Library of Congress, (1989), Lebanon: a country study. Claitor's Pub. Division. ISBN 0844408328
- Hugh Chisholm, (ed.), (1911), Encyclopædia Britannica, Eleventh edition, Cambridge University Press
The Climate of
Lebanon
In summary:
Lebanon has a varied climate with a hot, Mediterranean climate on the coast and cooler conditions in the mountains. The average annual temperature in Beirut is 21°C (70°F), with a range from 13°C (55°F) in winter to 28°C (82°F) in summer.
Rainfall is abundant by Middle Eastern standards, with about 890 mm (35 in) yearly along the coast, about 1250 mm (50 in) on the western slopes of the mountains, and less than 380 mm (15 in) in the Bekaa. About 80% of the rain falls from November to March.