The Climate of
Madagascar
_km17.2.jpg) Road from Diego Suarez to Ramena, Diana Region
Road from Diego Suarez to Ramena, Diana Region
Climate Map
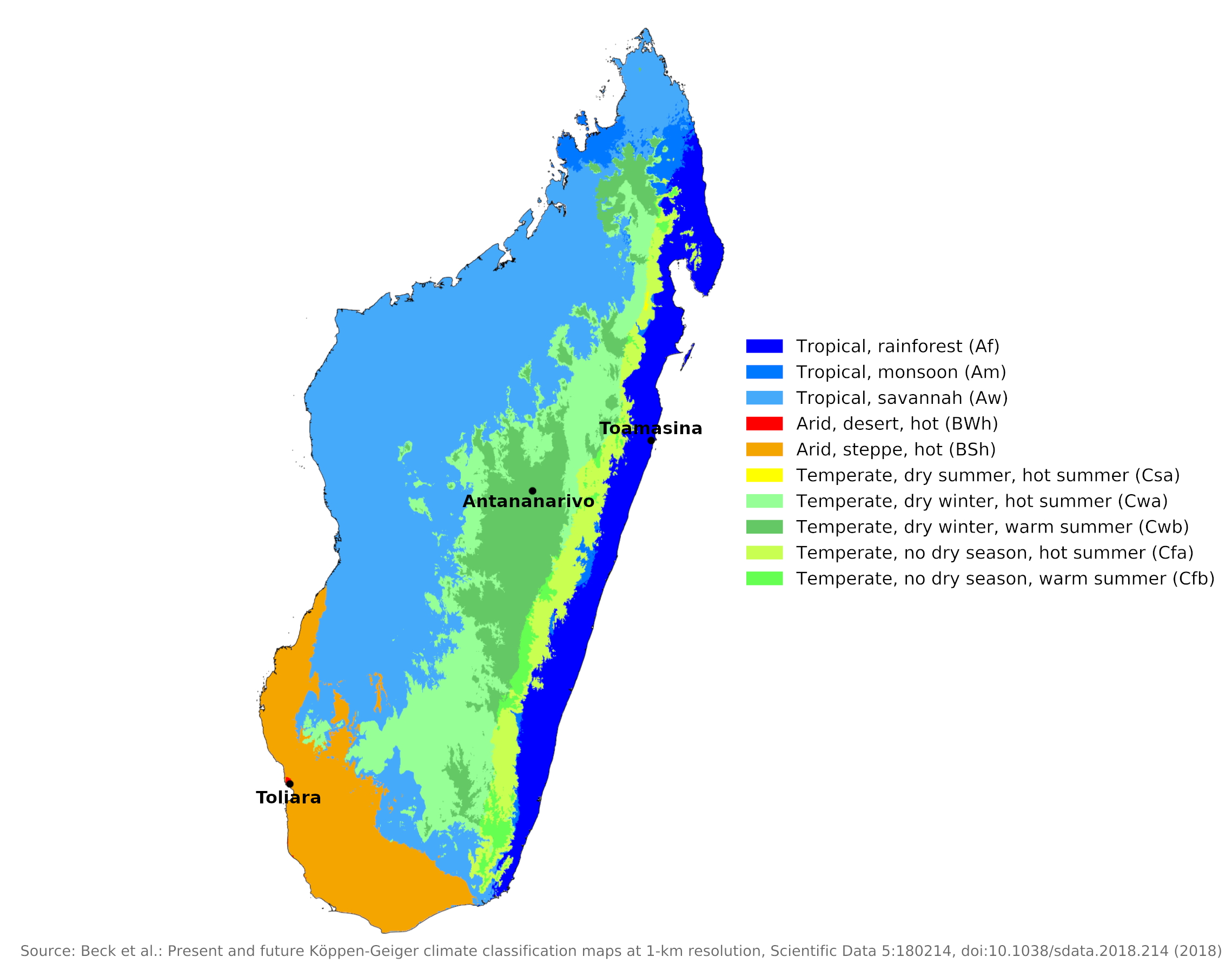 Climate map of Madagascar
Climate map of Madagascar
What is the climate of Madagascar like?
Madagascar is a large island, about the size of France. It lies in the Indian Ocean between latitudes 12° and 26° S at a distance of 400 km (250 miles) from the coast of Mozambique in southern Africa. It is the fourth largest island in the world. It is a mountainous island with a steep escarpment rising to 1,200 to 1,800 meters (4,000 to 6,000 feet) behind the east coast. Much of the interior is a plateau above which a few isolated, extinct volcanoes reach elevations of 2,100 to 2,900 meters (7,000 to 9,500 feet). The island slopes more gradually to the south and west, where broader coastal plains are found.
There are basically two seasons in Madagascar: dry from May to October, and rainy from November to April. Two short seasons of approximately one month duration separate these two seasons.
From May to October, the climate is conditioned by the Indian Ocean anticyclone, a center of high atmospheric pressure that seasonally changes its position over the ocean. This directs the southeastern trade winds. During the dry season (winter), the eastern part of the island experiences reduced rainfall, while the western part undergoes drought-like conditions. During the wet season (summer), the Indian Ocean anticyclone, and the trade wind regime becomes less regular, although the eastern side of Madagascar always remains under this influence. During this season, when the sun is high, the island is affected by cloud belts and heavy rain associated with the Intertropical Convergence, where the trade winds merge with the monsoons. Unstable storm-like conditions develop almost daily.
The entire island has a tropical climate, but above 900 meters (3,000 feet) temperatures are low enough to rarely be oppressive or uncomfortable. The lowlands are hot and quite humid, especially during the rainy season. The east coast is wet most of the year as it is exposed to the trade winds, which are forced to rise when they meet the steep, east-facing escarpment. Toamasina has an annual rainfall of 3,370 millimeters (132 inches). Most of the east coast receives over 2,000 millimeters (80 inches) of annual rainfall, as does another small area to the northwest around Antsiranana. Precipitation is lower on the inner plateau and decreases to the west and south.
| Climate data for Toamasina (1961–1990) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 30.1 (86.2) | 30.3 (86.5) | 29.5 (85.1) | 28.8 (83.8) | 27.3 (81.1) | 25.6 (78.1) | 24.8 (76.6) | 24.9 (76.8) | 25.8 (78.4) | 26.9 (80.4) | 28.4 (83.1) | 29.4 (84.9) | 27.6 (81.7) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 26.0 (78.8) | 26.1 (79.0) | 25.5 (77.9) | 24.6 (76.3) | 22.9 (73.2) | 21.1 (70.0) | 20.4 (68.7) | 20.5 (68.9) | 21.3 (70.3) | 22.7 (72.9) | 24.3 (75.7) | 25.5 (77.9) | 23.4 (74.1) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 22.5 (72.5) | 22.7 (72.9) | 22.4 (72.3) | 21.4 (70.5) | 19.5 (67.1) | 17.8 (64.0) | 17.1 (62.8) | 17.0 (62.6) | 17.3 (63.1) | 18.7 (65.7) | 20.4 (68.7) | 21.9 (71.4) | 19.9 (67.8) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 410.1 (16.15) | 382.1 (15.04) | 478.4 (18.83) | 322.8 (12.71) | 228.3 (8.99) | 259.0 (10.20) | 288.6 (11.36) | 218.2 (8.59) | 121.1 (4.77) | 132.6 (5.22) | 169.7 (6.68) | 357.3 (14.07) | 3,368.2 (132.61) |
| Source: NOAA | |||||||||||||
The lowlands in the southwest of the island only receive between 400 and 800 millimeters (16 to 32 inches) of rain per year, mainly between December and March. Toliara is located in this dry part of the country.
| Climate data for Toliara (1961–1990) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 32.2 (90.0) | 32.3 (90.1) | 32.0 (89.6) | 30.6 (87.1) | 28.6 (83.5) | 26.9 (80.4) | 26.8 (80.2) | 27.7 (81.9) | 28.5 (83.3) | 29.3 (84.7) | 30.3 (86.5) | 31.3 (88.3) | 29.8 (85.6) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 27.5 (81.5) | 27.5 (81.5) | 26.8 (80.2) | 25.0 (77.0) | 22.7 (72.9) | 20.7 (69.3) | 20.3 (68.5) | 21.0 (69.8) | 22.3 (72.1) | 23.9 (75.0) | 25.3 (77.5) | 26.6 (79.9) | 24.1 (75.4) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 22.9 (73.2) | 22.9 (73.2) | 21.9 (71.4) | 19.9 (67.8) | 16.9 (62.4) | 14.8 (58.6) | 14.4 (57.9) | 14.8 (58.6) | 16.2 (61.2) | 18.5 (65.3) | 20.3 (68.5) | 22.1 (71.8) | 18.8 (65.8) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 94.7 (3.73) | 88.7 (3.49) | 35.9 (1.41) | 17.7 (0.70) | 15.8 (0.62) | 14.9 (0.59) | 6.2 (0.24) | 5.6 (0.22) | 7.8 (0.31) | 11.9 (0.47) | 21.7 (0.85) | 97.0 (3.82) | 417.9 (16.45) |
| Source: NOAA | |||||||||||||
The central plateau areas receive an annual rainfall intermediate between these extremes, varying between 1,000 and 1,500 millimeters (40 to 60 inches). Most rain here falls between November and March, much of it in heavy downpours associated with hail and thunder. The rainfall during the rest of the year is mostly very light and sporadic (see the climate of Antananarivo). On the plateau temperatures fall to moderate levels during the dry season and the nights may be chilly, but frost only occurs on the highest mountains.
| Climate data for Antananarivo (1981–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 26.6 (79.9) | 26.5 (79.7) | 26.5 (79.7) | 25.5 (77.9) | 23.7 (74.7) | 21.2 (70.2) | 20.6 (69.1) | 21.7 (71.1) | 24.2 (75.6) | 26.0 (78.8) | 27.0 (80.6) | 27.2 (81.0) | 24.7 (76.5) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 20.8 (69.4) | 20.8 (69.4) | 20.7 (69.3) | 19.5 (67.1) | 17.3 (63.1) | 15.1 (59.2) | 14.3 (57.7) | 14.9 (58.8) | 16.8 (62.2) | 18.7 (65.7) | 20.1 (68.2) | 20.7 (69.3) | 18.3 (64.9) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 17.3 (63.1) | 17.3 (63.1) | 17.0 (62.6) | 15.4 (59.7) | 13.2 (55.8) | 10.9 (51.6) | 9.9 (49.8) | 10.3 (50.5) | 11.4 (52.5) | 13.6 (56.5) | 15.2 (59.4) | 16.7 (62.1) | 14.0 (57.2) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 340 (13.4) | 290 (11.4) | 191 (7.5) | 55 (2.2) | 19 (0.7) | 4 (0.2) | 8 (0.3) | 6 (0.2) | 10 (0.4) | 68 (2.7) | 135 (5.3) | 311 (12.2) | 1,437 (56.5) |
| Source: NOAA | |||||||||||||
Sunshine hours are fairly high year-round, even on the wetter east coast. In Toamasina, average daily hours of sunshine range from six in the cloudier, wetter months to eight in the drier months. In the drier parts of the island, sunshine hours range from eight to ten hours a day. Aside from the combination of heat and humidity that affects the lower reaches of the island during the rainy season, much of the island has a sunny, warm and comfortable weather and climate for much of the year, and this is particularly true on the plateau.
Two or three times a year, part of Madagascar is hit by torrential rains and high winds associated with tropical cyclones developing in the Indian Ocean north of the island. These can move south on either the west or east side of the island and the most damaging effects of their strong winds are felt in the coastal areas.
References
- E. A. Pearce, Charles Gordon Smith, (1990) The Hutchinson World Weather Guide, John Murray Press. ISBN 1859863426
- Timothy L. Gall, (ed.), (2003), Worldmark Encyclopedia of the Nations, Eleventh Edition, Thomson Gale
- Modeste Kameni Nematchoua; Paola Ricciardi; José A. Orosa; Cinzia Buratti, (2018) A detailed study of climate change and some vulnerabilities in Indian Ocean: A case of Madagascar island. Sustainable Cities and Society 41 886-898. DOI 10.1016/j.scs.2018.05.040
- Hugh Chisholm, (ed.), (1911), Encyclopædia Britannica, Eleventh edition, Cambridge University Press
The Climate of
Madagascar
In summary:
Madagascar’s climate is strongly influenced by southeasterly trade winds which converge with the monsoon winds, but the temperatures are also moderated by altitude. The central plateau enjoys a tropical mountain climate with well-differentiated seasons. Generally speaking, the coast is hotter (average temperatures 21–27°C, or 70–80°F) than the plateau (average temperatures 13–19°C, or 55–67°F).
The hot season between November and April is also the rainy season, while drier weather prevails throughout the rest of the year. Rainfall is heaviest on the eastern, or windward, side of the island, with an annual average up to 3800 mm (150 in). Monsoons bring rain to the northwestern coast, which averages 2100 mm (83 in) of rainfall annually, compared with the arid southwest, where the average drops to a mere 360 mm (14 in). Annual rain on the plateau averages about 1350 mm (53 in).