The Climate of
South Korea
 Buddhist temple in Boseong-gun
Buddhist temple in Boseong-gun
Climate Map
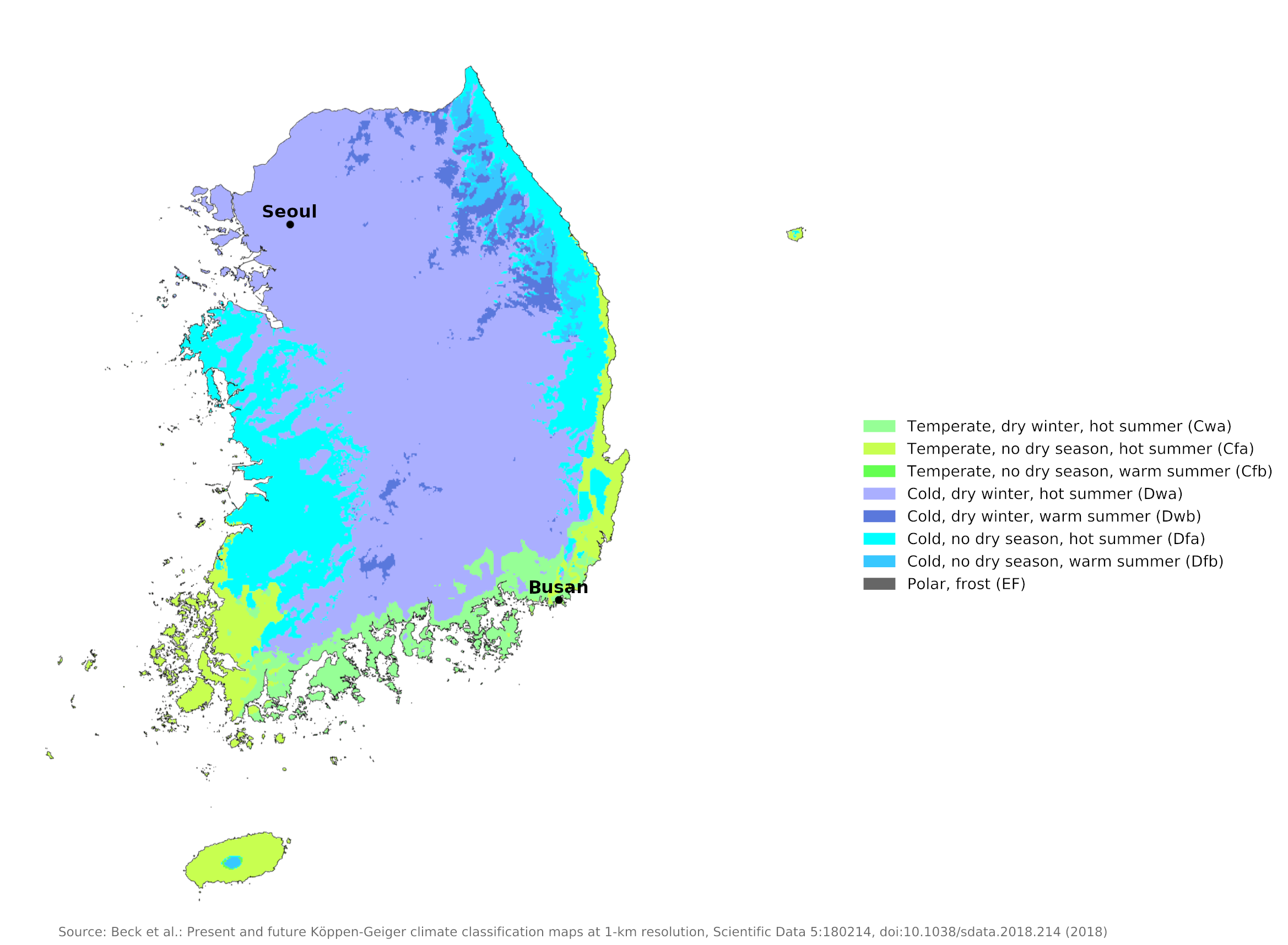 Climate map of South Korea
Climate map of South Korea
What is the climate of South Korea like?
South Korea occupies the southern half of the Korean peninsula, between the Yellow Sea and the Sea of Japan. In area the country is a little smaller than England. It has a border with North Korea approximately along the 38° parallel of latitude. Much of the country is hilly or even mountainous; in the east there are many hills rising above 1,000 meters (3,000 feet). The largest areas of lowland are in the west.
Although surrounded by water on three sides, the movement of air masses from the Asian continent exerts greater influence on South Korea's weather than does air movement from the Pacific Ocean. South Korea has a rather continental climate, with four distinct seasons. Winters are usually long, cold, and dry, whereas summers are short, hot, and humid. Spring and autumn are pleasant but short in duration.
The average January temperature ranges from –2°C (29°F) at Seoul to 4°C (39°F) at Busan and 6°C (42°F) on Jeju Island. In the hottest part of the summer, however, the regional variation in temperature is not nearly so marked, with average temperatures ranging from 25°C to 27°C (76–81°F) in most lowland areas.
In summer the winds are mainly from the east and south, bringing warm, moist air from the Pacific Ocean. The weather can be somewhat variable from day to day at all seasons, since the country is affected by frontal systems and depressions moving from the west. These bring rain or snow and occasional thaws in winter. In summer these disturbances are associated with the spells of heaviest rainfall.
South Korea is part of the East Asian monsoonal region. Most of the rainfall occurs in the April–September period, especially during the rainy season, late June to early August. Average rainfall is 1,000 to 1,500 millimeters (40 and 50 inches). Rainfall is greatest in the south and in inland mountainous regions. The coastal areas receive the least rainfall. Amounts of precipitation, however, can vary from year to year. Serious droughts occur about once every eight years, especially in the rice-producing southwestern part of the country.
South Korea is less vulnerable to typhoons than Japan, Taiwan, the east coast of China, or the Philippines. From one to three mild typhoons normally strike the south in late summer, especially in August, and bring torrential rains. A severe typhoon occurs once every two or three years. Flooding occasionally causes considerable damage.
Temperatures increase from north to south, particularly in winter, so that south is rather warmer than the north around the year. There are about 240 frost-free days in the southern regions. The climate of Seoul near the border with North Korea shows the conditions in the north. Busan in the south of the country, shows the warmer conditions farther south.
| Climate data for Seoul (1991–2020) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 2.1 (35.8) | 5.1 (41.2) | 11.0 (51.8) | 17.9 (64.2) | 23.6 (74.5) | 27.6 (81.7) | 29.0 (84.2) | 30.0 (86.0) | 26.2 (79.2) | 20.2 (68.4) | 11.9 (53.4) | 4.2 (39.6) | 17.4 (63.3) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −1.9 (28.6) | 0.7 (33.3) | 6.1 (43.0) | 12.6 (54.7) | 18.2 (64.8) | 22.7 (72.9) | 25.3 (77.5) | 26.1 (79.0) | 21.6 (70.9) | 15.0 (59.0) | 7.5 (45.5) | 0.2 (32.4) | 12.8 (55.0) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −5.5 (22.1) | −3.2 (26.2) | 1.9 (35.4) | 8.0 (46.4) | 13.5 (56.3) | 18.7 (65.7) | 22.3 (72.1) | 22.9 (73.2) | 17.7 (63.9) | 10.6 (51.1) | 3.5 (38.3) | −3.4 (25.9) | 8.9 (48.0) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 16.8 (0.66) | 28.2 (1.11) | 36.9 (1.45) | 72.9 (2.87) | 103.6 (4.08) | 129.5 (5.10) | 414.4 (16.31) | 348.2 (13.71) | 141.5 (5.57) | 52.2 (2.06) | 51.1 (2.01) | 22.6 (0.89) | 1,417.9 (55.82) |
| Source: Korea Meteorological Administration | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Busan (1991–2020) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 8.2 (46.8) | 10.2 (50.4) | 13.8 (56.8) | 18.2 (64.8) | 22.0 (71.6) | 24.6 (76.3) | 27.5 (81.5) | 29.5 (85.1) | 26.4 (79.5) | 22.5 (72.5) | 16.6 (61.9) | 10.4 (50.7) | 19.2 (66.6) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 3.6 (38.5) | 5.4 (41.7) | 9.1 (48.4) | 13.8 (56.8) | 17.9 (64.2) | 21.0 (69.8) | 24.4 (75.9) | 26.1 (79.0) | 22.6 (72.7) | 17.9 (64.2) | 11.9 (53.4) | 5.8 (42.4) | 15.0 (59.0) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −0.1 (31.8) | 1.5 (34.7) | 5.3 (41.5) | 10.1 (50.2) | 14.6 (58.3) | 18.3 (64.9) | 22.1 (71.8) | 23.7 (74.7) | 19.8 (67.6) | 14.5 (58.1) | 8.3 (46.9) | 2.0 (35.6) | 11.7 (53.1) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 34.5 (1.36) | 49.6 (1.95) | 89.7 (3.53) | 140.9 (5.55) | 155.9 (6.14) | 188.4 (7.42) | 326.8 (12.87) | 266.5 (10.49) | 160.6 (6.32) | 79.6 (3.13) | 50.4 (1.98) | 33.8 (1.33) | 1,576.7 (62.07) |
| Source: Korea Meteorological Administration | |||||||||||||
References
- E. A. Pearce, Charles Gordon Smith, (1990) The Hutchinson World Weather Guide, John Murray Press. ISBN 1859863426
- Timothy L. Gall, (ed.), (2003), Worldmark Encyclopedia of the Nations, Eleventh Edition, Thomson Gale
- Federal Research Division, Library of Congress, (1992), South Korea: a country study. Claitor's Pub. Division. ISBN 0844407364
- Hugh Chisholm, (ed.), (1911), Encyclopædia Britannica, Eleventh edition, Cambridge University Press
The Climate of
South Korea
In summary:
South Korea has a somewhat continental climate, with hot, rainy summers and cold winters. Mean temperatures in lowland areas range from 25°C to 27°C (76°F to 81°F) in the summer months and from -5°C to 4°C (23°F to 39°F) in the winter months, with warmer winter temperatures along the southern coast and cooler temperatures in the interior.
Annual rainfall averages between 1000 and 1500 mm (40 and 50 in), but many areas experience less rainfall. Rainfall is greatest in the south and in inland mountainous regions.