The Climate of
North Korea
 Pyongyang cityscape, with a city park
Pyongyang cityscape, with a city park
Climate Map
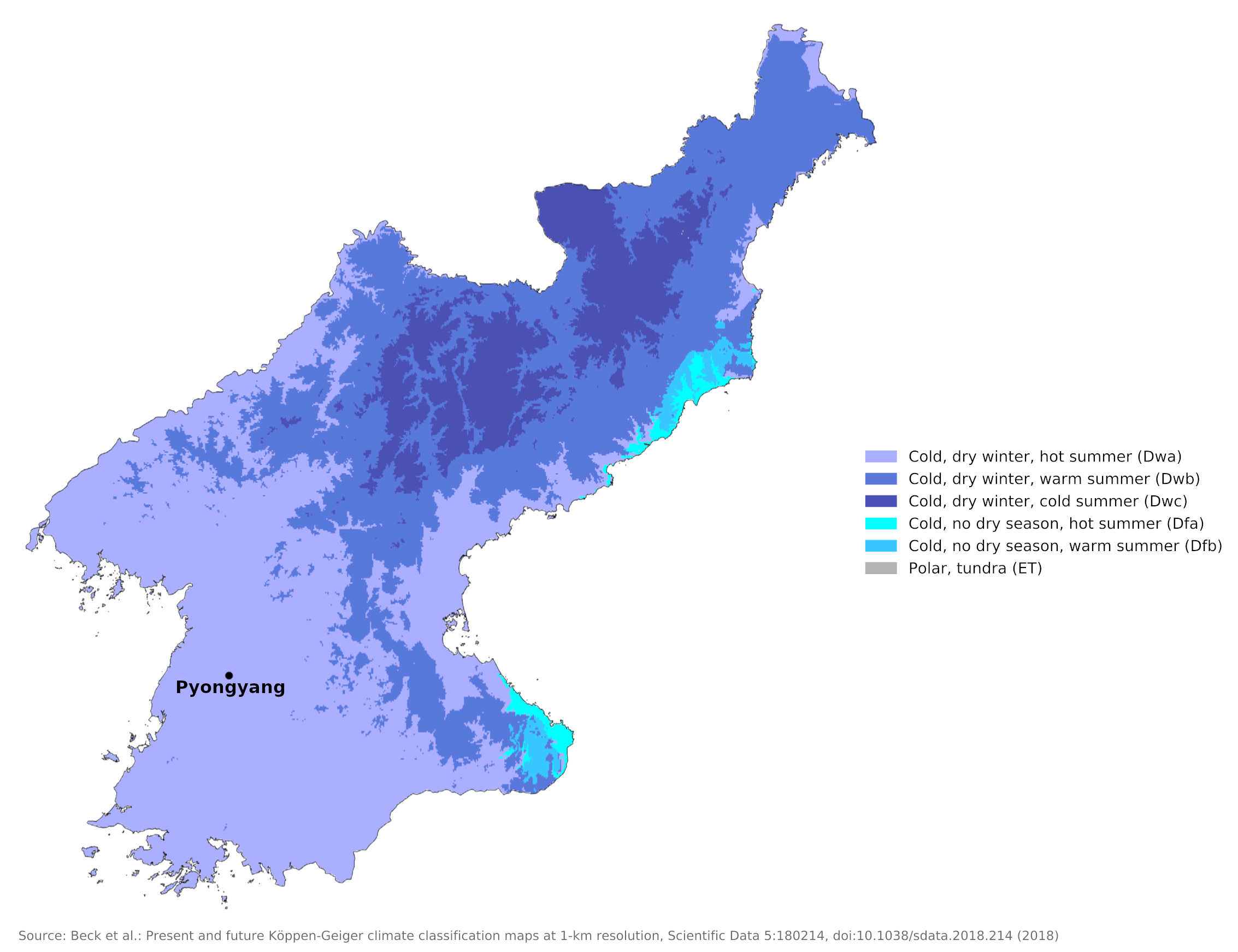 Climate map of North Korea
Climate map of North Korea
What is the climate of North Korea like?
North Korea occupies the northern half of the Korean peninsula between the countries of China and South Korea. It has a relatively long land border, along the Yalu river, with the Chinese province of Manchuria. The north is a mountainous region with many areas rising to between 1,800 and 2,500 meters (6,000–8,000 feet).
North Korea has long, cold, dry winters and short, hot, humid summers. The climate of North Korea is rather more continental and extreme than that of the south. This is because it has a long land border and is more open to cold winds which blow from Manchuria and Siberia in winter. Conditions in winter can be very cold; rivers freeze up for between three and four months and ice forms along the coast, blocking harbours and impeding navigation. Snow falls on as many as thirty-seven days at Pyongyang, and on many more days in the far north. In the north there may be as many as 200 days with frost a year. The average January temperature is -16°C (3°F) at Chunggang on the north-central border and -6°C (22°F) at Pyongyang.
In the hottest part of the summer, however, the variation is not nearly so marked, average temperatures ranging from 25°C (77°F) in Pyongyang to 21°C (70°F) along the relatively cool northeast coast. Spring and fall are usually pleasant, but winters are colder than average for the latitude, and summers are hot and humid.
Rainfall is around 500 millimeters (20 inches) in the far north, but more than half of the country receives 750 to 1,000 millimeters (30–40 inches) per year. Nearly all the rainfall occurs in the April–September period, especially during the rainy season, from late June to early August. These averages disguise the somewhat erratic weather conditions which can occur in North Korea. Heavy rain can cause devastating floods, and some years have seen periods of prolonged drought. Typhoons can be expected on an average of at least once every summer or in the early fall, contributing to the heavy rainfall at this time. There is no very great difference between temperatures and rainfall throughout the year from one side of the country to the other.
| Climate data for Pyongyang (1991–2020) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | −0.4 (31.3) | 3.1 (37.6) | 9.7 (49.5) | 17.6 (63.7) | 23.5 (74.3) | 27.5 (81.5) | 29.1 (84.4) | 29.6 (85.3) | 25.7 (78.3) | 18.8 (65.8) | 9.7 (49.5) | 1.4 (34.5) | 16.3 (61.3) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −5.4 (22.3) | −2.0 (28.4) | 4.0 (39.2) | 11.4 (52.5) | 17.4 (63.3) | 21.9 (71.4) | 24.7 (76.5) | 25.0 (77.0) | 20.2 (68.4) | 12.9 (55.2) | 4.8 (40.6) | −2.9 (26.8) | 11.0 (51.8) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −9.8 (14.4) | −6.6 (20.1) | −0.9 (30.4) | 5.9 (42.6) | 12.0 (53.6) | 17.4 (63.3) | 21.4 (70.5) | 21.5 (70.7) | 15.6 (60.1) | 7.8 (46.0) | 0.5 (32.9) | −6.8 (19.8) | 6.5 (43.7) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 9.6 (0.38) | 14.5 (0.57) | 23.9 (0.94) | 44.8 (1.76) | 74.7 (2.94) | 90.2 (3.55) | 274.7 (10.81) | 209.6 (8.25) | 90.8 (3.57) | 47.2 (1.86) | 38.4 (1.51) | 18.0 (0.71) | 936.4 (36.87) |
| Source: Korea Meteorological Administration | |||||||||||||
References
- E. A. Pearce, Charles Gordon Smith, (1990) The Hutchinson World Weather Guide, John Murray Press. ISBN 1859863426
- Timothy L. Gall, (ed.), (2003), Worldmark Encyclopedia of the Nations, Eleventh Edition, Thomson Gale
- Federal Research Division, Library of Congress, (1992), North Korea: a country study. Claitor's Pub. Division. ISBN 9780844411880
- Hugh Chisholm, (ed.), (1911), Encyclopædia Britannica, Eleventh edition, Cambridge University Press
The Climate of
North Korea
In summary:
North Korea has a humid continental climate. The temperature varies from north to south during the winter, with the average January temperature at -16°C (3°F) along the northern border and -6°C (22°F) at Pyongyang, the capital. Summer temperatures have less variation from north to south, averaging 21°C (70°F) in the north, and 25°C (77°F) at Pyongyang.
Approximately 60 percent of the annual rainfall, from 750 to 1000 mm (30 to 40 in), occurs from June through September. The northernmost regions receive less rainfall, averaging 500 mm (20 in).