The Climate of
Bangladesh
 A launch at Mohanganj in Netrakona district
A launch at Mohanganj in Netrakona district
Climate Map
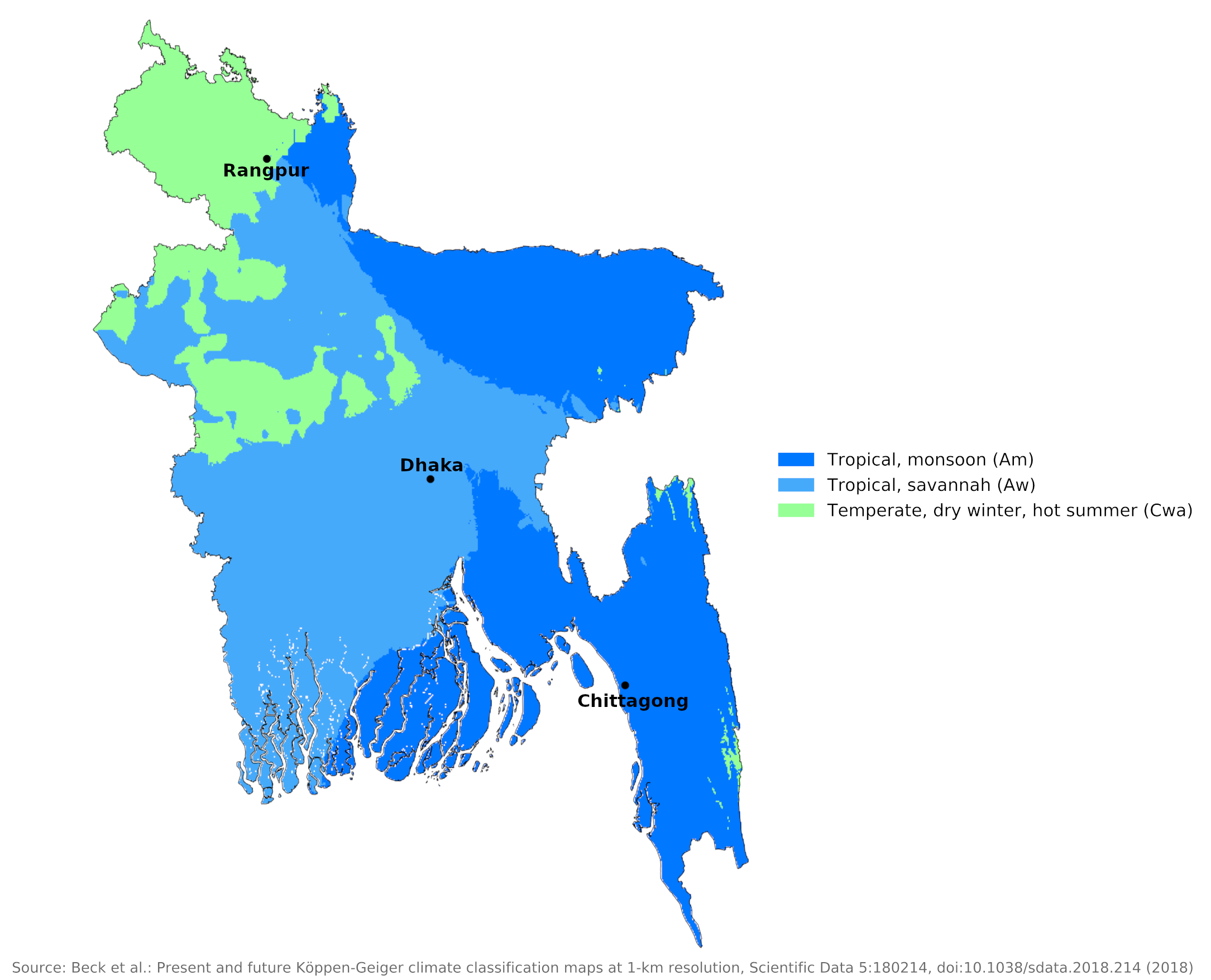 Climate map of Bangladesh
Climate map of Bangladesh
What is the climate of Bangladesh like?
Bangladesh is a very low-lying country at the tip of the Bay of Bengal. Except for the Chittagong Hill District in the far southeast on the border with Myanmar, all of the country is below 180 meters (600 feet). Most of the country consists of the swampy plains of the great delta of the Ganges and Brahmaputra rivers. Most of the land border is with India.
Bangladesh has a tropical monsoon climate with the same tripartite division of the year as India. Winter, which lasts from October to early March, is cool and dry with temperatures ranging from 5°C to 25°C (41°F to 77°F); Total winter precipitation is about 180 millimeters (7 in) in the east and less than 80 millimeters (3 in) in the northwest. Temperatures rise quickly in March, averaging around 29°C (84°F) during the summer season—March to May. Precipitation also increases during this period—some rainstorms occur and these are often thunderstorms. However, almost 80% of annual precipitation falls from May to September, the monsoon season, when humid winds blow from the south and south-east. Temperatures may drop a bit, but humidity remains high.
About 80 percent of Bangladesh's rain falls during the monsoon season. The monsoons result from the contrasts between low and high air pressure areas that result from differential heating of land and water. During the hot months of April and May hot air rises over the Indian subcontinent, creating low-pressure areas into which rush cooler, moisture-bearing winds from the Indian Ocean. This is the southwest monsoon, commencing in June and usually lasting through September. Dividing against the Indian landmass, the monsoon flows in two branches, one of which strikes western India. The other travels up the Bay of Bengal and over eastern India and Bangladesh, crossing the plain to the north and northeast before being turned to the west and northwest by the foothills of the Himalayas.
Heavy rainfall is characteristic of Bangladesh. With the exception of the relatively dry western region of Rajshahi, where the annual rainfall is about 1,600 millimeters (63 inches), most parts of the country receive at least 2,000 millimeters (80 inches) of rainfall per year. The northeastern region of Sylhet receives the greatest average precipitation of 3,750 millimeters (150 inches) or more, because of its location just south of the foothills of the Himalayas, where monsoon winds turn west and northwest.
Rainfall is most reliable and frequent during the southwest monsoon season and is brought by depressions in the northern Bay of Bengal. Rainfall in the September-November period is less reliable but occasionally very heavy and is usually associated with violent tropical cyclones. These severe storms which bring very strong winds and torrential rains develop in the Bay of Bengal at this time and are the most dangerous feature of Bangladesh climate. The storm waves and sea tides raise the water level along the coast and in the numerous branched watercourses of the delta, causing widespread flooding of the low-lying areas, which also leads to the devastation caused by the strong winds. Such storms have claimed many lives and destroyed crops.
Although temperatures during the hot season in Bangladesh are slightly lower than in some parts of India, the high humidity makes the heat uncomfortable. This muggy, humid heat persists during the main rainy season. The heat is rarely dangerous, but certainly uncomfortable for the unacclimatized visitor. There is not much variation in temperature conditions from one part of the country to another throughout the year. During the hot season, temperatures in the north (e.g. Rangpur) and the center (e.g. Dhaka) are about the same as on the coast (e.g . Chittagong), although winter temperatures can be slightly lower in the north. Due to more cloud cover during the rainy season, average daily hours of sunshine are lowest between June and September, around four hours a day. During the rest of the year it averages six to eight hours.
| Climate data for Rangpur (1981–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 23.1 (73.6) | 26.3 (79.3) | 30.4 (86.7) | 31.7 (89.1) | 31.8 (89.2) | 31.9 (89.4) | 31.7 (89.1) | 32.2 (90.0) | 31.5 (88.7) | 30.7 (87.3) | 25.5 (77.9) | 25.1 (77.2) | 29.3 (84.8) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 16.3 (61.3) | 19.2 (66.6) | 23.4 (74.1) | 26.1 (79.0) | 27.4 (81.3) | 28.4 (83.1) | 28.6 (83.5) | 28.9 (84.0) | 28.0 (82.4) | 25.2 (77.4) | 21.2 (70.2) | 18.2 (64.8) | 24.2 (75.6) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 10.9 (51.6) | 13.2 (55.8) | 17.3 (63.1) | 21.2 (70.2) | 23.3 (73.9) | 25.3 (77.5) | 26.0 (78.8) | 26.3 (79.3) | 25.3 (77.5) | 21.6 (70.9) | 17.4 (63.3) | 13.0 (55.4) | 20.1 (68.1) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 9.2 (0.36) | 12.5 (0.49) | 25.9 (1.02) | 118.4 (4.66) | 267.7 (10.54) | 467.1 (18.39) | 476.5 (18.76) | 344.8 (13.57) | 390.1 (15.36) | 180.5 (7.11) | 8.7 (0.34) | 8.1 (0.32) | 2,309.5 (90.92) |
| Source: Bangladesh Meteorological Department | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Dhaka (1981–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 25.1 (77.2) | 28.3 (82.9) | 32.5 (90.5) | 33.8 (92.8) | 33.4 (92.1) | 32.5 (90.5) | 31.8 (89.2) | 32.1 (89.8) | 32.0 (89.6) | 31.8 (89.2) | 29.7 (85.5) | 26.5 (79.7) | 30.8 (87.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 18.6 (65.5) | 22.0 (71.6) | 26.3 (79.3) | 28.4 (83.1) | 28.8 (83.8) | 29.0 (84.2) | 28.7 (83.7) | 28.9 (84.0) | 28.5 (83.3) | 27.4 (81.3) | 24.0 (75.2) | 20.0 (68.0) | 25.9 (78.6) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 13.1 (55.6) | 16.2 (61.2) | 20.8 (69.4) | 23.8 (74.8) | 24.8 (76.6) | 26.2 (79.2) | 26.3 (79.3) | 26.4 (79.5) | 25.9 (78.6) | 23.9 (75.0) | 19.4 (66.9) | 14.8 (58.6) | 21.8 (71.2) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 7.5 (0.30) | 23.7 (0.93) | 61.7 (2.43) | 140.6 (5.54) | 278.4 (10.96) | 346.5 (13.64) | 375.5 (14.78) | 292.9 (11.53) | 340.0 (13.39) | 174.5 (6.87) | 31.1 (1.22) | 12.1 (0.48) | 2,084.5 (82.07) |
| Source: Bangladesh Meteorological Department | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Chittagong (1981–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 26.0 (78.8) | 28.3 (82.9) | 30.8 (87.4) | 31.9 (89.4) | 32.4 (90.3) | 31.7 (89.1) | 31.0 (87.8) | 31.4 (88.5) | 31.8 (89.2) | 31.7 (89.1) | 30.0 (86.0) | 27.2 (81.0) | 30.4 (86.7) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 19.8 (67.6) | 22.3 (72.1) | 25.7 (78.3) | 27.9 (82.2) | 28.6 (83.5) | 28.4 (83.1) | 27.9 (82.2) | 28.1 (82.6) | 28.3 (82.9) | 27.7 (81.9) | 24.9 (76.8) | 21.2 (70.2) | 25.9 (78.6) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 14.0 (57.2) | 16.3 (61.3) | 20.5 (68.9) | 23.6 (74.5) | 24.9 (76.8) | 25.4 (77.7) | 25.2 (77.4) | 25.3 (77.5) | 25.2 (77.4) | 24.1 (75.4) | 20.3 (68.5) | 15.8 (60.4) | 21.7 (71.1) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 7.3 (0.29) | 25.0 (0.98) | 55.5 (2.19) | 136.4 (5.37) | 314.0 (12.36) | 591.3 (23.28) | 735.6 (28.96) | 513.9 (20.23) | 239.3 (9.42) | 197.8 (7.79) | 59.5 (2.34) | 14.1 (0.56) | 2,889.7 (113.77) |
| Source: Bangladesh Meteorological Department | |||||||||||||
References
- E. A. Pearce, Charles Gordon Smith, (1990) The Hutchinson World Weather Guide, John Murray Press. ISBN 1859863426
- Timothy L. Gall, (ed.), (2003), Worldmark Encyclopedia of the Nations, Eleventh Edition, Thomson Gale
- Federal Research Division, Library of Congress, (1989), Bangladesh: a country study. Claitor's Pub. Division.
- Hugh Chisholm, (ed.), (1911), Encyclopædia Britannica, Eleventh edition, Cambridge University Press
The Climate of
Bangladesh
In summary:
The climate of Bangladesh is generally tropical with three seasons. The winter, which lasts from October through early March, is cool and dry. Temperatures rise rapidly in March, and during the summer season—March through May—average about 29°C (84°F). Rainfall also increases during this period.
However, nearly 80% of the annual rainfall falls from May to September, the monsoon season, when moisture-laden winds blow from the south and southeast. Temperatures may drop a little, but humidity remains high. Parts of Bangladesh are also subject to severe seasonal flooding and cyclones.