The Climate of
Bhutan
 Taj Tashi Hotel Chubachu, Thimphu
Taj Tashi Hotel Chubachu, Thimphu
Climate Map
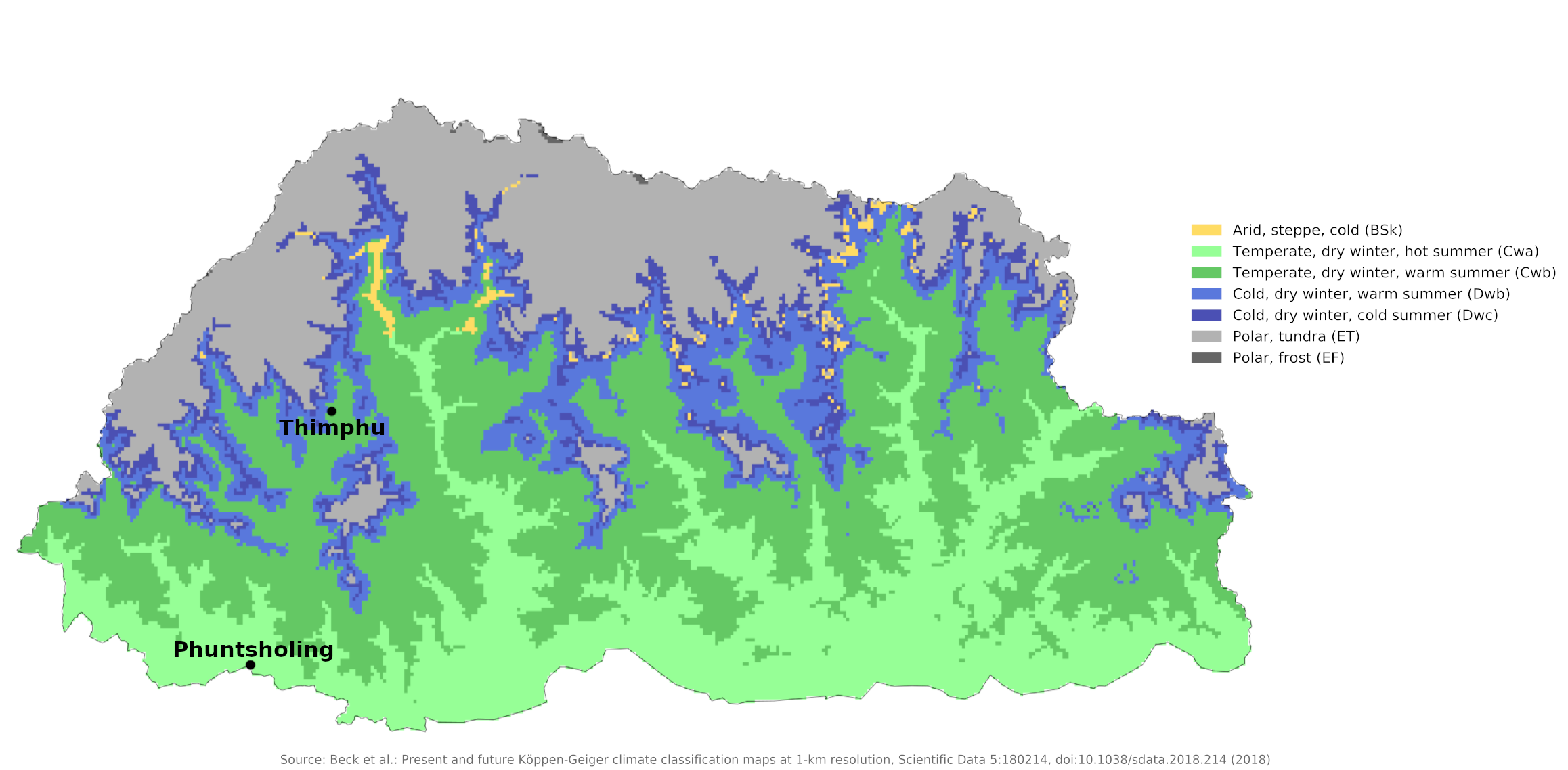 Climate map of Bhutan
Climate map of Bhutan
What is the climate of Bhutan like?
Bhutan is a small independent state in treaty relationship with its larger neighbour, India, to the south. It is bordered by Sikkim on the west and China on the north. It is a mountainous country, extending from the highest parts of the Himalayas to the foothill region on the Indian border. The climate and weather of Bhutan are similar to Nepal.
Bhutan's climate is as diverse as its landscape and, like most of Asia, is influenced by the monsoons. Western Bhutan is particularly affected by the monsoon, which brings between 60 and 90 percent of the region's rainfall. The climate is humid and subtropical in the southern plains and foothills, temperate in the inner Himalayan valleys of the southern and central regions, and cold in the north, with year-round snow on the main Himalayan peaks.
The Duārs Plain areas in the south have a hot, humid, subtropical climate, with heavy rainfall. Temperatures generally average between 15°C (59°F) and 30°C (86°F) year-round. Temperatures in the valleys of the southern foothills of the Himalayas may rise as high as 40°C (104°F) in the summer. The central Inner Himalayan region has a temperate climate, with hot summers, cool winters, and moderate rainfall. Temperatures in the capital city of Thimphu, located in the western part of this region, generally range from about 15°C (59°F) to 26°C (79°F) between June and September (the monsoon season), falling to between -2°C (28°F) and 16°C (61°F) in January. The high mountains of the Greater Himalayas in the north have more severe weather than the regions to the south. At their highest elevations, they are snow-covered year-round, with an arctic climate.
Like other aspects of Bhutan's climate, rainfall varies by region. The northern Himalayas are relatively dry, and most precipitation falls as snow. The Inner Himalayan slopes and valleys have moderate rainfall, averaging between 1,000 and 1,500 millimeters (40 and 60 inches) annually. The rains descend in floods upon the heights; but in the vicinity of Thimphu, they are moderate; there are frequent showers, but nothing that can be compared to the tropical rains of the south. Thimphu experiences dry winter months (November to February) and almost no rainfall until March, after which it rises steadily to a high in July.
Rainfall in the subtropical southern regions averages between about 4,000 millimeters and 7,500 millimeters (160 to 300 inches) per year, ensuring the thick tropical forest, or savanna. The greatest amount of rain falls during the summer monsoon season, from June through September (see the climate of Phuntsholing).
Bhutan's generally dry spring begins in early March and lasts until mid-April. Summer weather starts in mid-April with occasional showers and continues through the pre-monsoon rains in late June. The summer monsoon lasts from late June to late September with heavy rainfall from the southwest. Blocked from advancing north by the Himalayas, monsoon weather brings heavy rains, high humidity, flash floods and landslides, and numerous foggy, overcast days. Autumn, from late September or early October to late November, follows the rainy season. It is characterized by bright, sunny days and some early snowfall at higher elevations. From the end of November to March, winter begins with frost in large parts of the country and snowfall over altitudes of 3,000 meters (10,000 feet).
The forests are hot and steaming in the rainy season, while the higher hills are cold, wet, and misty. Violent Himalayan thunderstorms gave rise to Bhutan's Dzongkha name, Druk-Yul, which translates as "Land of the Thunder Dragon."
| Climate data for Thimphu (1996-2017) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 14.8 (58.6) | 16.6 (61.9) | 19.3 (66.7) | 22.4 (72.3) | 24.8 (76.6) | 26.7 (80.1) | 27.0 (80.6) | 27.3 (81.1) | 26.0 (78.8) | 23.7 (74.7) | 19.7 (67.5) | 16.6 (61.9) | 22.1 (71.7) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 6.3 (43.3) | 8.5 (47.3) | 11.6 (52.9) | 15.1 (59.2) | 18.2 (64.8) | 21.0 (69.8) | 21.8 (71.2) | 21.7 (71.1) | 20.3 (68.5) | 16.3 (61.3) | 11.5 (52.7) | 7.9 (46.2) | 15.0 (59.0) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −2.2 (28.0) | 0.3 (32.5) | 3.8 (38.8) | 7.9 (46.2) | 11.6 (52.9) | 15.3 (59.5) | 16.5 (61.7) | 16.1 (61.0) | 14.6 (58.3) | 9.0 (48.2) | 3.2 (37.8) | −0.8 (30.6) | 8.0 (46.4) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 6.3 (0.25) | 9.2 (0.36) | 20.4 (0.80) | 29.9 (1.18) | 49.8 (1.96) | 97.7 (3.85) | 152.8 (6.02) | 120.8 (4.76) | 73.9 (2.91) | 43.1 (1.70) | 1.2 (0.05) | 3.7 (0.15) | 608.9 (23.97) |
| Source: National Center for Hydrology and Meteorology | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Phuntsholing (1996-2017) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 23.9 (75.0) | 26.6 (79.9) | 29.8 (85.6) | 31.1 (88.0) | 32.3 (90.1) | 32.3 (90.1) | 31.9 (89.4) | 32.3 (90.1) | 31.7 (89.1) | 31.2 (88.2) | 28.7 (83.7) | 25.4 (77.7) | 29.8 (85.6) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 18.6 (65.5) | 21.5 (70.7) | 24.2 (75.6) | 25.6 (78.1) | 27.0 (80.6) | 27.7 (81.9) | 27.8 (82.0) | 28.1 (82.6) | 27.4 (81.3) | 26.2 (79.2) | 23.3 (73.9) | 20.2 (68.4) | 24.8 (76.6) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 13.4 (56.1) | 16.3 (61.3) | 18.5 (65.3) | 20.1 (68.2) | 21.7 (71.1) | 23.1 (73.6) | 23.7 (74.7) | 23.8 (74.8) | 23.1 (73.6) | 21.1 (70.0) | 17.9 (64.2) | 15.0 (59.0) | 19.8 (67.7) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 17.3 (0.68) | 31.1 (1.22) | 80.2 (3.16) | 216.5 (8.52) | 380.3 (14.97) | 807.2 (31.78) | 962.6 (37.90) | 779.1 (30.67) | 492.6 (19.39) | 162.9 (6.41) | 13.2 (0.52) | 10.4 (0.41) | 3,953.4 (155.63) |
| Source: National Center for Hydrology and Meteorology | |||||||||||||
References
- E. A. Pearce, Charles Gordon Smith, (1990) The Hutchinson World Weather Guide, John Murray Press. ISBN 1859863426
- Timothy L. Gall, (ed.), (2003), Worldmark Encyclopedia of the Nations, Eleventh Edition, Thomson Gale
- Federal Research Division, Library of Congress, (1993), Nepal and Bhutan: country studies. Claitor's Pub. Division. ISBN 0844407771
- Hugh Chisholm, (ed.), (1911), Encyclopædia Britannica, Eleventh edition, Cambridge University Press
The Climate of
Bhutan
In summary:
Because of the irregular terrain, the climate varies greatly from place to place. The south has a hot, humid, subtropical climate, with heavy rainfall, while the inland hills have a temperate climate, with hot summers, cool winters, and moderate rainfall. The mountainous areas are cold most of the year, and are relatively dry.