The Climate of
Kazakhstan
.jpg) Grain fields near Kokshetau
Grain fields near Kokshetau
Climate Map
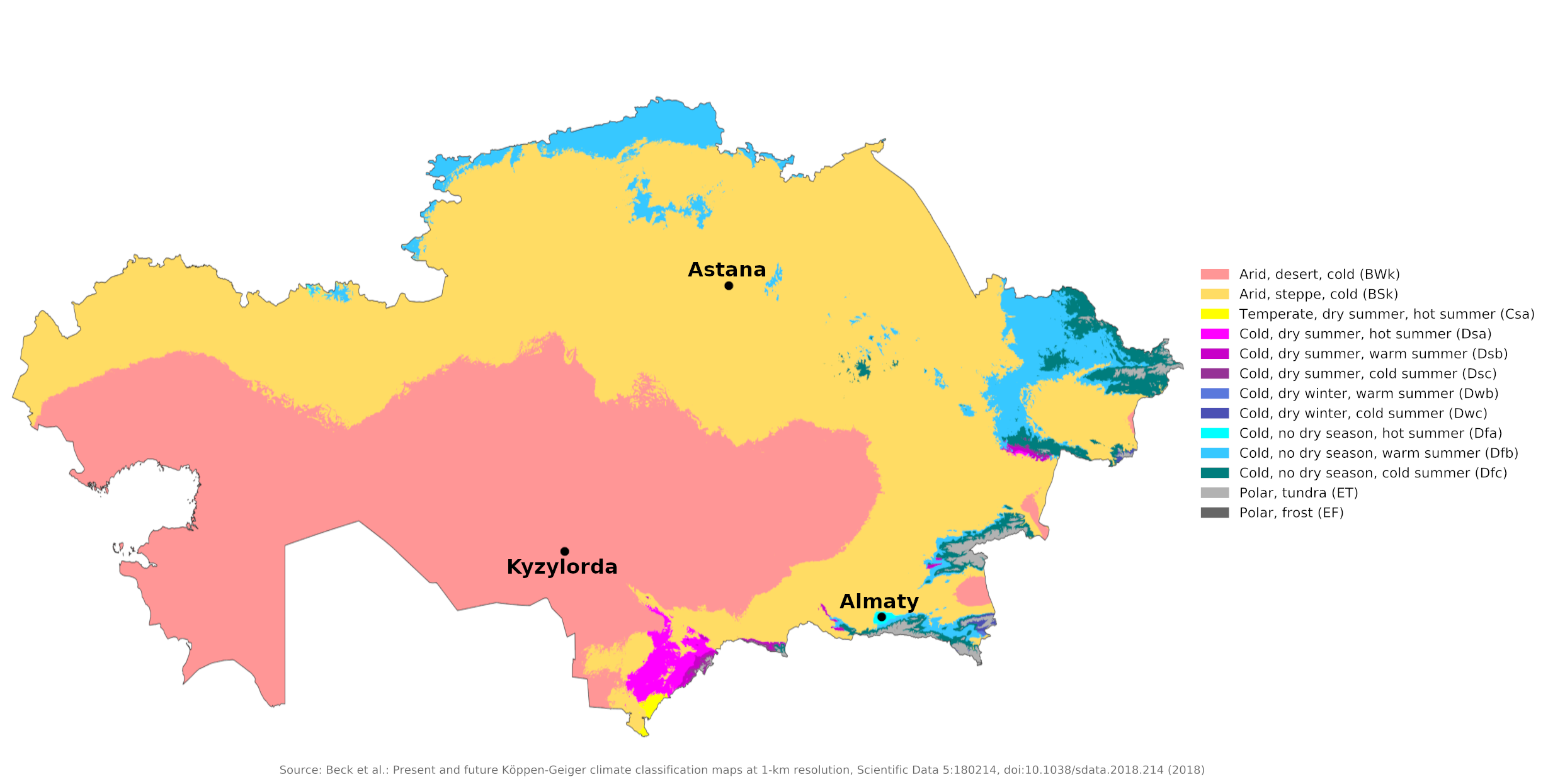 Climate map of Kazakhstan
Climate map of Kazakhstan
What is the climate of Kazakhstan like?
Kazakhstan is located in central western Asia between Russia and Uzbekistan, bordering on the Caspian Sea and the Aral Sea. It is the seventh largest country in the world, the largest country in Central Asia. Kazakhstan includes extensive deserts as well as semi-arid steppes. Part of eastern Kazakhstan belongs to the mountainous region on the borders of Kyrgyzstan and China.
As one of the largest countries in the world, Kazakhstan has a wide variety of seasonal temperatures and rainfalls depending on the region. Kazakhstan is thousands of miles from the ocean, making the climate very dry and extremely continental, with cold winters and hot summers. Winters are cold but generally dry and sunny. Average January temperatures are -15°C (5°F) in the north and -7°C (20°F) in the south; July temperatures average 20°C (68°F) in the north and reach 30°C (86°F) in the south. However, temperature extremes can be much higher or lower than these averages. In winter they can drop below -45°C (-49°F) and in summer they can reach 45°C (113°F).
In the steppes and deserts, summers range from warm to hot, but low humidity makes the heat more bearable. Strong, cold northerly winds make winters in the steppes particularly harsh. Astana is representative of the steppes of northern Kazakhstan, while Kyzylorda shows the desert conditions of southwestern Kazakhstan.
| Climate data for Astana (1991–2020) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | −10.3 (13.5) | −8.8 (16.2) | −1.5 (29.3) | 12.2 (54.0) | 20.9 (69.6) | 25.8 (78.4) | 26.6 (79.9) | 25.5 (77.9) | 18.9 (66.0) | 10.4 (50.7) | −1.3 (29.7) | −8.0 (17.6) | 9.2 (48.6) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −14.5 (5.9) | −13.6 (7.5) | −6.0 (21.2) | 6.5 (43.7) | 14.5 (58.1) | 19.6 (67.3) | 20.6 (69.1) | 19.1 (66.4) | 12.6 (54.7) | 5.0 (41.0) | −5.2 (22.6) | −12.0 (10.4) | 3.9 (39.0) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −18.7 (−1.7) | −18.0 (−0.4) | −10.4 (13.3) | 1.2 (34.2) | 8.2 (46.8) | 13.4 (56.1) | 14.9 (58.8) | 13.0 (55.4) | 6.8 (44.2) | 0.5 (32.9) | −8.7 (16.3) | −16.0 (3.2) | −1.2 (29.8) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 18 (0.7) | 17 (0.7) | 20 (0.8) | 22 (0.9) | 33 (1.3) | 40 (1.6) | 56 (2.2) | 31 (1.2) | 21 (0.8) | 26 (1.0) | 29 (1.1) | 25 (1.0) | 338 (13.3) |
| Source: www.pogodaiklimat.ru | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Kyzylorda (1991–2020) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | −2.5 (27.5) | 0.8 (33.4) | 10.4 (50.7) | 20.9 (69.6) | 28.2 (82.8) | 33.6 (92.5) | 35.1 (95.2) | 33.4 (92.1) | 26.6 (79.9) | 18.1 (64.6) | 7.1 (44.8) | −0.5 (31.1) | 17.6 (63.7) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −6.8 (19.8) | −4.5 (23.9) | 4.0 (39.2) | 14.0 (57.2) | 21.1 (70.0) | 26.7 (80.1) | 28.3 (82.9) | 26.2 (79.2) | 19.0 (66.2) | 10.6 (51.1) | 1.7 (35.1) | −4.9 (23.2) | 11.3 (52.3) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −10.6 (12.9) | −9.1 (15.6) | −1.4 (29.5) | 7.3 (45.1) | 13.8 (56.8) | 19.2 (66.6) | 21.0 (69.8) | 18.9 (66.0) | 11.7 (53.1) | 4.2 (39.6) | −2.8 (27.0) | −8.5 (16.7) | 5.3 (41.5) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 19 (0.7) | 14 (0.6) | 14 (0.6) | 21 (0.8) | 17 (0.7) | 8 (0.3) | 5 (0.2) | 3 (0.1) | 3 (0.1) | 9 (0.4) | 16 (0.6) | 16 (0.6) | 145 (5.7) |
| Source: www.pogodaiklimat.ru | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Almaty (1991–2020) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 0.5 (32.9) | 2.7 (36.9) | 9.9 (49.8) | 17.8 (64.0) | 22.9 (73.2) | 27.9 (82.2) | 30.5 (86.9) | 29.7 (85.5) | 24.5 (76.1) | 16.9 (62.4) | 8.1 (46.6) | 2.0 (35.6) | 16.1 (61.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −4.6 (23.7) | −2.4 (27.7) | 4.5 (40.1) | 12.1 (53.8) | 17.1 (62.8) | 22.1 (71.8) | 24.4 (75.9) | 23.3 (73.9) | 18.0 (64.4) | 10.6 (51.1) | 2.9 (37.2) | −2.7 (27.1) | 10.4 (50.7) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −8.1 (17.4) | −6.2 (20.8) | −0.2 (31.6) | 6.8 (44.2) | 11.5 (52.7) | 16.4 (61.5) | 18.6 (65.5) | 17.3 (63.1) | 12.0 (53.6) | 5.3 (41.5) | −1.0 (30.2) | −6.1 (21.0) | 5.5 (41.9) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 34 (1.3) | 43 (1.7) | 73 (2.9) | 113 (4.4) | 99 (3.9) | 59 (2.3) | 43 (1.7) | 34 (1.3) | 28 (1.1) | 49 (1.9) | 55 (2.2) | 44 (1.7) | 674 (26.5) |
| Source: www.pogodaiklimat.ru | |||||||||||||
In general, it rains very little in Kazakhstan; about three quarters of the country is classified as arid or semi-arid. Annual rainfall ranges from less than 100 millimeters (4 inches) in the south-central desert regions to between 250 and 350 millimeters (10 and 14 inches) in the steppes, where flash floods are common after summer thunderstorms. In the mountains, annual precipitation (mainly in the form of snow) averages 1,500 millimeters (60 inches). A lack of rain makes Kazakstan a sunny country; on average, the country experiences 260 sunny days in the south and 120 sunny days in the north.
References
- E. A. Pearce, Charles Gordon Smith, (1990) The Hutchinson World Weather Guide, John Murray Press. ISBN 1859863426
- Timothy L. Gall, (ed.), (2003), Worldmark Encyclopedia of the Nations, Eleventh Edition, Thomson Gale
- Hugh Chisholm, (ed.), (1911), Encyclopædia Britannica, Eleventh edition, Cambridge University Press
The Climate of
Kazakhstan
In summary:
Kazakhstan has an arid continental climate, with cold winters and hot summers. Roughly three-quarters of the country is considered arid or semi-arid with low rainfall. Because of the wide ranges in elevation in the country, there are wide variations in temperature and rainfall.