The Geography of
Lithuania
Why visit Lithuania?
Lithuania is the self-styled "Jewel of the Baltics". Whether it's getting some fresh air in the exuberant forests, berry picking, walking on specialized trails through the well-preserved wetlands, or just having a picnic near one of many lakes, Lithuania is a great place for nature-related activities.
Contents
Map
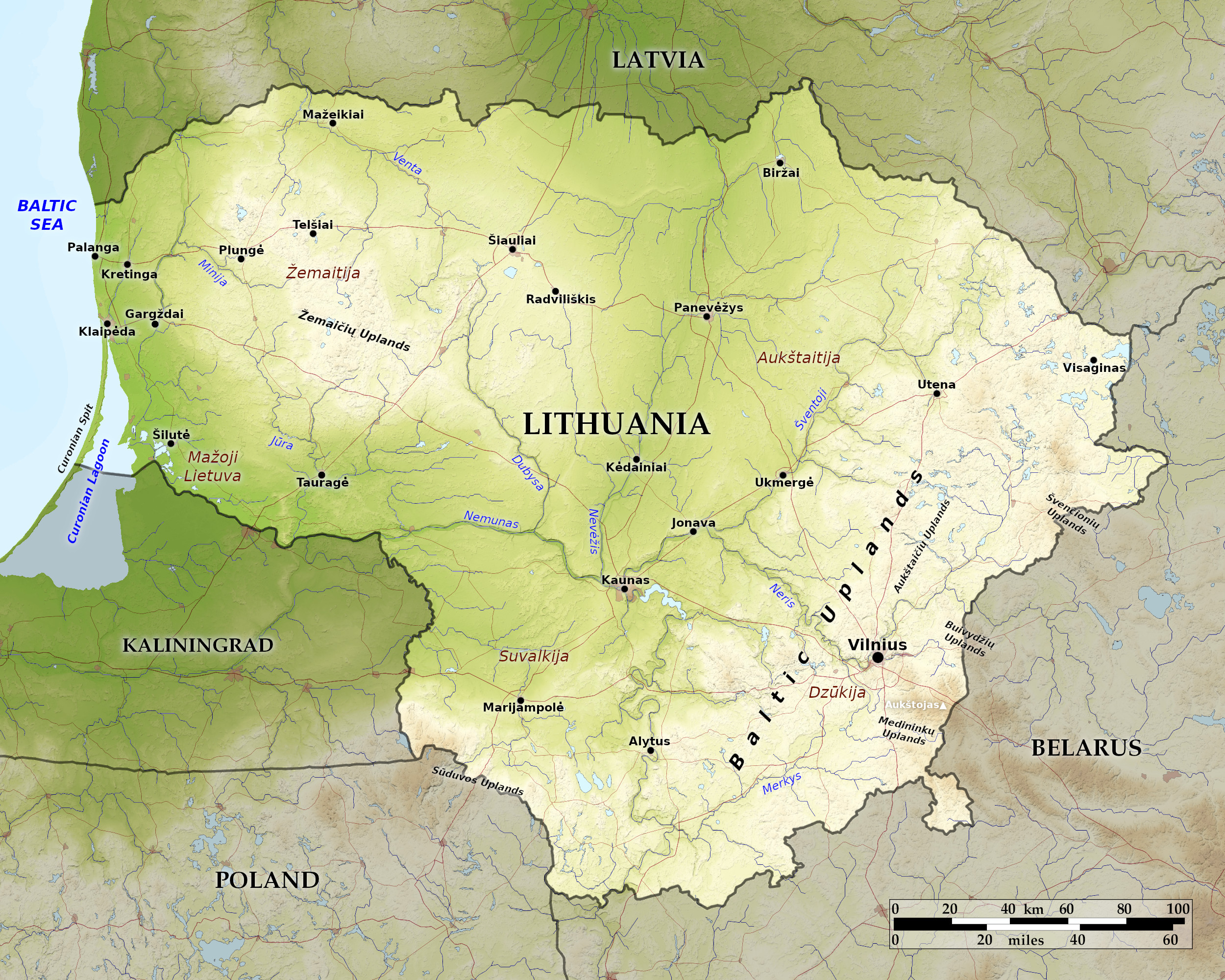 Relief map of Lithuania
Relief map of Lithuania
What is the landscape of Lithuania like?
The landscape of Lithuania is one of alternating regions of highlands and lowlands with a low-lying central plain. Highlands lie to the east and southeast of the central plain, while to the west the land is hilly but becomes low again along the coast. The western hills are known as the Žemaičių Upland. To the southeast are the Baltic Highlands. None of these hills are very tall, but they make for a varied landscape. The highest elevation, Aukštojas Hill (294 meters / 964 feet), is situated in the southeast.
Of the major cities, Vilnius, the only Baltic capital not situated on the coast, is a glorious example of Baroque architecture in a very northern setting. Vilnius has an interesting old center and is dominated by its historic Castle of Guediminas. Kaunas, the second largest city, is considered the most "Lithuanian" of cities. Klaipeda has a distinct port feel to it, and its timber-framed houses are a reminder of past German influence.
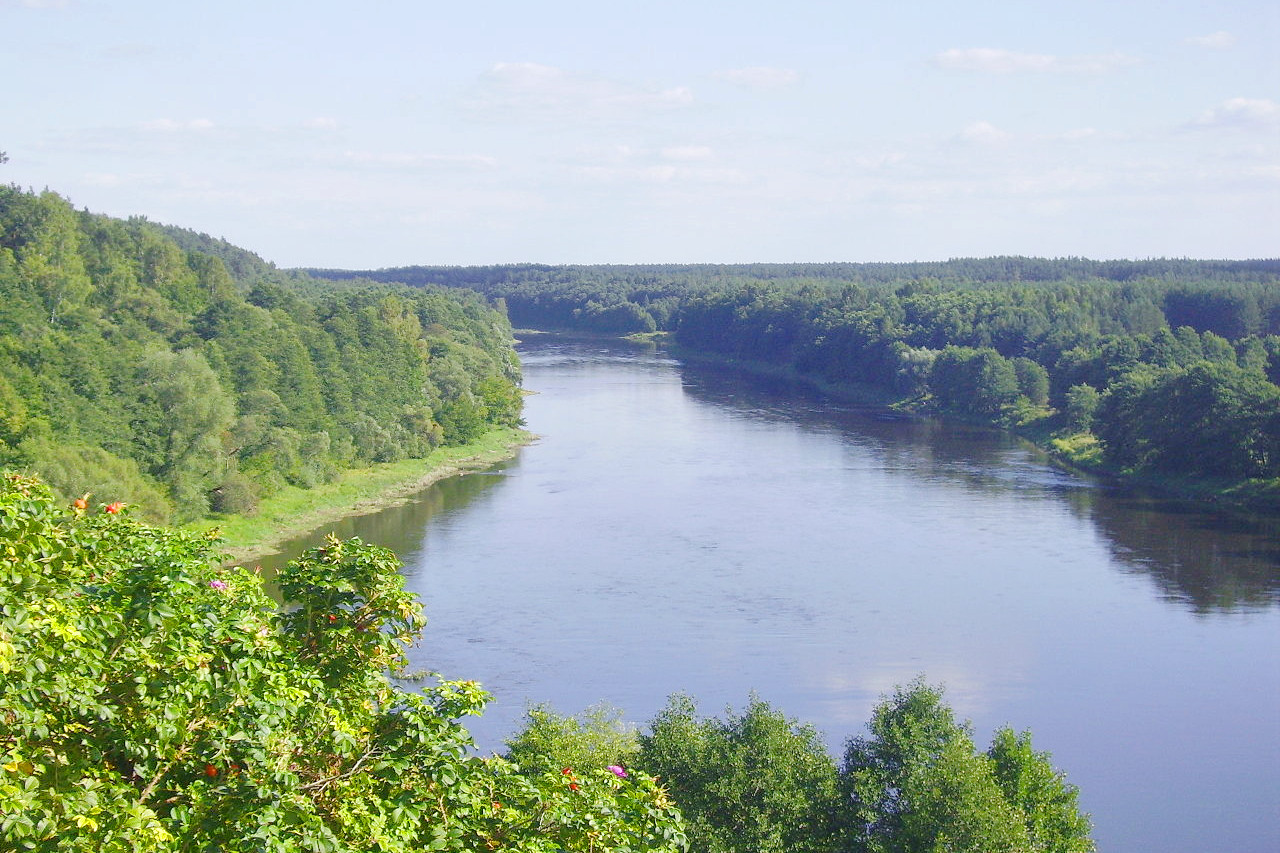
Lithuania has a wealth of inland waterways. It is honeycombed with about 4,000 lakes and some 800 rivers. Although many of the country’s original wetlands have been drained for agriculture, there still many remaining wetlands in the north and west.
Lithuania has a western coast along the Baltic Sea. The coastline is only around 108 kilometers (67 miles) long yet it has some of the most breathtaking scenery. A long, narrow sandbar forms an offshore lagoon along the southern half of the coastline called the Curonian Lagoon (Kuršiu Marios). A designated national park, the spit is a long, curving peninsula of sand dunes and pine forests, a mile wide and 60 miles (97 km) long.
What is the nature of Lithuania like?
About a third of the countryside is forested. Lithuania has mixed forests. The vegetation is a mixture of coniferous, broadleaf woodlands, arctic, and steppe species. Oak trees dominate in the north and central regions, while pine is found mostly in the southern and western coast zone. Other less common trees are birch, aspen, spruce, and black alder.
There are many species of mammals including rabbit, fox, red deer, roe, elk, wild boar, badger, wolf, and lynx. Lithuania also sports over two-hundred breeding bird species. Ducks, geese, swans, herons, and terns flourish in the wetlands near the coast, while white storks and other birds of prey abound in the eastern uplands.
What is the climate of Lithuania like?
See our main article: The Climate of Lithuania
Lithuania's climate is transitional between maritime and continental—the western coastal region has a maritime climate and the eastern region a more continental one. Winter can be very cold when there cold winds from the interior of Russia. Summers are warm though: the mean temperature in July is 18°C (64°F). Annual rainfall varies from around 500 mm (25 in) inland to 850 mm (33 in) towards the coast.
| Climate data for Vilnius (1991–2020) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | −1.7 (28.9) | −0.5 (31.1) | 4.4 (39.9) | 12.6 (54.7) | 18.4 (65.1) | 21.7 (71.1) | 23.8 (74.8) | 23.1 (73.6) | 17.4 (63.3) | 10.2 (50.4) | 3.7 (38.7) | −0.3 (31.5) | 11.2 (52.2) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −3.9 (25.0) | −3.1 (26.4) | 0.9 (33.6) | 7.6 (45.7) | 13.0 (55.4) | 16.4 (61.5) | 18.7 (65.7) | 17.9 (64.2) | 13.0 (55.4) | 7.0 (44.6) | 1.8 (35.2) | −2.2 (28.0) | 7.3 (45.1) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −5.9 (21.4) | −5.6 (21.9) | −2.7 (27.1) | 2.6 (36.7) | 7.5 (45.5) | 11.1 (52.0) | 13.6 (56.5) | 12.7 (54.9) | 8.5 (47.3) | 3.7 (38.7) | −0.1 (31.8) | −4.1 (24.6) | 3.5 (38.3) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 38.9 (1.53) | 34.4 (1.35) | 37.0 (1.46) | 46.2 (1.82) | 52.1 (2.05) | 72.7 (2.86) | 79.3 (3.12) | 75.8 (2.98) | 65.2 (2.57) | 51.5 (2.03) | 51.5 (2.03) | 49.2 (1.94) | 653.8 (25.74) |
| Source: World Meteorological Organization | |||||||||||||
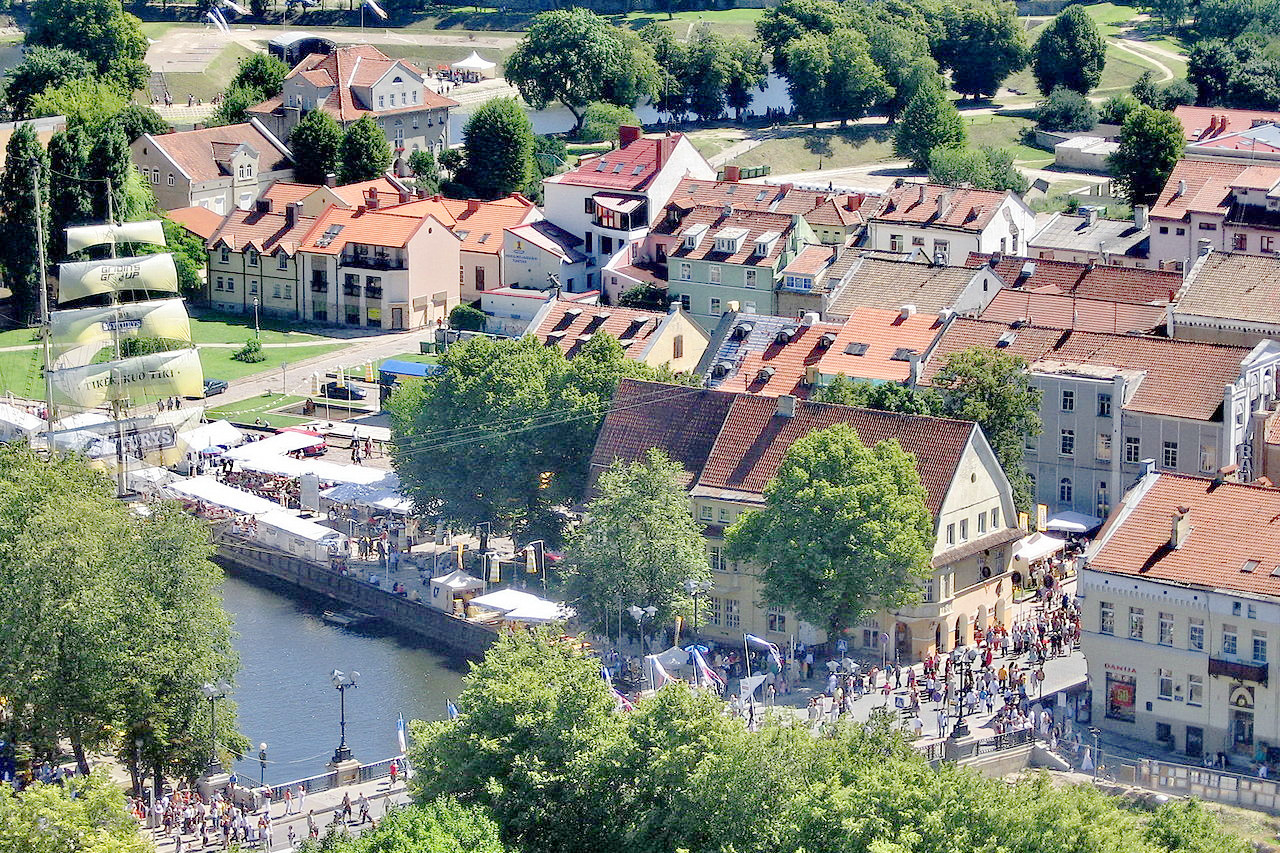 Klaipėda is a Lithuanian city situated at the mouth of the Curonian Lagoon
Klaipėda is a Lithuanian city situated at the mouth of the Curonian Lagoon
The official websites
Lithuania
Real is Beautiful
| Location: | Eastern Europe, bordering the Baltic Sea, between Latvia and Russia, west of Belarus |
| Coordinates: | 55° 15′ N, 24° 00′ E |
| Size: | • 285 km N-S; 375 km E-W • 175 miles N-S; 230 miles E-W |
| Terrain: | A central lowland with many scattered small lakes, surrounded by low ranges of hills |
| Climate: | The climate is transitional between maritime and continental; cool winters and warm summers |
| Highest point: | Aukštojas 294 m / 964 ft |
| Forest: | 37% (2010 est.) (source) |
| Population: | 2,683,546 (2022 est.) |
| Population density: | Low (43/km²) |
| Capital: | Vilnius |
| Languages: | Lithuanian (official) 85.3%, Russian 6.8%, Polish 5.1%, other 1.1% |
| Human Development Index: | Very high (0.882) |
.jpg)



