The Geography of
Vietnam
Why visit Vietnam?
Vietnam is a beautiful country with some of the most scenic views in Southeast Asia. The country is extraordinarily scenic—the mountains, the rivers, and the villages are all stunning. Green dominates the landscape—a profusion of vegetation nourished by abundant rainfall and countless rivers. Vietnam has an amazing culture and history, with centuries of beauty and mystery to explore.
Map
 Relief map of Vietnam
Relief map of Vietnam
What is the landscape of Vietnam like?
South (Nam Bo)
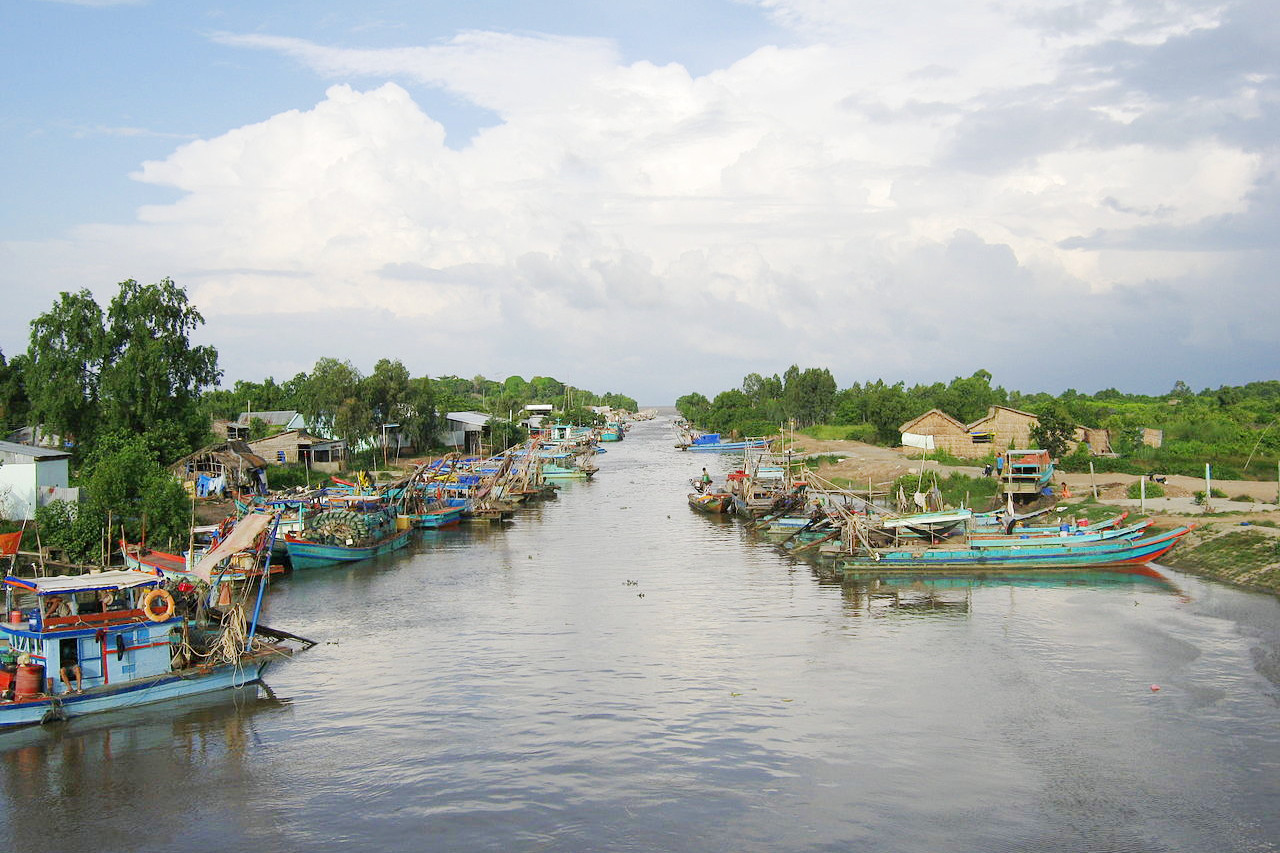
Southern Vietnam is a lowland, which consists mainly of the combined delta of the Mekong and several lesser rivers. It is very flat and is crossed by a network of irrigation channels. The conditions are very dry in some locations, including a few scattered areas with desertlike sand dunes. The remainder is a great agricultural province for rice, sugar, coconuts, bananas, pineapples, sweet potatoes, and betel nuts. Ho Chi Minh city (or "Saigon"), is the most important city of southern Vietnam, and is the chief port. It is situated on the Saigon River, a tributary of the Mekong delta.
Center (Trung Bo)
Running down the middle of the country are the Central Highlands or "Annamese Cordillera" (Vietnamese: Trường Sơn), a mountain system that spans nearly the entire length of the country. There is coastal plain which is narrow and broken, and it is here that most of the people of the region live. Behind it are the mountains, which project southward from Yunnan Province in China, extending along the country's entire border with Laos and separating the Red River Basin from that of the Mekong River. In this central region, many rivers are marked by rapid descent as they cascade from the mountains to the nearby coast. This creates some stunning vistas.
The mountains extend along Vietnam's boundary with Laos and part of its boundary with Cambodia until it reaches the Mekong Delta. Its peaks range in height from about 1,500 meters (5,000 feet) to 2,500 meters (8,500 feet). The hill city of Da Lat is in the center of this area.
North (Bac Bo)
Northern Vietnam is dominated by forests, mountains, and the country’s second great waterway, the Red River (Sông Hồng in Vietnamese). The northern mountains, called the Hoàng Liên Mountains, includes Vietnam's highest peak, Fansipan (Vietnamese: Phan Xi Păng) at 3,147 meters or 10,326 feet. North Vietnam is an undulating area drained by the Red and Black Rivers, which unite to form a common delta in a flat, triangular region.
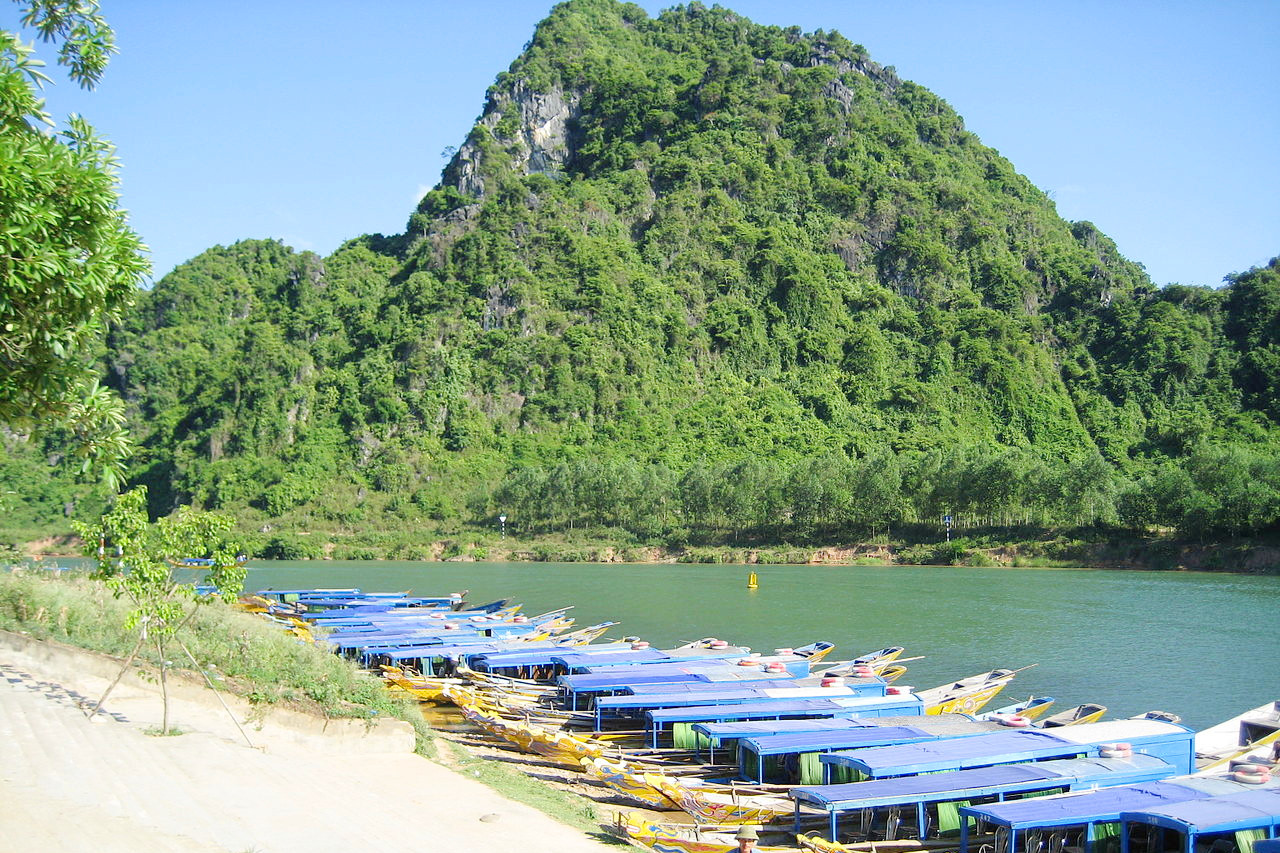
The extreme north consists of a limestone region, whose chief characteristic is the enormous blocks of limestone standing 100 feet high and riddled by caves and tunnels. Phong Nha-Ke Bang National Park is a karst (limestone formation) treasure trove of grottos, caves, and other limestone formations that attracts researchers and tourists from around the world.
The capital city, Hanoi, is one of the finest cities of the Far East. It is situated at the head of the Red River delta, a crowded region with a very-high population density. A second major branch of Vietnam’s mountains, sometimes referred to as the Northern Highlands, extends along the border with China, terminating in a series of islands northeast of Haiphong in the Gulf of Tonkin.
What is the nature of Vietnam like?
Vietnam has a wealth of plant and animal species, and the country has been blessed with incredible biodiversity. The mountainous regions of north, as well as the Central Highlands, are tropical rain forest regions broken by large areas of monsoon forest. In the higher altitudes of the far northwest there are pine forests. Tropical grasses are widespread elsewhere, and there are mangrove forests fringing parts of the Red River Delta and in the Ca Mau peninsula, which juts into the Gulf of Thailand. Tropical evergreen forests predominate in the south, with extensive savanna in the southwest. Deer and wild oxen are found in the more mountainous areas. Some endangered species include primates like the Delacour’s langur, golden-headed langur, Tonkin snub-nosed monkey, and the eastern black-crested gibbon. There are close to 1,000 species of tropical birds.
What is the climate of Vietnam like?
See our main article: The Climate of Vietnam
Vietnam has a tropical climate, and temperatures remain high around the year. The average annual temperature in Ho Chi Minh City is 27°C (81°F), compared with 23°C (74°F) in Hanoi. In the north there is a definite cooler season between October and March. In the south of Vietnam, the lowlands are sheltered from any outbreaks of cold, northerly air and the dry season is warm to hot with much sunshine.
Over most of Vietnam there is a single rainy season at the time of the south monsoon between May and September, although the central coastal region gets maximum rainfall between September and January. Average annual rainfall ranges from 1600 mm (64 in) in Hanoi to more than 4000 mm (160 in) in the mountains. Typhoons strike the central coastal region between July and November.
| Climate data for Hanoi | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 19.7 (67.5) | 20.1 (68.2) | 22.9 (73.2) | 27.2 (81.0) | 31.4 (88.5) | 32.9 (91.2) | 33.1 (91.6) | 32.3 (90.1) | 31.2 (88.2) | 28.8 (83.8) | 25.3 (77.5) | 22.0 (71.6) | 27.2 (81.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 16.4 (61.5) | 17.2 (63.0) | 20.0 (68.0) | 23.9 (75.0) | 27.4 (81.3) | 28.9 (84.0) | 29.2 (84.6) | 28.6 (83.5) | 27.5 (81.5) | 24.9 (76.8) | 21.5 (70.7) | 18.2 (64.8) | 23.6 (74.5) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 14.3 (57.7) | 15.3 (59.5) | 18.1 (64.6) | 21.7 (71.1) | 24.6 (76.3) | 26.1 (79.0) | 26.3 (79.3) | 26.0 (78.8) | 24.9 (76.8) | 22.3 (72.1) | 18.9 (66.0) | 15.6 (60.1) | 21.2 (70.2) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 18 (0.7) | 19 (0.7) | 34 (1.3) | 105 (4.1) | 165 (6.5) | 266 (10.5) | 253 (10.0) | 274 (10.8) | 243 (9.6) | 156 (6.1) | 59 (2.3) | 20 (0.8) | 1,612 (63.4) |
| Source: Vietnam Institute for Building Science and Technology | |||||||||||||
The official websites
Vietnam
Timeless Charm
| Location: | Southeastern Asia, bordering the Gulf of Tonkin, and the South China Sea |
| Coordinates: | 16° 30′ N, 107° 30′ E |
| Size: | • 1650 km N-S; 780 km E-W • 1025 miles N-S; 485 miles E-W |
| Terrain: | Mountains span the length of the country together with a narrow coastal plain. Broad, flat river plains in the far north and south |
| Climate: | Tropical climate with high rainfall in the summer months. The south is warmer than the north. Cooler in the mountains |
| Highest point: | Phan Xi Păng 3,147 m / 10,326 m |
| Forest: | 50% (2010 est.) (source) |
| Population: | 96,208,984 (2019) |
| Population density: | High (295/km²) |
| Capital: | Hanoi |
| Languages: | Vietnamese. Others include: Tày, Mường, Cham, Khmer, Chinese, Nùng, Hmong) |
| Human Development Index: | High (0.704) |
| Currency: | Đồng |
.jpg)




