The Climate of
Libya
 El Manar Palace of Benghazi
El Manar Palace of Benghazi
Climate Map
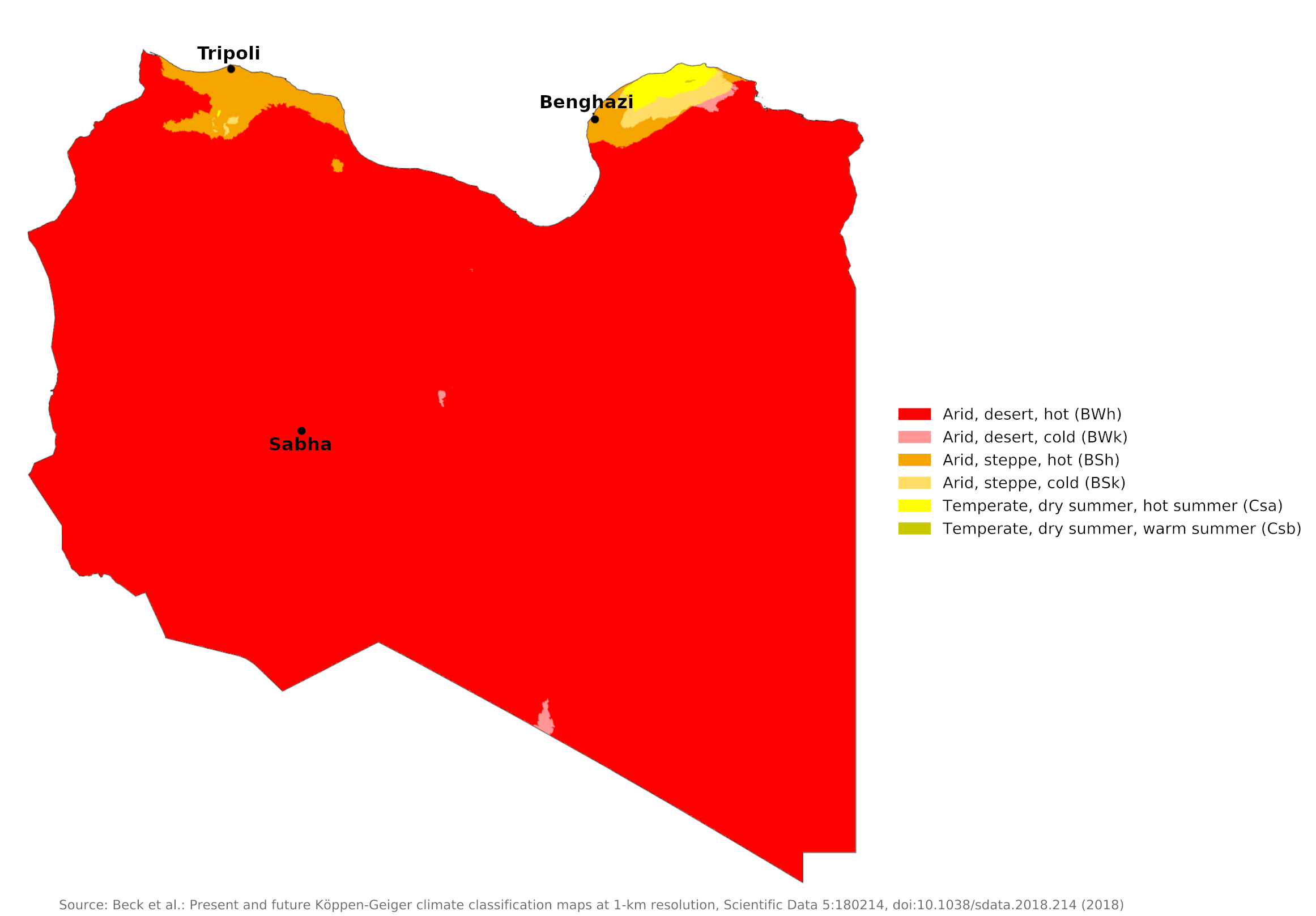 Climate map of Libya
Climate map of Libya
What is the climate of Libya like?
Libya is a large country in North Africa. The country shares borders with Egypt, Sudan, Chad, Niger, Algeria, and Tunisia. It has a long Mediterranean coastline, but most of it is made up of the central Sahara Desert. The Mediterranean coastal fringes have a Mediterranean climate with some rain between October and March, but the vast inland desert area has very little rain and has recorded some of the highest temperatures in the world.
Coast
Libya's climate has pronounced seasonal variations, influenced by both the Mediterranean and the Sahara desert. Tripoli in western Libya (Tripolitania) and Benghazi in eastern Libya (Cyrenaica) are representative of year-round conditions in the coastal regions. Here the climate is a Mediterranean one, with hot summers and mild winters.
Along the coast of Tripolitania and Cyrenaica mean summer temperatures range from 27 to 32°C (81–90°F), but can go much higher. Summer temperatures can reach between 40 and 46°C (104–115°F). The Ghibli, a hot, dry desert wind, can change temperatures by 15 to 20°C (27–36°F) in both summer and winter. The weather is cooler in the highlands, and winter frosts occur at maximum elevations.
As elsewhere on the southern Mediterranean coasts, winter weather can be changeable from day to day, with cool, cloudy and rainy spells interrupting the generally warm, sunny and calm weather. The meager winter rainfall is brought by Mediterranean lows, but rainfall is often erratic, and a pronounced drought can occur. Along the coast of the Gulf of Sidra, between Tripolitania and Cyrenaica, it rains even less, so that the desert reaches the coast. The heaviest rainfall occurs in the Jebel Akhdar plateau in the northeast, which receives 400 to 600 millimeters (16 to 24 inches) of rain annually. Many coastal regions receive less than 200 millimeters (8 inches).
| Climate data for Tripoli (1961–1990) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 17.9 (64.2) | 19.1 (66.4) | 20.7 (69.3) | 23.7 (74.7) | 27.1 (80.8) | 30.4 (86.7) | 31.7 (89.1) | 32.6 (90.7) | 31.0 (87.8) | 27.7 (81.9) | 23.3 (73.9) | 19.3 (66.7) | 25.4 (77.7) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 13.4 (56.1) | 14.3 (57.7) | 16.0 (60.8) | 18.7 (65.7) | 21.9 (71.4) | 25.3 (77.5) | 26.7 (80.1) | 27.7 (81.9) | 26.2 (79.2) | 22.9 (73.2) | 18.4 (65.1) | 14.6 (58.3) | 20.5 (68.9) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 8.9 (48.0) | 9.5 (49.1) | 11.2 (52.2) | 13.7 (56.7) | 16.7 (62.1) | 20.1 (68.2) | 21.7 (71.1) | 22.7 (72.9) | 21.4 (70.5) | 18.0 (64.4) | 13.4 (56.1) | 9.9 (49.8) | 15.6 (60.1) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 62.1 (2.44) | 32.2 (1.27) | 29.6 (1.17) | 14.3 (0.56) | 4.6 (0.18) | 1.3 (0.05) | 0.7 (0.03) | 0.1 (0.00) | 16.7 (0.66) | 46.6 (1.83) | 58.2 (2.29) | 67.5 (2.66) | 333.9 (13.15) |
| Source: World Meteorological Organization | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Benghazi | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 16.7 (62.1) | 18.0 (64.4) | 20.3 (68.5) | 24.7 (76.5) | 28.9 (84.0) | 31.8 (89.2) | 31.7 (89.1) | 32.3 (90.1) | 30.8 (87.4) | 27.8 (82.0) | 23.2 (73.8) | 18.4 (65.1) | 25.4 (77.7) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 12.5 (54.5) | 13.2 (55.8) | 14.9 (58.8) | 18.7 (65.7) | 22.5 (72.5) | 25.5 (77.9) | 25.9 (78.6) | 26.5 (79.7) | 25.1 (77.2) | 22.1 (71.8) | 18.2 (64.8) | 14.1 (57.4) | 19.9 (67.8) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 8.3 (46.9) | 8.4 (47.1) | 9.5 (49.1) | 12.8 (55.0) | 16.0 (60.8) | 19.2 (66.6) | 20.2 (68.4) | 20.8 (69.4) | 19.4 (66.9) | 16.5 (61.7) | 13.3 (55.9) | 9.9 (49.8) | 14.5 (58.1) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 67 (2.6) | 42 (1.7) | 29 (1.1) | 9 (0.4) | 4 (0.2) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 4 (0.2) | 18 (0.7) | 30 (1.2) | 65 (2.6) | 270 (10.6) |
| Source: Deutscher Wetterdienst | |||||||||||||
Desert
In the desert interior the climate has very hot summers and extreme daily temperature ranges. During the summer months, there is virtually no rain in southern Libya and temperatures quickly soar to over 40°C (104°F). Winter daytime temperatures range between 15°C and 20°C (59°F and 68°F) and can fall below 0°C (32°F) at night.
Beyond 160 km (100 miles) or less from the coast, annual rainfall falls below 100 millimeters (4 inches) and is often much less. The Sahara receives less than 50 millimeters (2 inches) of rain annually. Indeed, in much of the Sahara, rainfall is so small and erratic that any average number becomes almost meaningless. The climate here is shown by the southern oasis city of Sabha.
| Climate data for Sabha (1962–1990) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 18.9 (66.0) | 22.0 (71.6) | 26.1 (79.0) | 31.8 (89.2) | 35.7 (96.3) | 39.2 (102.6) | 38.3 (100.9) | 37.8 (100.0) | 35.9 (96.6) | 31.3 (88.3) | 24.9 (76.8) | 20.0 (68.0) | 30.2 (86.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 11.7 (53.1) | 14.4 (57.9) | 18.4 (65.1) | 23.9 (75.0) | 27.9 (82.2) | 31.4 (88.5) | 30.7 (87.3) | 30.4 (86.7) | 28.6 (83.5) | 24.1 (75.4) | 17.8 (64.0) | 12.9 (55.2) | 22.7 (72.9) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 4.5 (40.1) | 6.8 (44.2) | 10.6 (51.1) | 15.9 (60.6) | 20.1 (68.2) | 23.6 (74.5) | 23.0 (73.4) | 22.9 (73.2) | 21.3 (70.3) | 16.9 (62.4) | 10.7 (51.3) | 5.7 (42.3) | 15.2 (59.4) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 1.1 (0.04) | 0.8 (0.03) | 0.5 (0.02) | 0.5 (0.02) | 0.3 (0.01) | 0.5 (0.02) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.4 (0.02) | 2.1 (0.08) | 0.9 (0.04) | 1.1 (0.04) | 8.2 (0.32) |
| Source: World Meteorological Organization | |||||||||||||
References
- E. A. Pearce, Charles Gordon Smith, (1990) The Hutchinson World Weather Guide, John Murray Press. ISBN 1859863426
- Timothy L. Gall, (ed.), (2003), Worldmark Encyclopedia of the Nations, Eleventh Edition, Thomson Gale
- Federal Research Division, Library of Congress, (1989), Libya: a country study. Claitor's Pub. Division.
- Hugh Chisholm, (ed.), (1911), Encyclopædia Britannica, Eleventh edition, Cambridge University Press
The Climate of
Libya

In summary:
The climate is influenced by both the Mediterranean Sea and the desert. Along the coast, summer temperatures can reach between 40 and 46°C (104–115°F); farther south, temperatures can go even higher. The ghibli, a hot, dry desert wind, can change temperatures by 17–22°C (30–40°F) in both summer and winter.
Rain falls generally in a short winter period. Evaporation is high, and severe droughts are common. The northeast receives 400 to 600 mm (16 to 24 in) of rain yearly, while other regions receive less than 200 mm (8 in). The Sahara Desert receives less than 50 mm (2 in) of rain annually.