The Geography of
Emilia–Romagna
Why visit Emilia-Romagna?
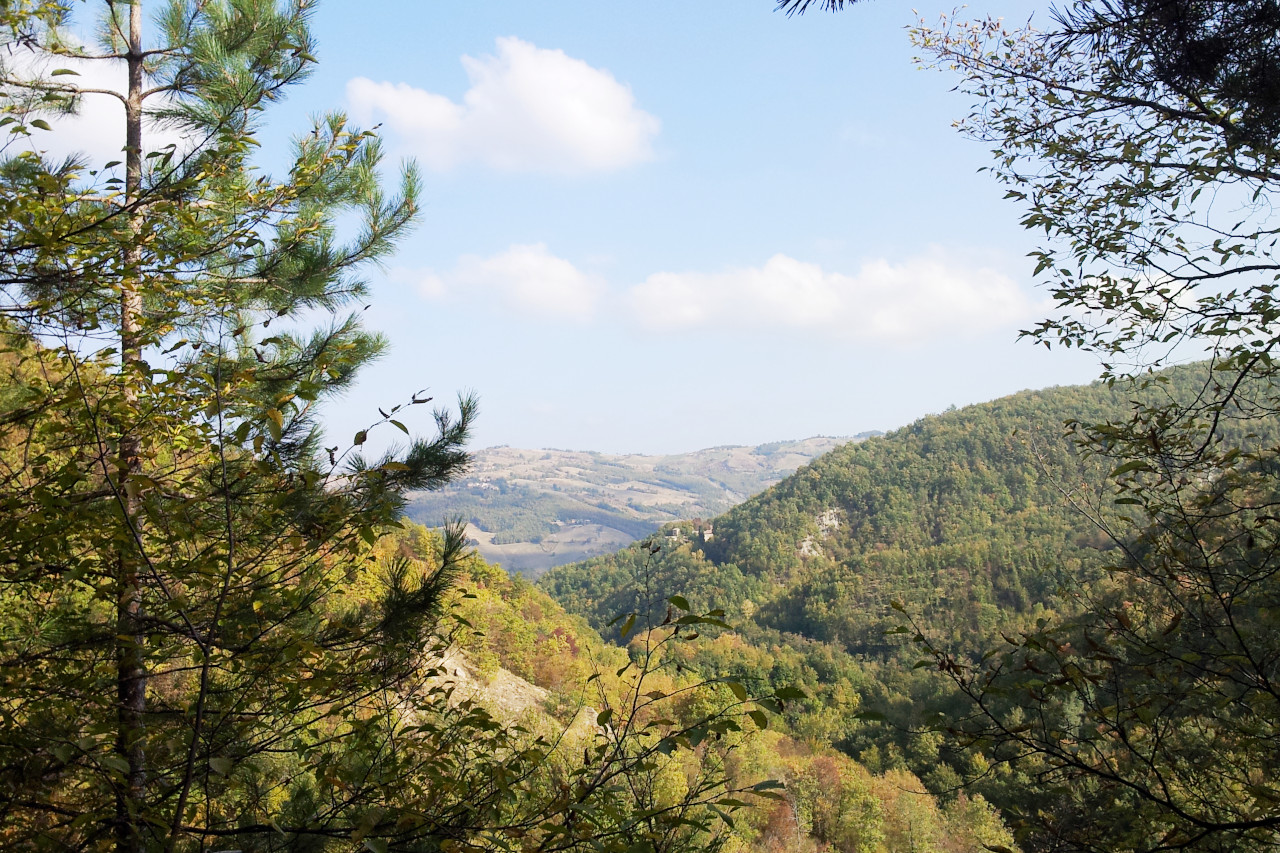
Emilia-Romagna is a treasure house filled with architectural gems and aritstic masterpieces. The northern Apennines, too, cross the whole width of this province. Throughout this region the Apennines are covered with beautiful forests of chestnut, oak and beech.
Contents
Map
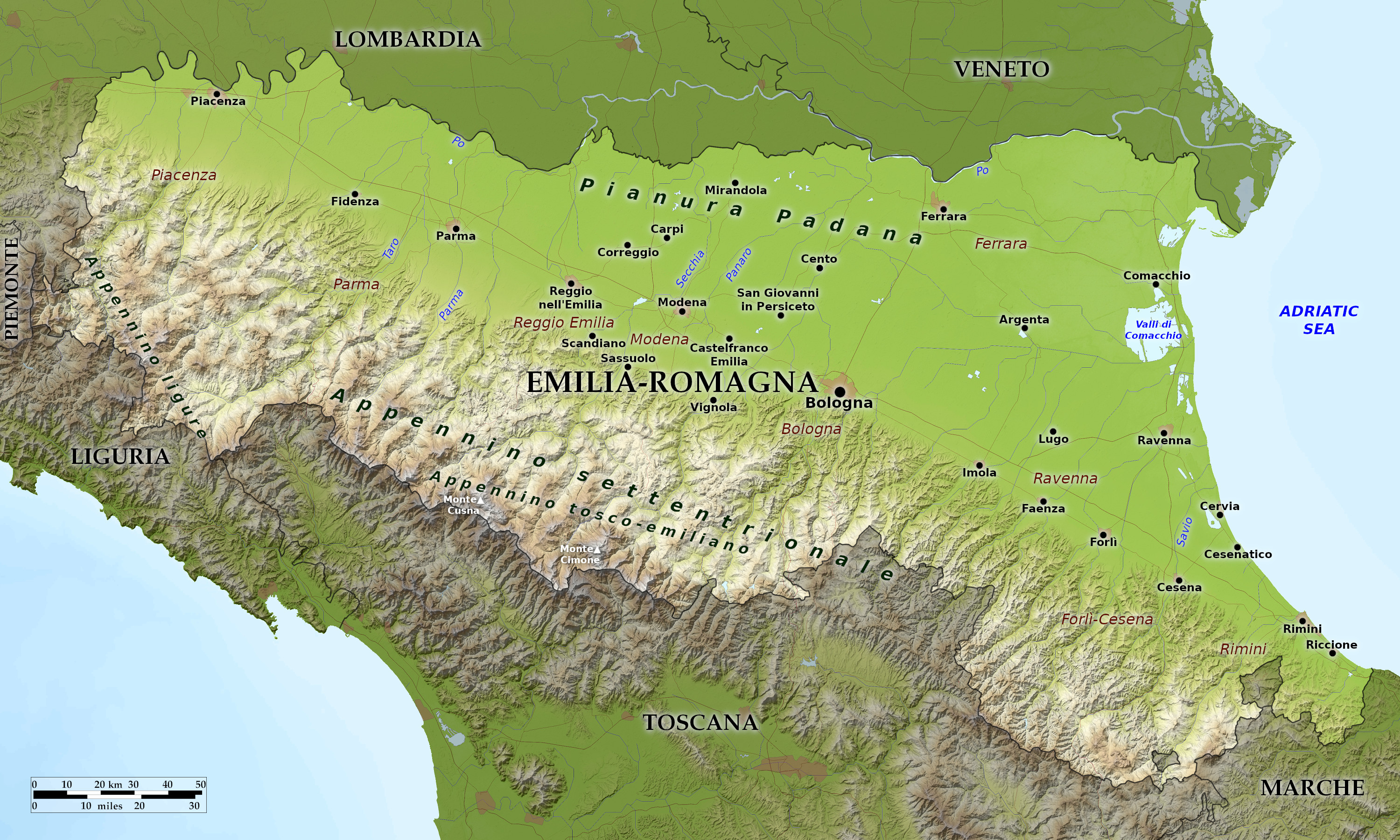 Relief map of Emilia-Romagna
Relief map of Emilia-Romagna
What is the landscape of Emilia-Romagna like?
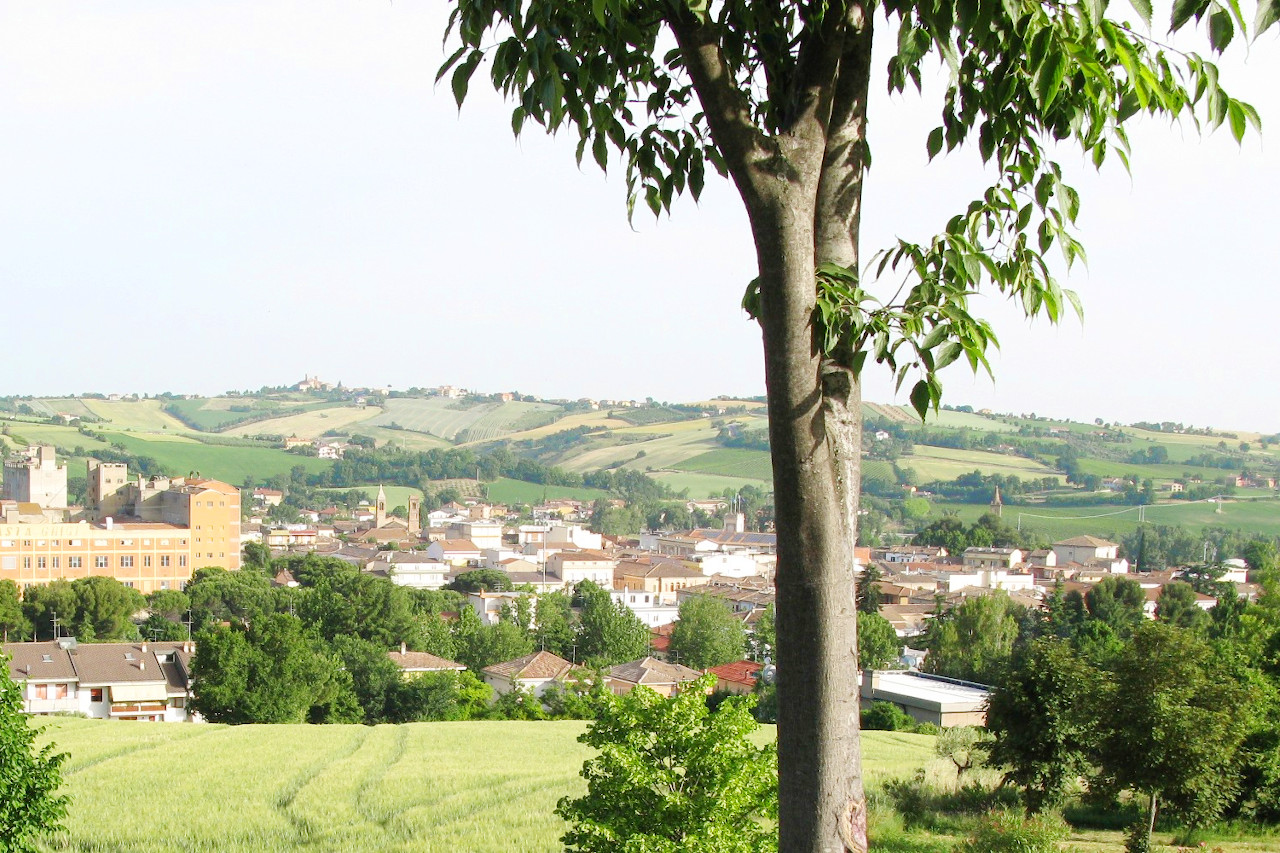
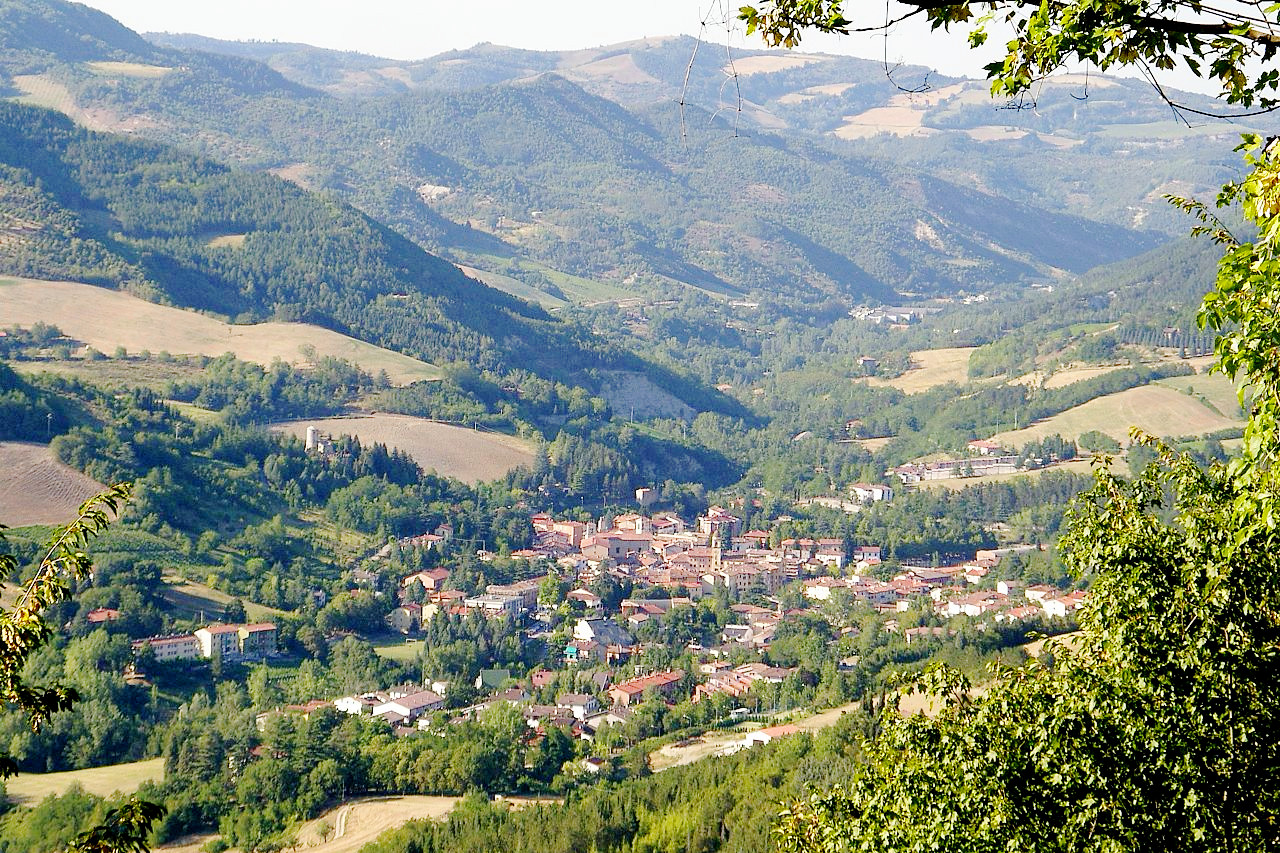
As its double name indicates, Emilia–Romagna is the union of two regions, Emilia in the west and Romagna in the east. The region, created in 1948, is the nation's transition from the Italy of the Po and the Alps to that of the peninsula: half of the region is plains and flatlands, and the other half are hills and mountains. The region is generally framed by the Po River on the north, the Apennines on the south, and the Adriatic Sea to the east. Between the mountains and the Po, much of Emilia Romagna is very flat with large fields of wheat and corn.
What is the nature of Emilia-Romagna like?
The plains are relatively deforested, although some important woodland nature reserves are preserved here. The most common trees here are broadleaf trees such as black poplar, white poplar, alders, willows, oak, elm and hornbeam. In the Apennines, forests are much more widespread and rich in species. The hills and lower mountains have mixed forests with oaks, chestnuts, maples, limes, hornbeams, cherries, rowan trees and ash trees. The higher mountains areas have extensive and widespread beech forests often with conifers such as the silver fir, and the most southern populations of Scots pine in Italy. High altitudes have an alpine flora with heaths, meadows and pastures.
What is the climate of Emilia-Romagna like?
The climate of Emilia–Romagna is a temperate one, but with hot, sultry summers and cold, prolonged winters. Rainfall is moderate in the plain, becoming heavier in the hills and mountains. In the Apennines snow falls between November and March, and even the plain receives some winter snow. The driest seasons are summer and winter, and the wettest are spring and autumn.
| Climate data for Bologna (1971–2000) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 6.0 (42.8) | 9.0 (48.2) | 14.2 (57.6) | 17.7 (63.9) | 23.0 (73.4) | 27.1 (80.8) | 30.4 (86.7) | 29.8 (85.6) | 25.4 (77.7) | 18.6 (65.5) | 11.1 (52.0) | 6.8 (44.2) | 18.3 (64.9) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 2.8 (37.0) | 5.0 (41.0) | 9.2 (48.6) | 12.5 (54.5) | 17.5 (63.5) | 21.4 (70.5) | 24.4 (75.9) | 24.1 (75.4) | 20.1 (68.2) | 14.4 (57.9) | 7.7 (45.9) | 3.6 (38.5) | 13.6 (56.5) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −0.5 (31.1) | 0.9 (33.6) | 4.1 (39.4) | 7.4 (45.3) | 12.0 (53.6) | 15.7 (60.3) | 18.5 (65.3) | 18.4 (65.1) | 14.8 (58.6) | 10.1 (50.2) | 4.3 (39.7) | 0.4 (32.7) | 8.8 (47.8) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 34.0 (1.34) | 44.3 (1.74) | 54.2 (2.13) | 74.2 (2.92) | 58.0 (2.28) | 57.3 (2.26) | 40.5 (1.59) | 52.5 (2.07) | 67.5 (2.66) | 72.3 (2.85) | 68.0 (2.68) | 48.5 (1.91) | 671.3 (26.43) |
| Source: Servizio Meteorologico | |||||||||||||
The official websites
Emilia–Romagna
Beauty and uniqueness
| Location: | North-central Italy |
| Coordinates: | 44° 30′ N, 11° 00′ E |
| Size: | • 155 km N-S; 285 km E-W • 95 miles N-S; 175 miles E-W |
| Terrain: | Plains and flatlands with mountains in the south. North of the Apennines the countryside is flat with large fields of wheat and corn. |
| Climate: | Hot, humid summers and cold, prolonged winters. Autumn is humid, foggy and cool. Spring is mild and rainy. Winter snow in the mountains sometimes reaches the plains |
| Highest point: | Monte Cimone 2,165 m |
| Forest: | 26% (2010 est.) (source) |
| Population: | 4,446,220 (2010) |
| Population density: | High (200/km²) |
| Capital: | Bologna |
| Languages: | Italian |
| Human Development Index: | Very High (0.921) |


.jpg)


