The Geography of
Veneto
Veneto presents a stark contrast with the rugged Dolomite Alps in the north and the plains of Venice where the Po divides into a wide delta with extensive salt water lagoons. At its heart lies Venice, the great medieval city.
Contents
Map
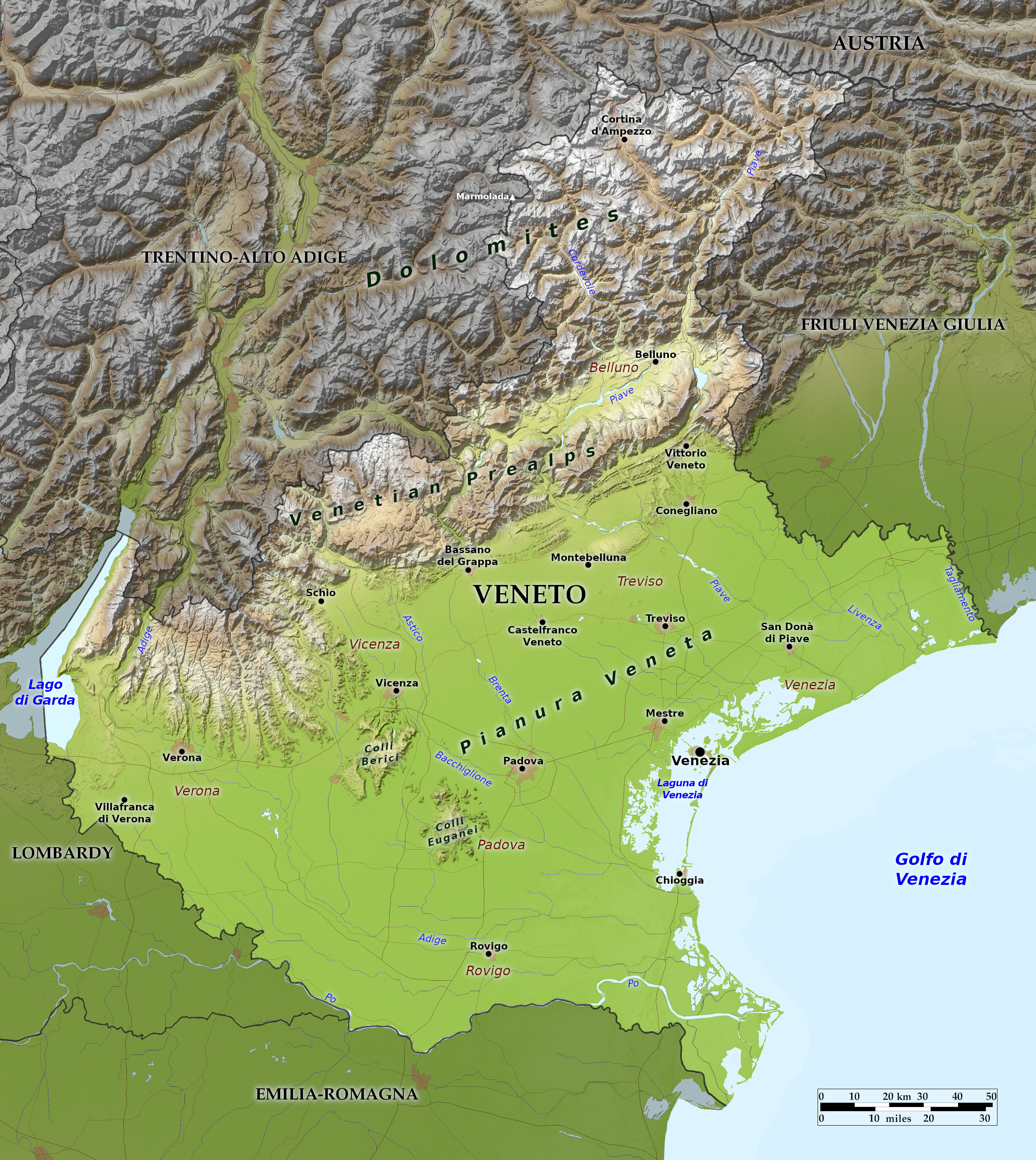 Relief map of Veneto
Relief map of Veneto
What is the landscape of Veneto like?
The Veneto region lies in northeast Italy. It is closely associated with its capital, Venice, the great medieval city which sits in a lagoon at the northwest corner of the Adriatic Sea. Three of Italy's most important rivers—the Po, the Piave, and the Adige—flow through the Veneto and empty into the Adriatic. To the west, the Veneto region is separated from Lombardy in part by Lake Garda.
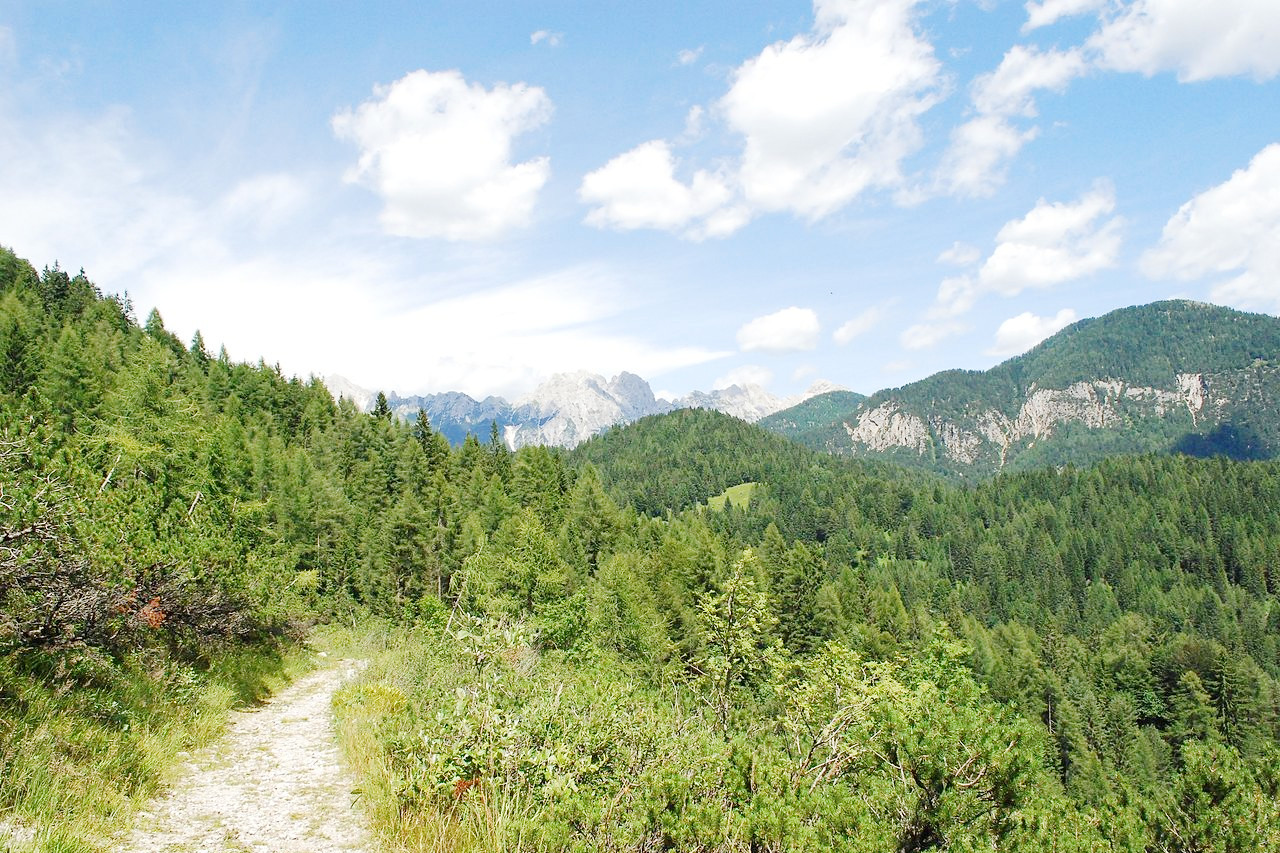
The Veneto region is a land of dramatic geographic contrasts, from rugged Dolomite Alps in the north to Piedmont and lowlands toward the shore. Lowland plains take up over half of the area of the region, but the northern reaches of Belluno province contain peaks over 3,000 meters (10,000 feet) in the Tofane range; the region's highest mountain is Marmolada (3,343 m or 10,968 feet), on the Veneto-Trentino border.
Venice
Venice sits in the middle of a lagoon dotted with small islands. These islands are little more than low mud banks, barely rising above the water-level. Yet the group of islands called Rialto, were first the asylum and then the magnificent and permanent home of a people that took a prominent part in the medieval and Renaissance history of Europe.
The city dates from ninth century when the government of this maritime republic was established upon the islands, separated from the sea by long banks, or "lidi", and from the mainland by estuaries and swamps. This unique position rendered Venice almost impregnable; and once the drawbacks and difficulties were surmounted, Venice became the most powerful and wealthiest of the commercial republics of Italy.
What is the nature of Veneto like?
Veneto is a region that includes many forms of natural landscape. The shore lagoons of Venice and the the river delta of the Po extend right along the coast. The lowlands of Padua and the delta area of Rovigo province yield are rich farmlands. The Veneto region also produces more wine than any region outside of Sicily and Apulia. The center of the region's winemaking is Verona province, which produces perhaps two-thirds of the total.
What is the climate of Veneto like?
From the cold of the Dolomite mountains to the warmth of the Mediterranean coast, Veneto has a very large range of climate. The climate of Veneto overall is sub-continental, but with the mitigating effect of the sea and the chain of the Alps to protect it from the north winds. The Alpine region has cool summers and cold temperatures in winter with frequent snowfall. Lake Garda is a special case in itself: thanks to its size, the area is relatively mild throughout the year, and has mild winters and very hot summers. In the lower hills and the plains the climate is mild, often with relatively cool wet winters and long hot, sultry summers.
| Climate data for Venice (1971–2000) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 6.6 (43.9) | 8.6 (47.5) | 12.5 (54.5) | 16.1 (61.0) | 21.5 (70.7) | 24.9 (76.8) | 27.7 (81.9) | 27.5 (81.5) | 23.5 (74.3) | 18.0 (64.4) | 11.6 (52.9) | 7.4 (45.3) | 17.2 (63.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 3.3 (37.9) | 4.7 (40.5) | 8.3 (46.9) | 12.0 (53.6) | 17.1 (62.8) | 20.5 (68.9) | 23.0 (73.4) | 22.6 (72.7) | 18.9 (66.0) | 13.8 (56.8) | 7.8 (46.0) | 4.0 (39.2) | 13.0 (55.4) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −0.1 (31.8) | 0.8 (33.4) | 4.1 (39.4) | 7.8 (46.0) | 12.7 (54.9) | 16.1 (61.0) | 18.3 (64.9) | 17.7 (63.9) | 14.3 (57.7) | 9.6 (49.3) | 4.0 (39.2) | 0.6 (33.1) | 8.8 (47.8) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 47.0 (1.85) | 48.3 (1.90) | 48.8 (1.92) | 70.0 (2.76) | 66.0 (2.60) | 78.0 (3.07) | 63.9 (2.52) | 64.8 (2.55) | 72.0 (2.83) | 73.5 (2.89) | 65.5 (2.58) | 50.6 (1.99) | 748.4 (29.46) |
| Source: Servizio Meteorologico | |||||||||||||
.jpg) Grand Canal, Venice
Grand Canal, Venice
The official websites
Veneto

One region, a thousand faces
| Location: | Northeast Italy |
| Coordinates: | 45° 45′ N, 11° 45′ E |
| Size: | • 210 km N-S; 195 km E-W • 130 miles N-S; 120 miles E-W |
| Terrain: | Plains in the south; hills in the north; Alpine mountains in the far north |
| Climate: | The plains have long, hot, sultry summers, and cool, humid winters. The alpine region has cool summers and cold winters with frequent snowfall |
| Highest point: | Marmolada 3,342 m |
| Forest: | 23% (2010 est.) (source) |
| Population: | 4,865,380 (2012) |
| Population density: | High (270/km²) |
| Capital: | Venezia (English: Venice) |
| Languages: | Italian |
| Human Development Index: | Very High (0.900) |


