The Geography of
Vermont
Why visit Vermont?
Vermont is home to the Green Mountains with its brilliant autumn foliage and winter sports. Here too is the Connecticut River, and the incredible Lake Champlain. Vermont has beautiful forests, lakes, rivers, and many miles of hiking trails which crisscross the state. Some of these trails lead right up into the heart of the Appalachian Mountains, while others wind through the forests or along sparkling rivers.
Contents
Map
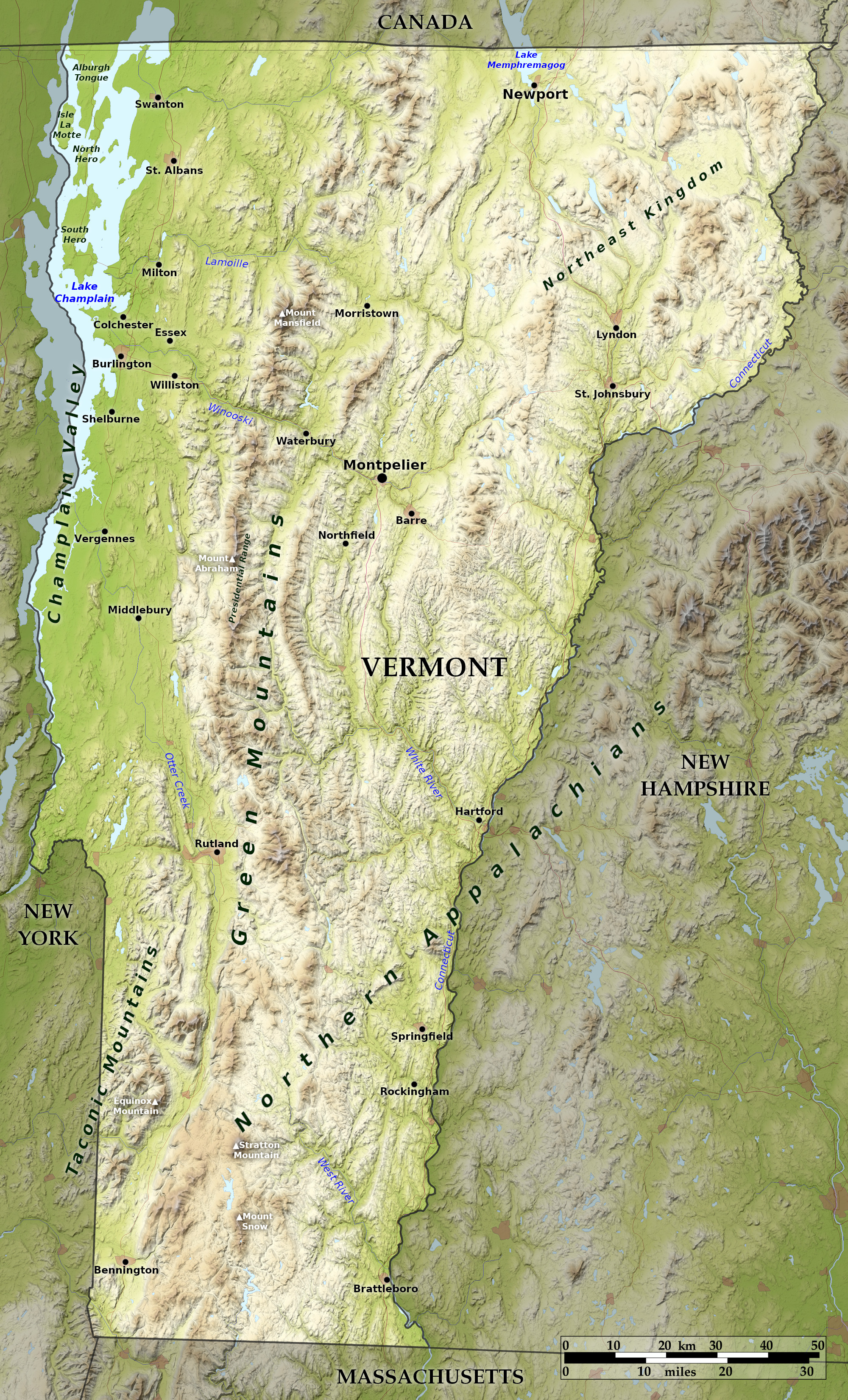 Relief map of Vermont
Relief map of Vermont
What is the landscape of Vermont like?
Vermont is a section of the New England upland; it rises up above the general upland surface and is broken by mountain ranges, individual mountains, high hills, and by deep narrow valleys. Most prominent are the Green Mountains, which extend north-to-south through the State. From the Massachusetts border northwards they form a continuous ridge, only broken in the north by the deep valleys of the Winooski and Lamoille rivers. The crest line is generally more than 2,000 feet high (600 m)—considerable areas are above 2,500 feet (760 m)—and culminates at Mount Mansfield at 4,395 feet (1340 m).
Southwest of the Green Mountains the Taconic Mountains form a nearly parallel, but distinct, range, extending from New York northwards nearly to the middle of Vermont. The Taconic Mountains rise in very irregular masses to 1,500–2,000 feet (450–600 m), and reach their maximum height at Mount Equinox at 3,840 feet (1,170 m).
Distributed along the entire eastern border are a number of tall and oval or conical shaped hills, and between these and the Green Mountains the country is largely occupied by high hills and deeply carved valleys. Vermont's rivers are generally swift, and in many places they are made very beautiful by their clear and sparkling waters, rapids, falls, gorges, and wooded banks. The flattest parts of Vermont are on the somewhat gentle slope of the Green Mountains in the northwest and on the islands in Lake Champlain.
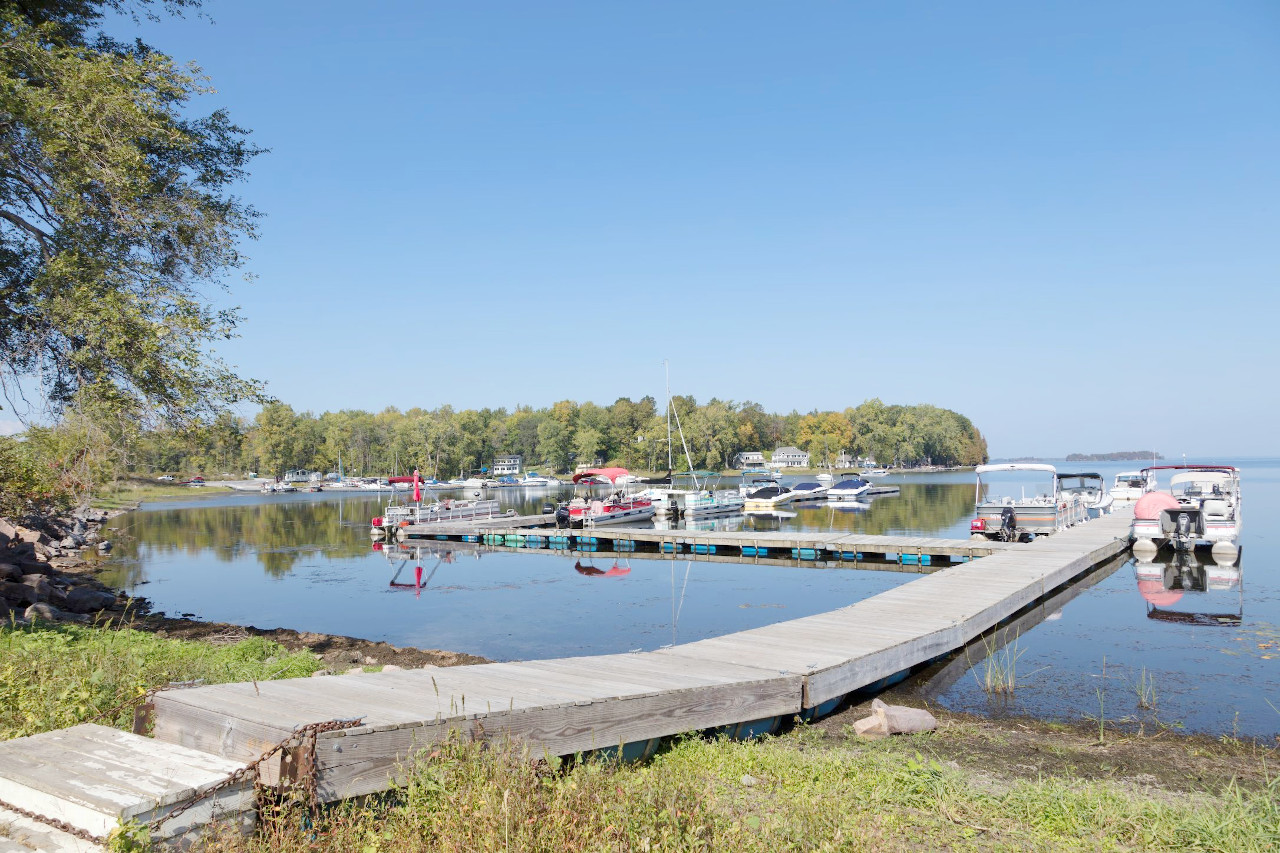
Lake Champlain, which lies beautifully in the valley between the Green and Adirondack mountains, lies mostly in Vermont. The Vermont shoreline on it runs for 150 miles or more, and in its northern portion are numerous islands, including Grand Isle, North Hero Island, and Isle La Motte, which are attractive summer resorts. On the northern border of the State is a smaller lake—Lake Memphremagog, and there are also many other small lakes and pools lying wholly within the State.
What is the nature of Vermont like?
Vermont ('vert mont'), the Green Mountain State, was so named from the evergreen forests of its mountains. The hills and valley-slopes, as well as the summits of the mountains, are covered with forests of pine and hemlock, with spruce and fir on the higher slopes. On the lower lands there are also forests of deciduous trees, the sugar maple being one of the most common trees. Birch and beech are common on the hills, and oaks, elm, hickory, ash, poplar, basswood, willow, chestnut and butternut in lower areas. Orchids are very prominent among a great variety of flowering plants. Along the shore of Lake Champlain are a few species of maritime plants that remain from the time when portions of western Vermont were covered by the sea, and on the upper slopes of some of the higher mountains are a few Alpine species.
What is the climate of Vermont like?
Vermont has warm, but short summers, and it is known for its long and severe winters, but sudden changes of temperature are common at all seasons. The central mountains are the coldest parts of the State, whereas the warmest regions lie in the west. More rain falls in summer than in any other season, and more rain falls in the southern part than in the northern. Winter sees heavy snow.
| Climate data for Montpelier, Vermont (1991–2020) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °F (°C) | 25.8 (−3.4) | 28.9 (−1.7) | 37.6 (3.1) | 51.5 (10.8) | 65.0 (18.3) | 73.2 (22.9) | 77.6 (25.3) | 76.1 (24.5) | 68.6 (20.3) | 55.3 (12.9) | 42.8 (6.0) | 31.3 (−0.4) | 52.8 (11.6) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 16.6 (−8.6) | 18.9 (−7.3) | 27.9 (−2.3) | 40.9 (4.9) | 53.3 (11.8) | 61.8 (16.6) | 66.5 (19.2) | 64.9 (18.3) | 57.4 (14.1) | 45.5 (7.5) | 34.4 (1.3) | 23.2 (−4.9) | 42.6 (5.9) |
| Average low °F (°C) | 7.4 (−13.7) | 8.9 (−12.8) | 18.1 (−7.7) | 30.3 (−0.9) | 41.7 (5.4) | 50.5 (10.3) | 55.5 (13.1) | 53.7 (12.1) | 46.3 (7.9) | 35.7 (2.1) | 26.0 (−3.3) | 15.1 (−9.4) | 32.4 (0.2) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 2.32 (59) | 2.06 (52) | 2.49 (63) | 3.04 (77) | 3.52 (89) | 4.21 (107) | 4.27 (108) | 3.81 (97) | 3.33 (85) | 3.87 (98) | 2.85 (72) | 2.93 (74) | 38.70 (983) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 22.6 (57) | 18.0 (46) | 16.8 (43) | 4.9 (12) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.9 (2.3) | 9.1 (23) | 21.9 (56) | 94.2 (239) |
| Source: NOAA | |||||||||||||
 1956 Owl Cottage Activity Center, at the Shelburne Museum in Shelburne
1956 Owl Cottage Activity Center, at the Shelburne Museum in Shelburne
The official websites
Vermont
The Green Mountain State
| Location: | Northeast United States |
| Coordinates: | 44° 00′ N, 72° 45′ W |
| Size: | • 255 km N-S; 145 km E-W • 160 miles N-S; 90 miles E-W |
| Terrain: | Mountains extending north to south through the State. Lowland to the west including Lake Champlain |
| Climate: | Short but warm summers; cold winters. Heavy winter snowfall |
| Highest point: | Mount Mansfield 1,340 m / 4,395 ft |
| Forest: | 78% (2016) (source) |
| Population: | 643,503 (2020) |
| Population density: | Low (26/km²) |
| Capital: | Montpelier |
| Languages: | English |
| Human Development Index: | Very High (0.940) |








.jpg)