The Geography of
New Brunswick
Why visit New Brunswick?
New Brunswick is a maritime province of Canada, situated on the eastern coast of Canada, between the coast of Maine and the Gaspé Peninsula. It features Grand Lake, St John River, and the Bay of Fundy. There are beautiful forests, hills, and lakes, as well as charming villages and towns. The landscape changes with every mile you travel.
Contents
Map
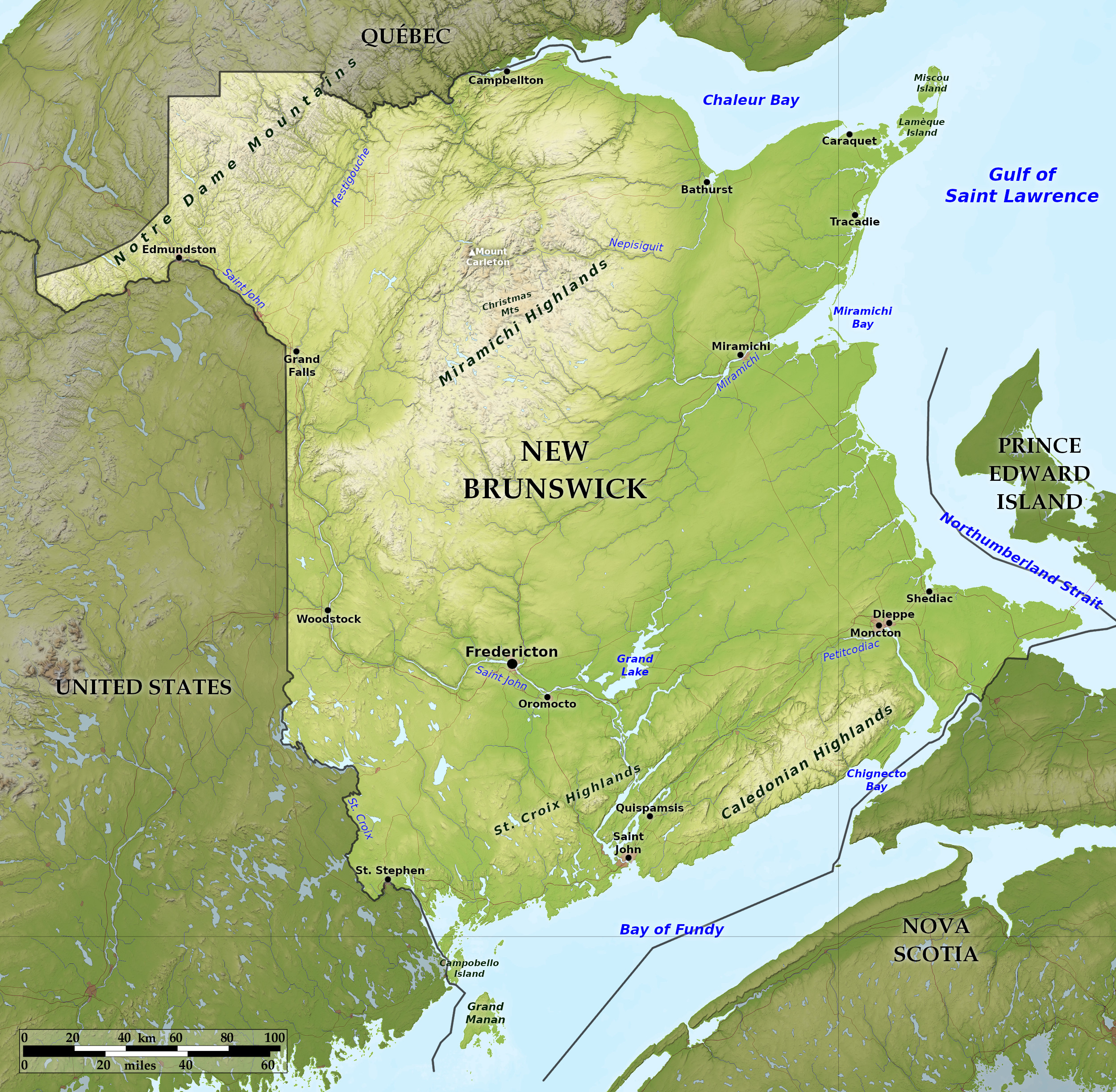 Relief map of New Brunswick
Relief map of New Brunswick
What is the landscape of New Brunswick like?
Northern New Brunswick has many ranges of hills from 300 to 600 meters (1,000–2,000 feet) in height, rising to Mount Carleton at 820 m / 2,690 feet. These hills are an extension of the Appalachian Mountains and enter the province from the US state of Maine. This whole section of the province is densely wooded.
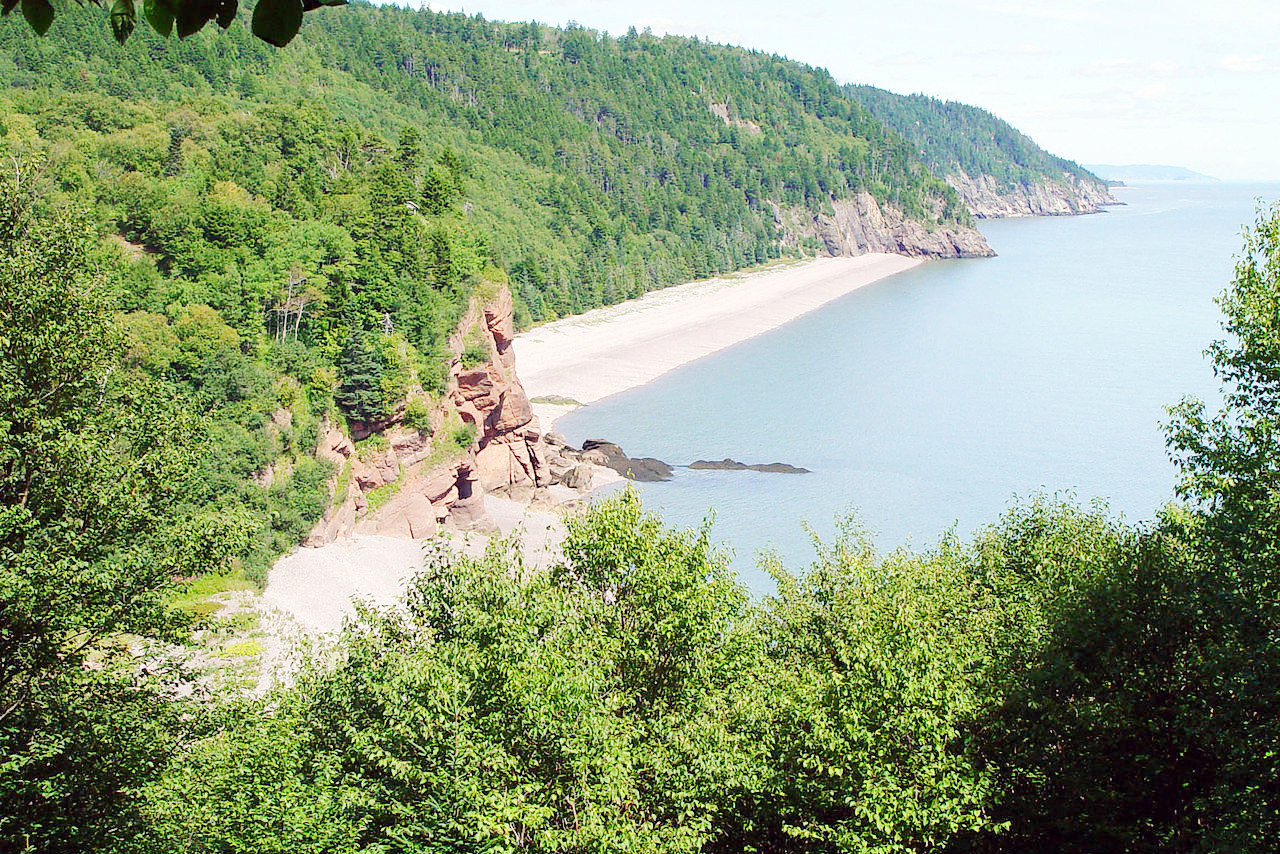
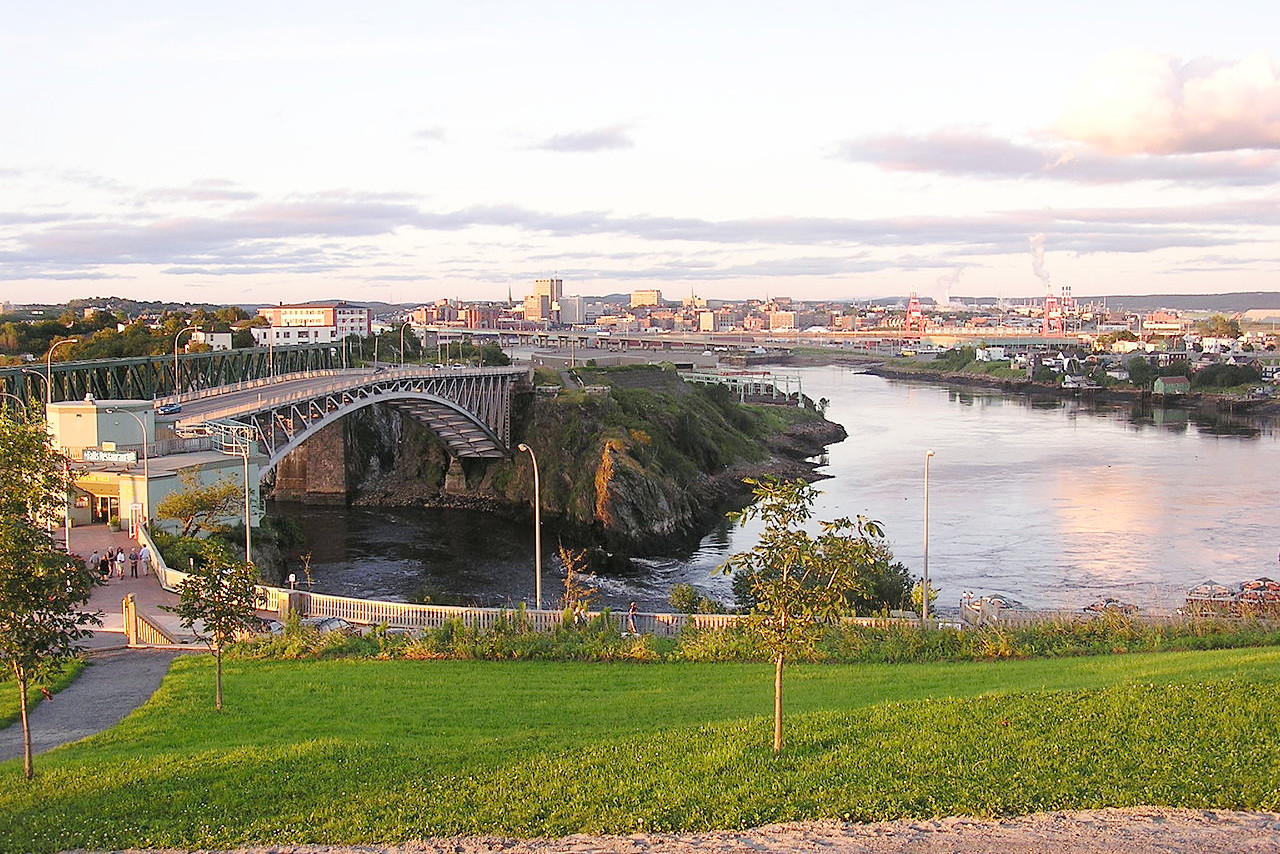
Southern New Brunswick embraces the district along the Bay of Fundy. The coast is rocky and bold and interrupted by ravines. Inland the numerous rivers, flowing through the soft sandstone rocks, have cut broad valleys. Along the shores on the east coast, the country is flat and composed of mosses and marshes, but inland it rises into gently sloping hills. New Brunswick is a network of rivers, bays and lakes. In the west the principal river is the St John, which is famous for its scenery; rises in the state of Maine and is over 450 miles in length. Among the many lakes which it drains is Grand Lake, 20 miles long, and varying from 3 to 9 miles in width.
The coastline of New Brunswick has many fine bays and harbours. The Bay of Fundy is an arm of the sea separating New Brunswick from Nova Scotia. It is 140 miles in length and its extreme width 45 miles. It is noted for its high tides, which rise about 10 meters (30 feet) at St John and over 15 meters (50 feet) at the head of Chignecto Bay.
What is the nature of New Brunswick like?
New Brunswick is heavily forested with a great variety of tree species. The predominant trees of the vast forests are black spruce, red spruce, white spruce, balsam fir, white pine, beech, sugar maple, yellow birch, and paper birch. A typical forest in the region is a mixed forest of spruce, fir, beech, maple, and birch. The remaining portion of the province is marshes, barrens, even tundra formations, and there are many flowering plants.
Hundreds of thousands of piping plovers and other shorebirds annually take flight from the salt marshes along the coastline at Marys Point, in Chignecto Bay. Every summer, more than 20 different kinds of whales come to the Bay of Fundy to feed in the plankton-rich waters.
What is the climate of New Brunswick like?
New Brunswick is subject to extremes of heat and cold. Spring opens later and summer lingers longer than in the provinces farther west. At inland points the extremes are greatest, with cold winters and hot summers. The winters are severe, and snow falls to a great depth, but the harbour of St John is open throughout the year. The autumn is delightful, especially after the first frost but before the weather has broken.
| Climate data for Fredericton (1981–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | −3.8 (25.2) | −2.0 (28.4) | 3.0 (37.4) | 10.0 (50.0) | 17.6 (63.7) | 22.7 (72.9) | 25.5 (77.9) | 24.8 (76.6) | 20.0 (68.0) | 13.2 (55.8) | 6.0 (42.8) | −0.7 (30.7) | 11.4 (52.5) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −9.4 (15.1) | −7.9 (17.8) | −2.4 (27.7) | 4.5 (40.1) | 11.1 (52.0) | 16.2 (61.2) | 19.3 (66.7) | 18.4 (65.1) | 13.6 (56.5) | 7.5 (45.5) | 1.5 (34.7) | −5.7 (21.7) | 5.6 (42.1) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −15.0 (5.0) | −13.7 (7.3) | −7.8 (18.0) | −1.0 (30.2) | 4.6 (40.3) | 9.7 (49.5) | 13.0 (55.4) | 12.1 (53.8) | 7.1 (44.8) | 1.6 (34.9) | −3.0 (26.6) | −10.7 (12.7) | −0.2 (31.6) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 95.3 (3.75) | 73.1 (2.88) | 93.2 (3.67) | 85.9 (3.38) | 96.2 (3.79) | 82.4 (3.24) | 88.3 (3.48) | 85.6 (3.37) | 87.5 (3.44) | 89.1 (3.51) | 106.3 (4.19) | 94.9 (3.74) | 1,077.7 (42.43) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 69.9 (27.5) | 47.5 (18.7) | 49.4 (19.4) | 18.6 (7.3) | 1.4 (0.6) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.8 (0.3) | 14.3 (5.6) | 50.5 (19.9) | 252.3 (99.3) |
| Source: Environment and Climate Change Canada | |||||||||||||
The official websites
New Brunswick
The Picture Province
| Location: | Southeastern Canada |
| Coordinates: | 46° 30′ N, 66° 00′ W |
| Size: | • 350 km N-S; 400 km E-W • 215 miles N-S; 250 miles E-W |
| Terrain: | Mountains in the north; rolling hills and plateau in the center and south |
| Climate: | Somewhat continental climate with warm summers and cold winters |
| Highest point: | Mount Carleton 820 m / 2,690 ft |
| Forest: | 85% (2010) (source) |
| Population: | 782,078 (2021) |
| Population density: | Low (11/km²) |
| Capital: | Fredericton |
| Languages: | English (65%); French (33%) |
| Human Development Index: | Very High (0.898) |




