The Geography of
Guatemala
Why visit Guatemala?
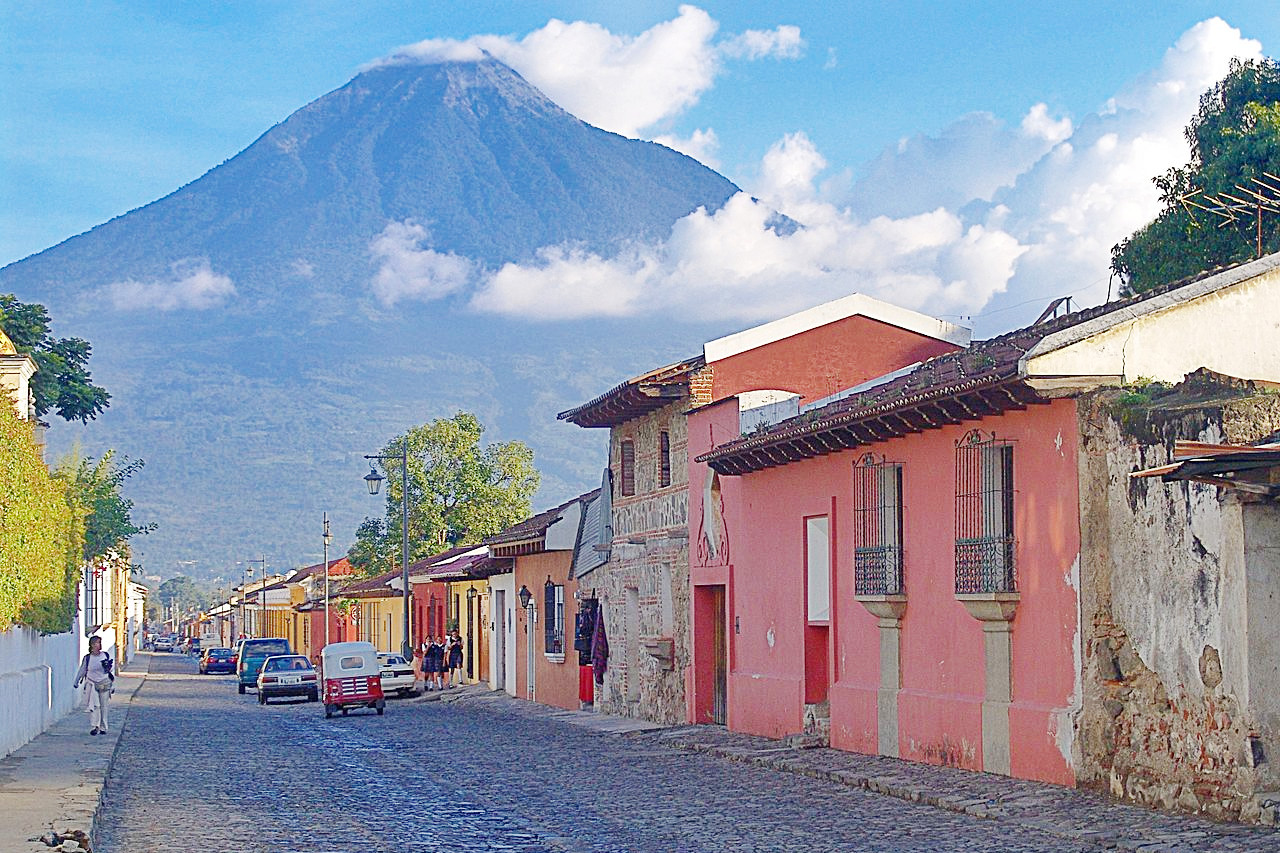
Guatemala has a beautiful geographical and cultural landscape, and famed for its scenery. There are rugged mountains, rain forests, jungles, pine forests, and volcanoes. There are also beautiful beaches. The dense rain forests are filled with wildlife and many rare beautiful birds. Guatemala is also the home of ancient Mayan temples and pyramids, and people come from all over the world to see them.
Contents
Map
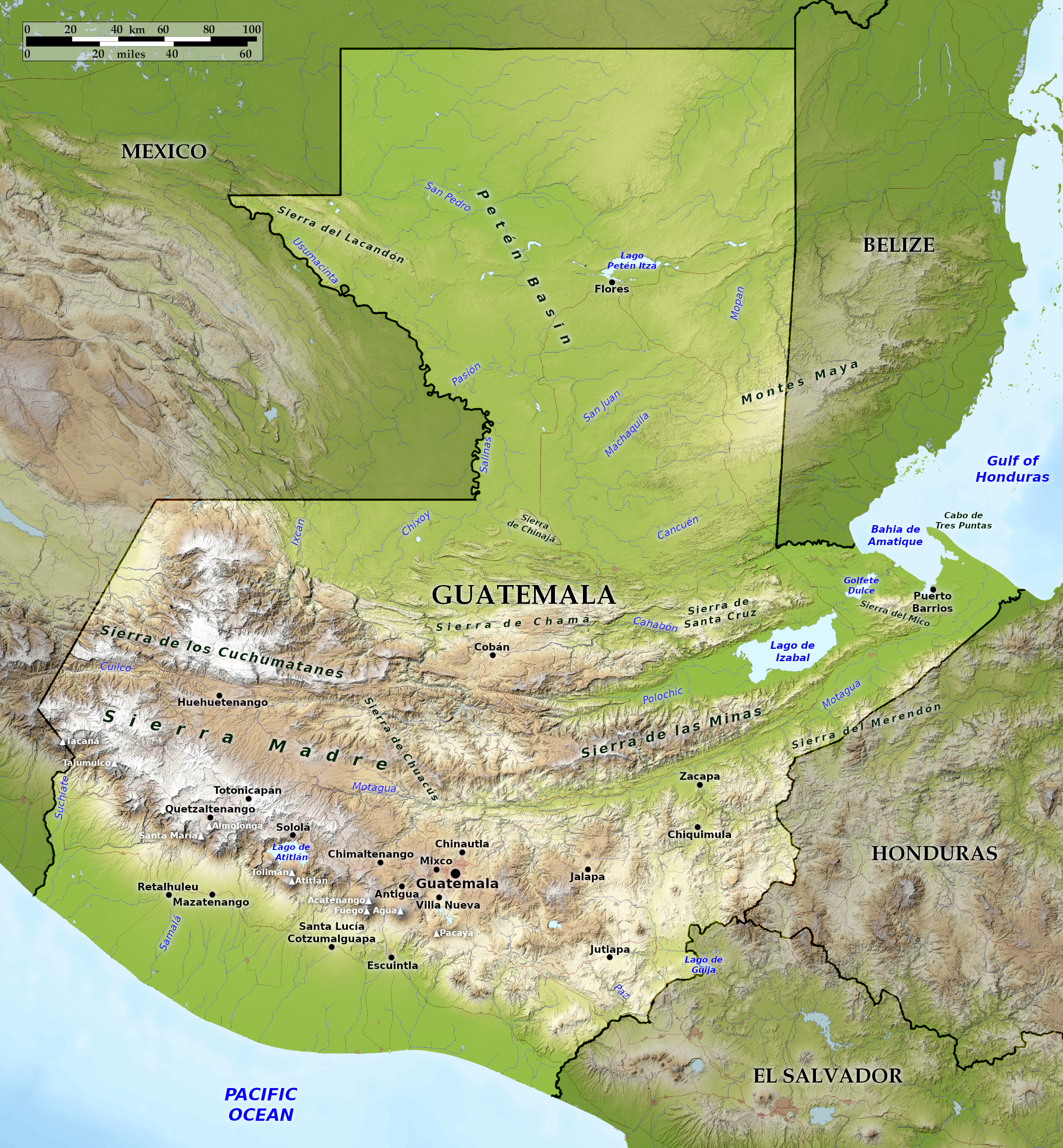 Relief map of Guatemala
Relief map of Guatemala
What is the landscape of Guatemala like?
Although Guatemala is entirely in the tropics, its varied terrain offers great contrasts. The climate ranges from hot and humid in most of the lowlands to cold, frost and occasional snow in the highlands.
Pacific Coast
Guatemala's Pacific coast has no natural harbors and the coastal waters are fairly shallow. Long black sandy beaches line the shore. Lagoons full of mangroves lie far inland from the beach. The coastal plain is predominantly savannah interspersed with forests lining the rivers that flow from the Highlands.
Further inland, tropical forests cover the foothills and lower slopes of the Highlands. The soils are well drained and fertile as they are composed of volcanic ash. The plain becomes a steeper, more dissected climb to the Highlands through upper Piedmont, 600 to 1,600 meters (2,000 to 5,250 feet) above sea level. Tropical broadleaf forests once covered these upper slopes. Rainfall is heavy, especially in the western part, where it averages over 2,500 millimeters (100 inches) annually. Most of the country's high-quality coffee is grown in this area, where the volcanic soil, heavy rainfall and many shady trees under which the coffee plants grow provide near-ideal conditions.
Highlands
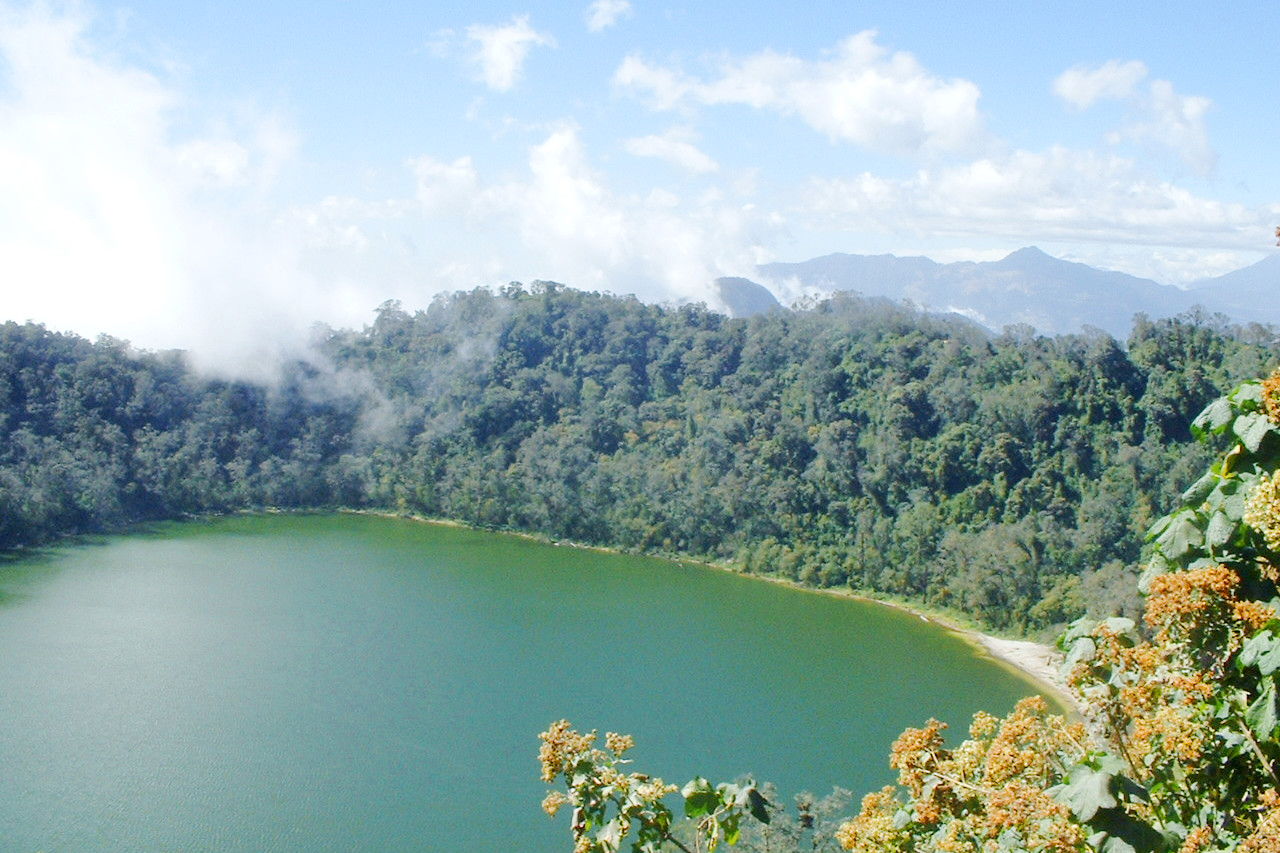
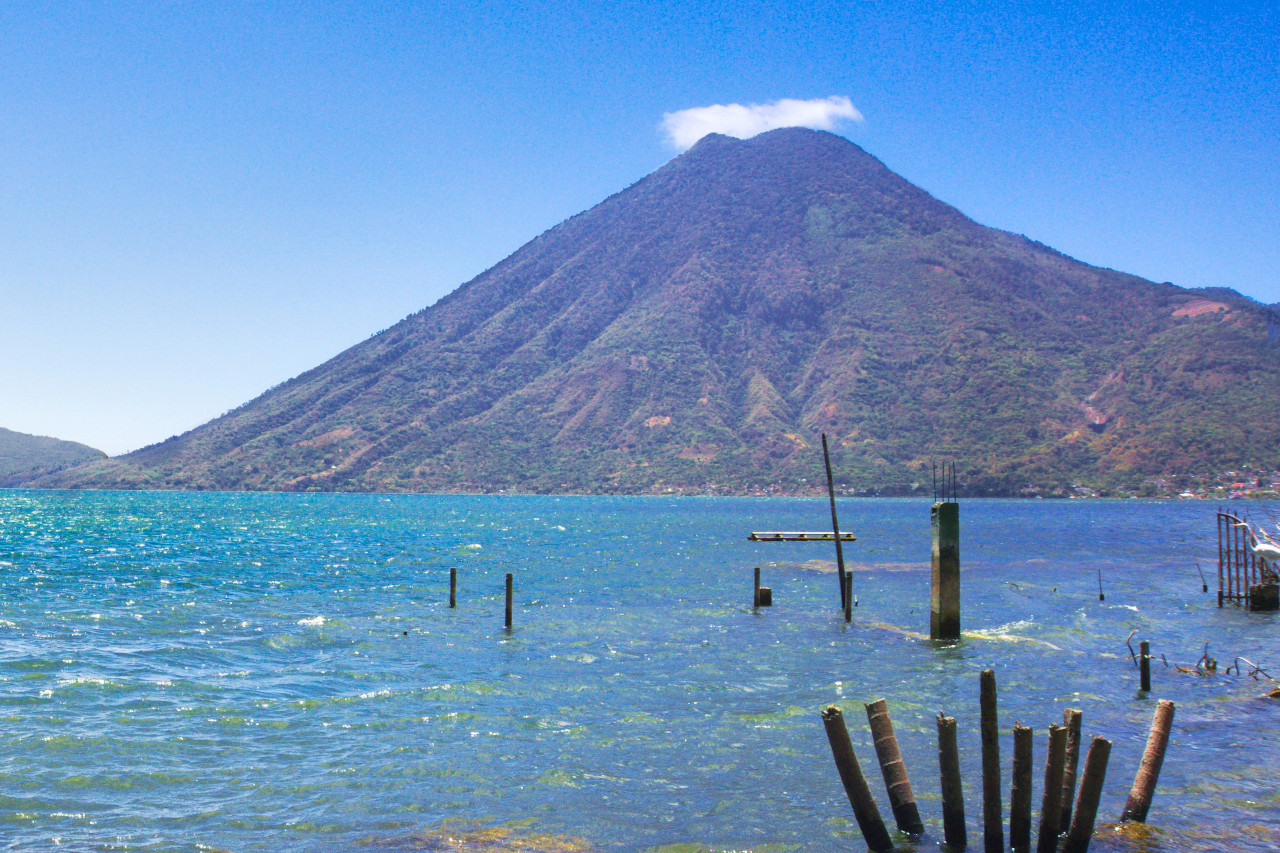
About half of the country is mountainous. The dominant mountain range is the Sierra Madre. which runs roughly parallel to the Pacific coast from the border with Mexico to El Salvador. There are 14 major volcanoes in this area, the two highest being Volcán Tajumulco at 4,203 meters (13,789 ft) and Volcán Tacaná at 4,060 meters (13,320 ft). Guatemala lies in an exceptionally seismic zone where five major tectonic plates meet: the American. Caribbean. Cocos, Nazca. and Pacific. Earthquakes are therefore frequent and sometimes violent.A series of rivers flow from the Sierra Madre to the Pacific Ocean. There are two important lakes within range. The Lago de Atitlán is considered one of the most beautiful in the world. The volcanoes Atitlán, San Pedro and Tolimán line its shores, as do numerous villages. The lake, some of which is more than 300 meters (1,000 feet) deep, is fed by several rivers. Lago Amatitlán south of Guatemala City is smaller and less spectacular. Steam rises from this warm-water lake, and healing sulfur springs are found near its shores.
Caribbean Coast and River Valleys
The coast along the Gulf of Honduras is flat and open to Caribbean storms. However, the 40 km (25 mile) long Bahía de Amatique is sheltered and on its shore is Puerto Barrios, as well as the smaller ports of Livingston and Santo Tomás de Castilla.
Tropical rainforest with deciduous evergreen trees covers much of the area except where modern plantations have been established. Three valley corridors extend inland from the coast. The valleys serve to connect the coast to various parts of the interior, particularly the Highlands, but the valley corridors are separated by mountain ranges.
Petén
The vast territory of Petén, which covers about a third of the national territory, extends into the Yucatan Peninsula. It is a hilly limestone plateau rising between 150 and 225 meters (500–750 ft) above sea level, covered with tropical rainforest interspersed with vast savannas. There are numerous small lakes that overflow and flood the country during particularly heavy rains. Most rivers flow either through Mexico into the Gulf of Mexico or through Belize into the Gulf of Honduras.
The Rio Salinas rises in Huehuetenango and flows north to contribute to the Rio Usumacinta. which empties into the Gulf of Mexico. The two rivers form part of the border between Mexico and Guatemala. Flores, the capital of Petén, is situated on an island in Lago Petén Itzá, which is about 24 kilometers (15 miles) long, three kilometers wide, and about 50 meters (165 feet) deep.
What is the nature of Guatemala like?
Guatemala’s Pacific coast is straight and open, with no natural harbors and relatively shallow offshore waters. Long stretches of black sand line the coast, flanked by mangrove swamps and a coastal plain farther inland. The Pacific coastal plain is predominantly savannah, predominantly flat and open to Caribbean storms.
Flowers of the highlands are found in great numbers. Of particular interest is the orchid family, which includes the white nun (monja blanca), the national flower. Indigenous fauna includes the armadillo, bear, coyote, deer, fox, jaguar, monkey, puma, tapir, and manatee. The national bird is the Resplendent quetzal, the symbol of love of liberty, which reputedly dies in captivity. There are more than 900 other species of native birds, as well as migratory varieties.
Northern Petén is home to Guatemala’s Maya Biosphere Reserve, a vast protected area comprising more than 13 percent of the country’s territory. This region contains critical habitat for rare tropical plants and animals, and is the largest single area of tropical rainforest in Central America.
What is the climate of Guatemala like?
See our main article: The Climate of Guatemala
The climate ranges from hot and humid in parts of the lowlands to very cold in the highlands, where frosts are common in some months and snow falls occasionally. Average annual temperatures at the coast range from 25°C to 30°C (77°F to 86°F); in the central highlands, they average 20°C (68°F); and in the higher mountain areas, they average 11°C (59°F).
The rainy season lasts from May through October inland, and into December along the coast; the dry season thus extends from November (or January) to April.
| Climate data for Guatemala City (1990-2011) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 24.3 (75.7) | 25.8 (78.4) | 26.8 (80.2) | 27.8 (82.0) | 27.1 (80.8) | 25.8 (78.4) | 25.4 (77.7) | 25.5 (77.9) | 25.1 (77.2) | 24.7 (76.5) | 24.2 (75.6) | 23.9 (75.0) | 25.5 (77.9) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 18.7 (65.7) | 19.7 (67.5) | 20.7 (69.3) | 21.9 (71.4) | 21.9 (71.4) | 21.3 (70.3) | 20.8 (69.4) | 21.0 (69.8) | 20.7 (69.3) | 20.3 (68.5) | 19.4 (66.9) | 18.8 (65.8) | 20.4 (68.7) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 13.2 (55.8) | 13.6 (56.5) | 14.6 (58.3) | 16.0 (60.8) | 16.8 (62.2) | 16.8 (62.2) | 16.3 (61.3) | 16.5 (61.7) | 16.4 (61.5) | 16.0 (60.8) | 14.7 (58.5) | 13.7 (56.7) | 15.4 (59.7) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 2.8 (0.11) | 5.4 (0.21) | 6.0 (0.24) | 31.0 (1.22) | 128.9 (5.07) | 271.8 (10.70) | 202.6 (7.98) | 202.7 (7.98) | 236.6 (9.31) | 131.6 (5.18) | 48.8 (1.92) | 6.6 (0.26) | 1,274.8 (50.18) |
| Source: Instituto Nacional de Sismologia, Vulcanologia, Meteorologia e Hidrología | |||||||||||||
 Plaza Park, Antigua Guatemala
Plaza Park, Antigua Guatemala
Guatemala
Heart of the Mayan World
| Location: | Central America, bordering the Pacific Ocean, between El Salvador and Mexico, and bordering the Caribbean Sea between Honduras and Belize |
| Coordinates: | 15° 30′ N, 90° 15′ W |
| Size: | • 455 km N-S; 430 km E-W • 280 miles N-S; 265 miles E-W |
| Terrain: | Two east-west mountain chains divide the country into three regions: the mountainous highlands, the southern Pacific coast, and the vast northern Peten lowlands |
| Climate: | Tropical; hot, humid in lowlands; cooler in highlands |
| Highest point: | Volcán Tajumulco 4,203 m / 13,789 ft |
| Forest: | 33.6% (2018 est.) |
| Population: | 17,703,190 (2022 est.) |
| Population density: | Medium (129/km²) |
| Capital: | Guatemala City |
| Languages: | Spanish (official) 69.9%, Maya languages 29.7% |
| Human Development Index: | Medium (0.627) |







