The Geography of
Maryland
Why visit Maryland?
Maryland offers such a wide variety of scenery out of all proportion to its area. The central feature of Maryland is Chesapeake Bay, the greatest inlet in the United States, with picturesque villages nestled among bluffs and sandy beaches. The rest of the State is very varied, and the west is quite rugged and mountainous.
Contents
Map
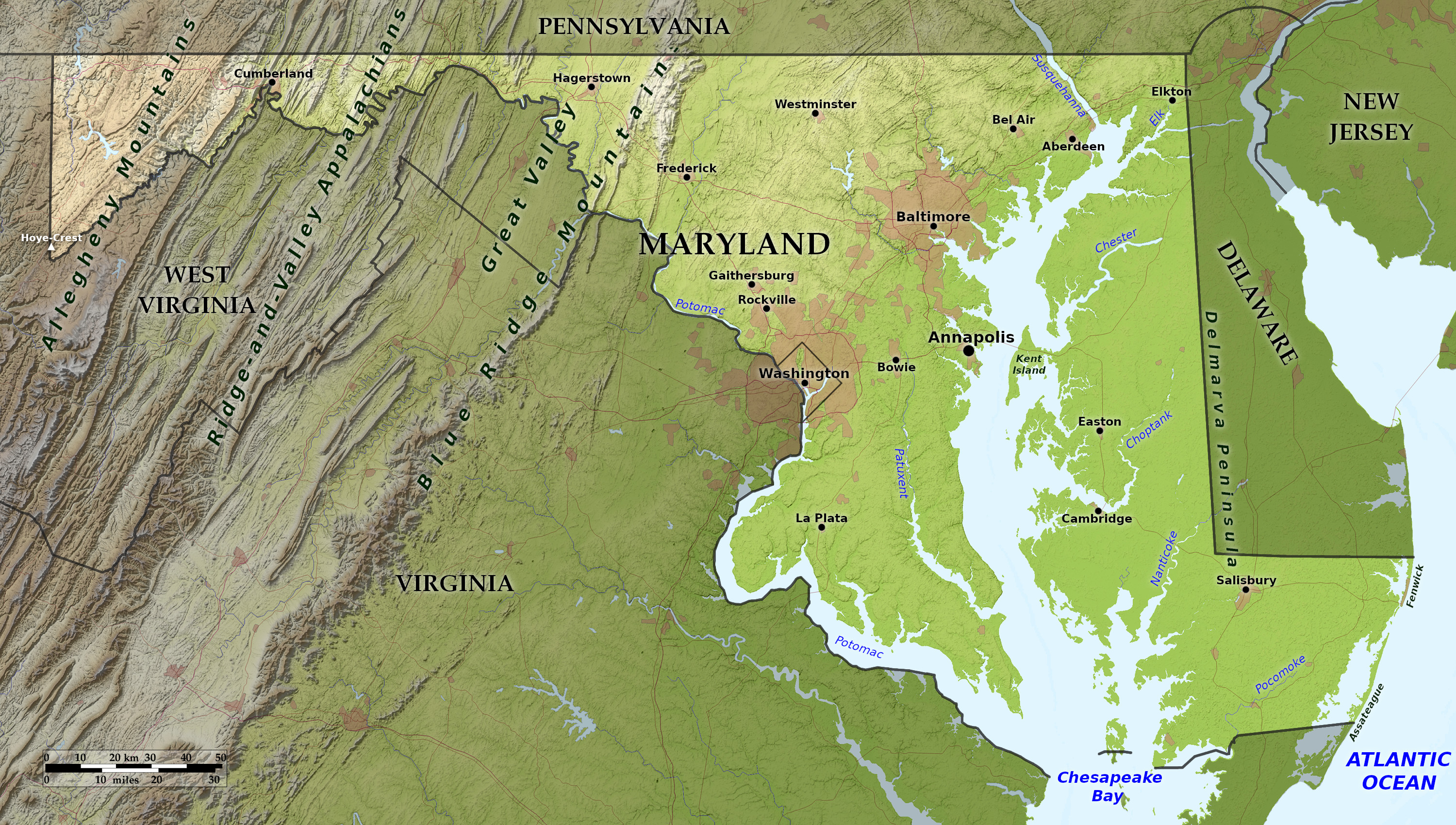 Relief map of Maryland
Relief map of Maryland
What is the landscape of Maryland like?
Coastal Plain
The Atlantic Coastal Plain is a level plain and the lowest part of the state. Along its entire Atlantic border extends a long, reef-like, sandy islands which enclose two shallow lagoons. The plain is bisected by the Chesapeake Bay, which divides Maryland into the Eastern Shore and the Western Shore. The eastern shore is low and level; most of it is less than 25 feet (8 m) above the sea. The western shore is higher, and rises to 300 feet (90 m) near Washington and Baltimore.
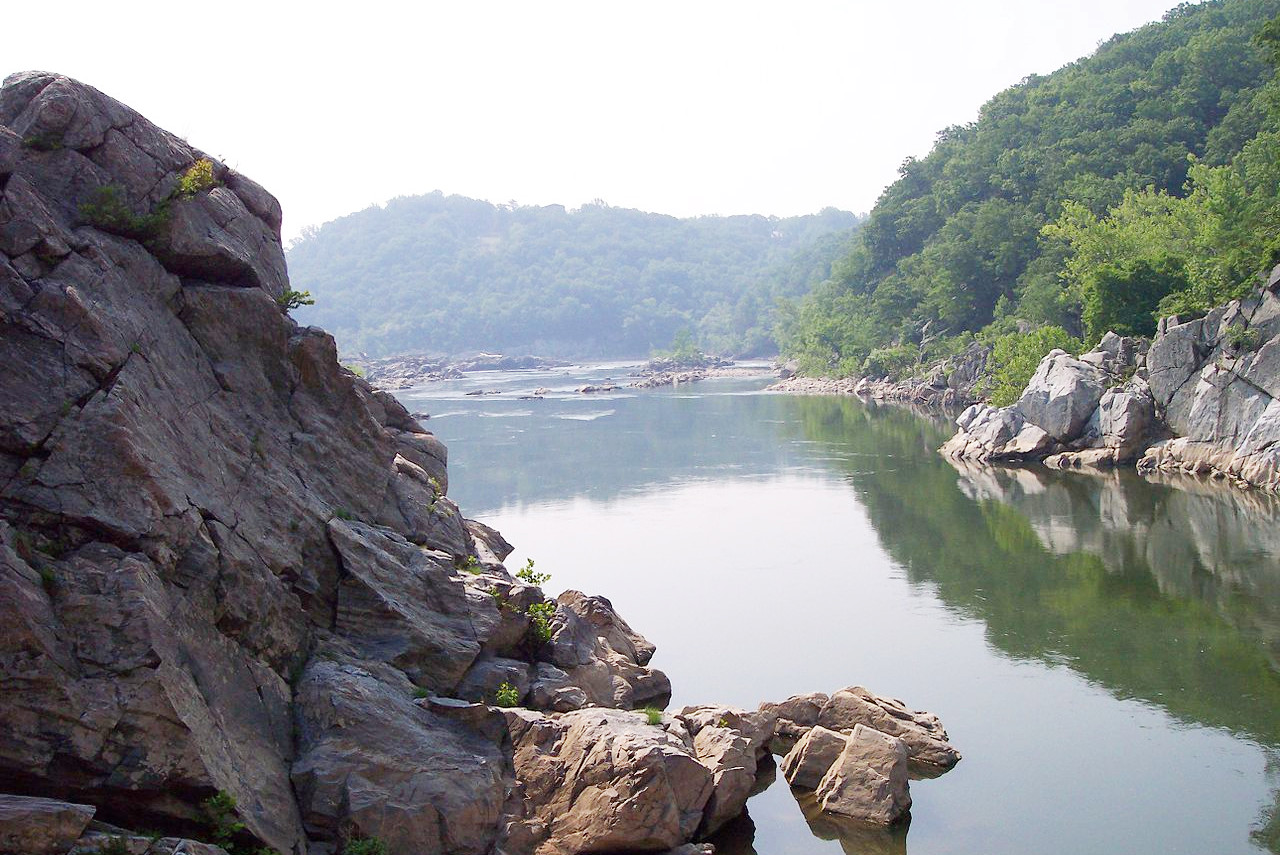
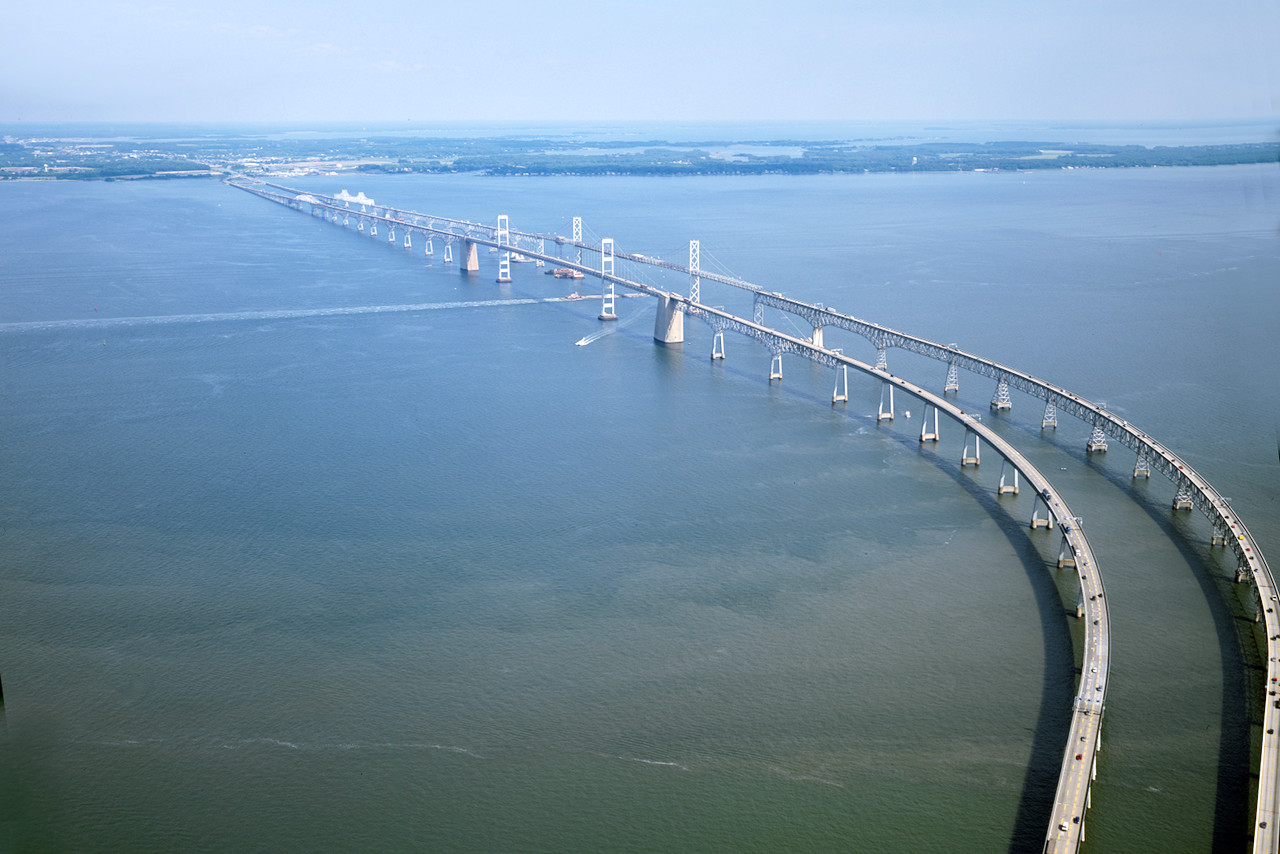
Chesapeake Bay is the most conspicuous feature of Maryland with its great system of estuaries, which extends 200 miles across the length of the State. It is from 10 to 40 miles wide and its numerous coves and estuaries cut the plain in every direction.
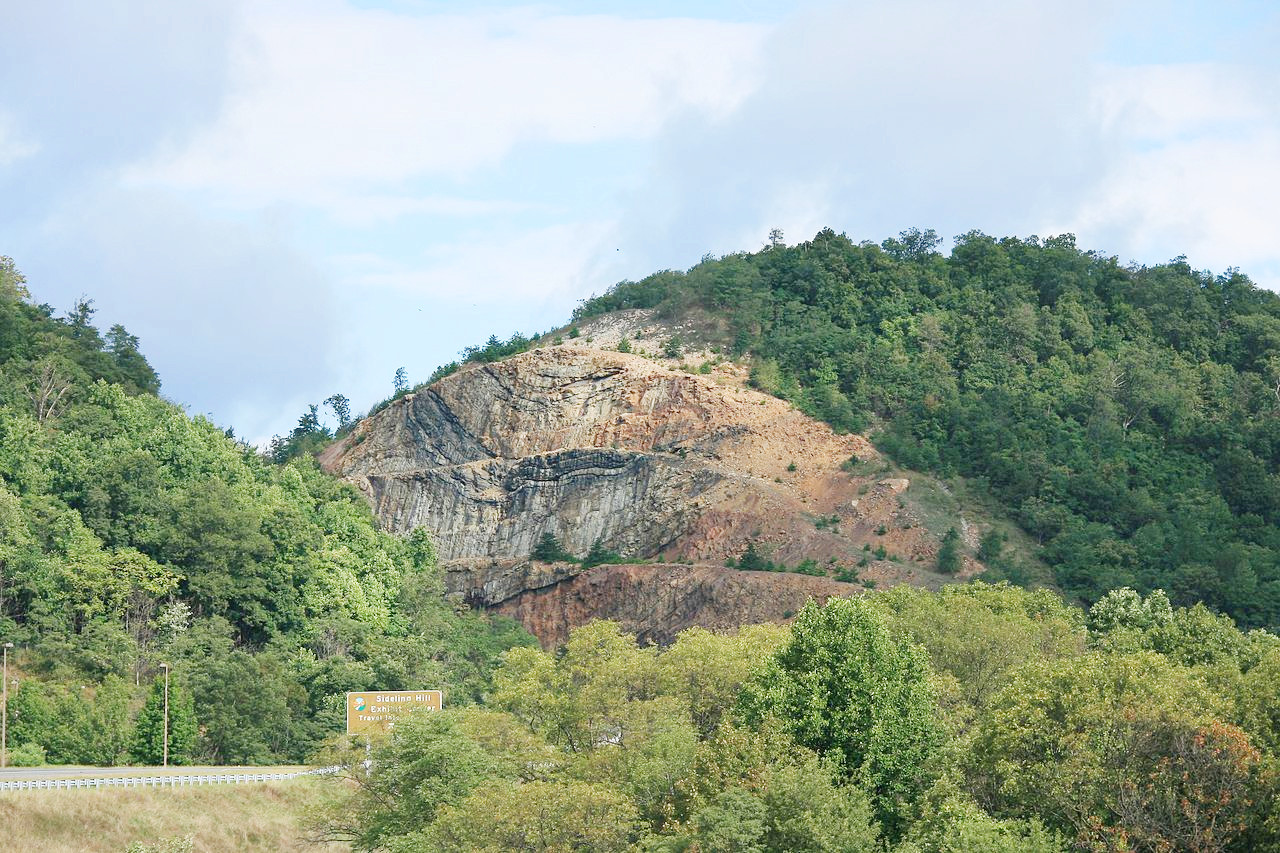
The Piedmont Plateau
West of the coastal lowlands, is a broad, rolling upland. This region is about 65 miles wide at the north and 40 miles wide at the south. The boundary with the lowlands is marked by several deep gorges cut by rivers forming waterfalls, cascades and rapids.
Mountains
Further west is the Appalachian Mountain region, containing the state's highest hills. To the eastward it abounds in mountains and valleys; to the westward it is a rolling plateau. The Appalachian Ridges are long, narrow, uniformly-sloping and level-crested mountains, extending along parallel lines from northeast to southwest. In the extreme west part of the state these mountains merge, as it were, into a rolling plateau, the Appalachian Plateau.
What is the nature of Maryland like?
The forests of Maryland include red and white oaks, yellow poplar, beech, blackgum, hickory, and white ash; shortleaf and loblolly pines are the main softwoods. Grape-vines and a large variety of berry-bushes grow wild and in abundance. Wooded hillsides are rich with wild flowers. The marshes and dunes are abundant in grasses and herbaceous plants.
The birdlife is exceedingly rich. Some of the species breeding along the marshes and beaches include: Gull-billed tern, Caspian tern, Forster's tern, least tern, black skimmer, king rail, clapper rail, willet, piping plover, Wilson's plover, saltmarsh sparrow, and the seaside sparrow.
What is the climate of Maryland like?
Although Maryland has a continental climate, it is greatly modified in the eastern portion of the state by the ocean and the Chesapeake Bay. In the south the normal winter is mild, the normal summer rather hot; in the west the normal winter is cold, the normal summer cool. The winters though are short and rarely severe, and there is rarely extreme heat in summer.
| Climate data for Annapolis (1981–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °F (°C) | 42.7 (5.9) | 45.5 (7.5) | 53.2 (11.8) | 63.9 (17.7) | 72.9 (22.7) | 81.6 (27.6) | 85.8 (29.9) | 84.0 (28.9) | 76.9 (24.9) | 66.3 (19.1) | 56.9 (13.8) | 46.8 (8.2) | 64.8 (18.2) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 36.5 (2.5) | 38.4 (3.6) | 45.7 (7.6) | 55.4 (13.0) | 65.1 (18.4) | 74.6 (23.7) | 79.0 (26.1) | 77.1 (25.1) | 71.1 (21.7) | 59.7 (15.4) | 49.3 (9.6) | 40.6 (4.8) | 57.7 (14.3) |
| Average low °F (°C) | 29.1 (−1.6) | 30.7 (−0.7) | 36.9 (2.7) | 45.8 (7.7) | 55.6 (13.1) | 66.4 (19.1) | 71.2 (21.8) | 69.1 (20.6) | 62.8 (17.1) | 50.5 (10.3) | 41.8 (5.4) | 31.9 (−0.1) | 49.4 (9.7) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 3.32 (84) | 2.94 (75) | 4.53 (115) | 3.66 (93) | 4.20 (107) | 4.17 (106) | 4.56 (116) | 3.88 (99) | 4.76 (121) | 3.89 (99) | 3.80 (97) | 3.56 (90) | 47.27 (1,202) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 4.4 (11) | 0.4 (1.0) | 0.3 (0.76) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.2 (0.51) | 0.8 (2.0) | 8.3 (21) |
| Source: NOAA | |||||||||||||
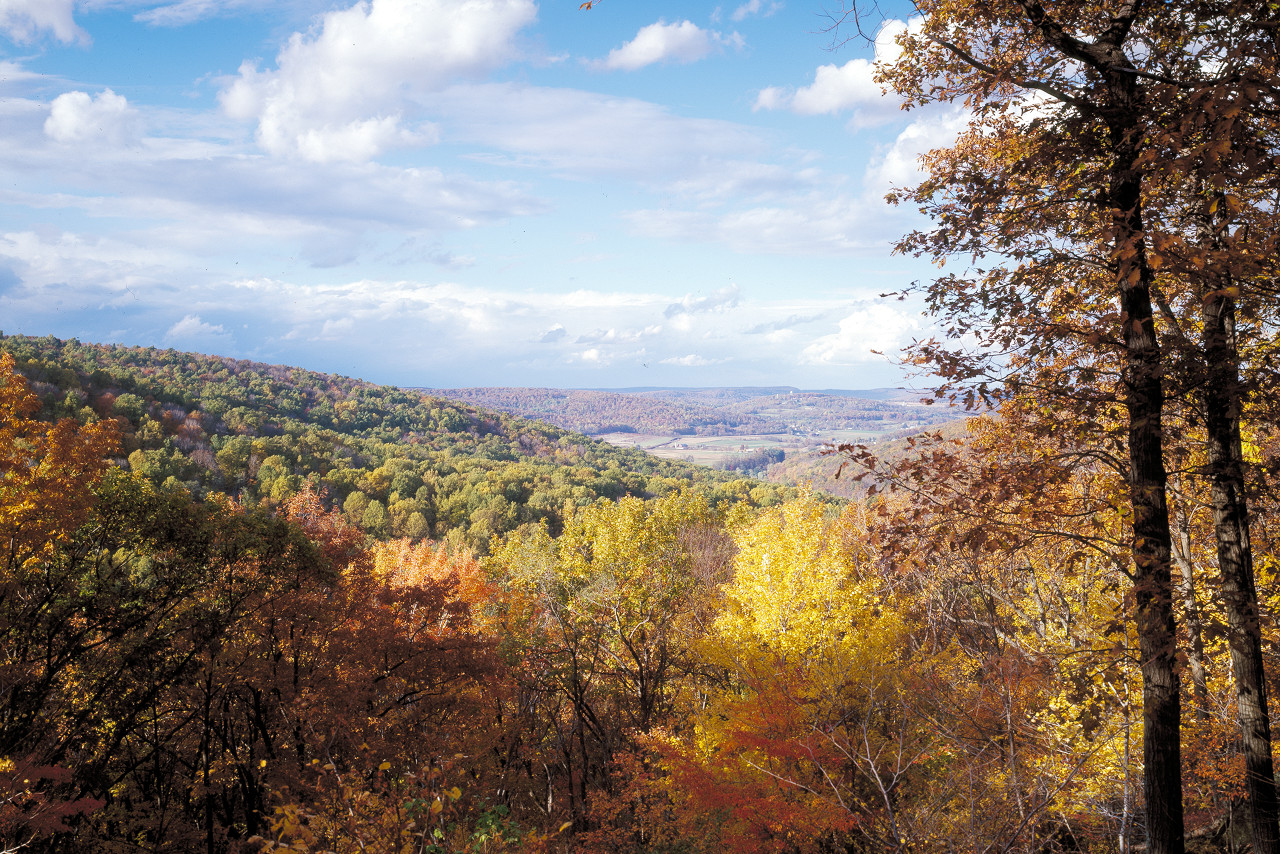 Catoctin Mountain Park in Maryland
Catoctin Mountain Park in Maryland
The official websites
Maryland
The Old Line State
| Location: | Eastern seaboard of the United States |
| Coordinates: | 39° 00′ N, 76° 45′ W |
| Size: | • 200 km N-S; 320 km E-W • 125 miles N-S; 200 miles E-W |
| Terrain: | Coastal plain bisected by Chesapeake Bay. Broad rolling hills inland. Appalachian Mountain region further west. |
| Climate: | Termperate climate in the east becoming cooler further west. Hot summers, cool winters with snow. |
| Highest point: | Hoye-Crest 1,020 m / 3,360 ft |
| Forest: | 39% (2016) (source) |
| Population: | 6,045,680 (2019) |
| Population density: | High (238/km²) |
| Capital: | Annapolis |
| Languages: | English |
| Human Development Index: | Very High (0.941) |






.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)