The Geography of
Michigan
Why visit Michigan?
Michigan is unique in many ways. From the rugged hills of the Huron and Porcupine Mountains in northern Michigan, to the vast coastlines of the Great Lakes—Superior, Michigan, Huron, and Erie. The nature is absolutely stunning, the forests are vast, and thousands of lakes of clear water, formed by glacial action, dot the surface of the state. All these things leave an impression that is impossible to forget.
Contents
Map
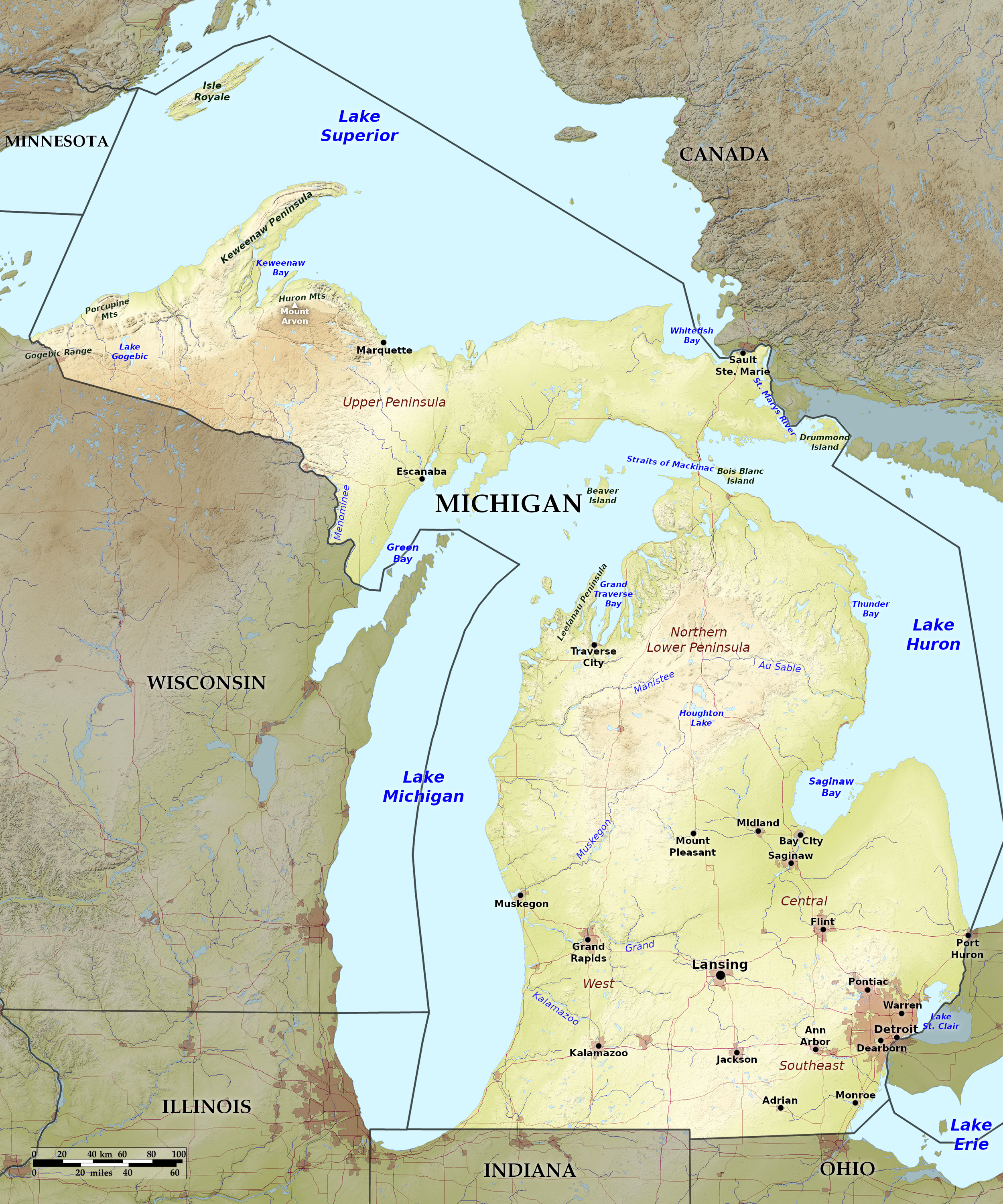 Relief map of Michigan
Relief map of Michigan
What is the landscape of Michigan like?
Michigan consists of two peninsulas—the Lower Peninsula, projecting northward between three of the Great Lakes, and the Upper Peninsula which projects eastwards.
Lower Peninsula
The north and northwest parts of the Lower Peninsula are occupied by a rolling plateau which attains an elevation at its highest point, of upwards of 1,700 feet (520 m). To the south of this plateau the land slopes gently down to the depression and to the low shores of Lake Michigan and Lake Huron.
Michigan has about 35,000 inland lakes and ponds, the largest of which is Houghton Lake on the Lower Peninsula, with an area of 31 square miles (80 square km). The state's leading river is the Grand River, about 260 miles (420 km) long, flowing through the lower peninsula into Lake Michigan. There are also sand dunes, which here and there rise to a height of from 100 to 200 feet (30–60 m) or more along the shore of Lake Michigan, and are formed by the west winds.
Upper Peninsula
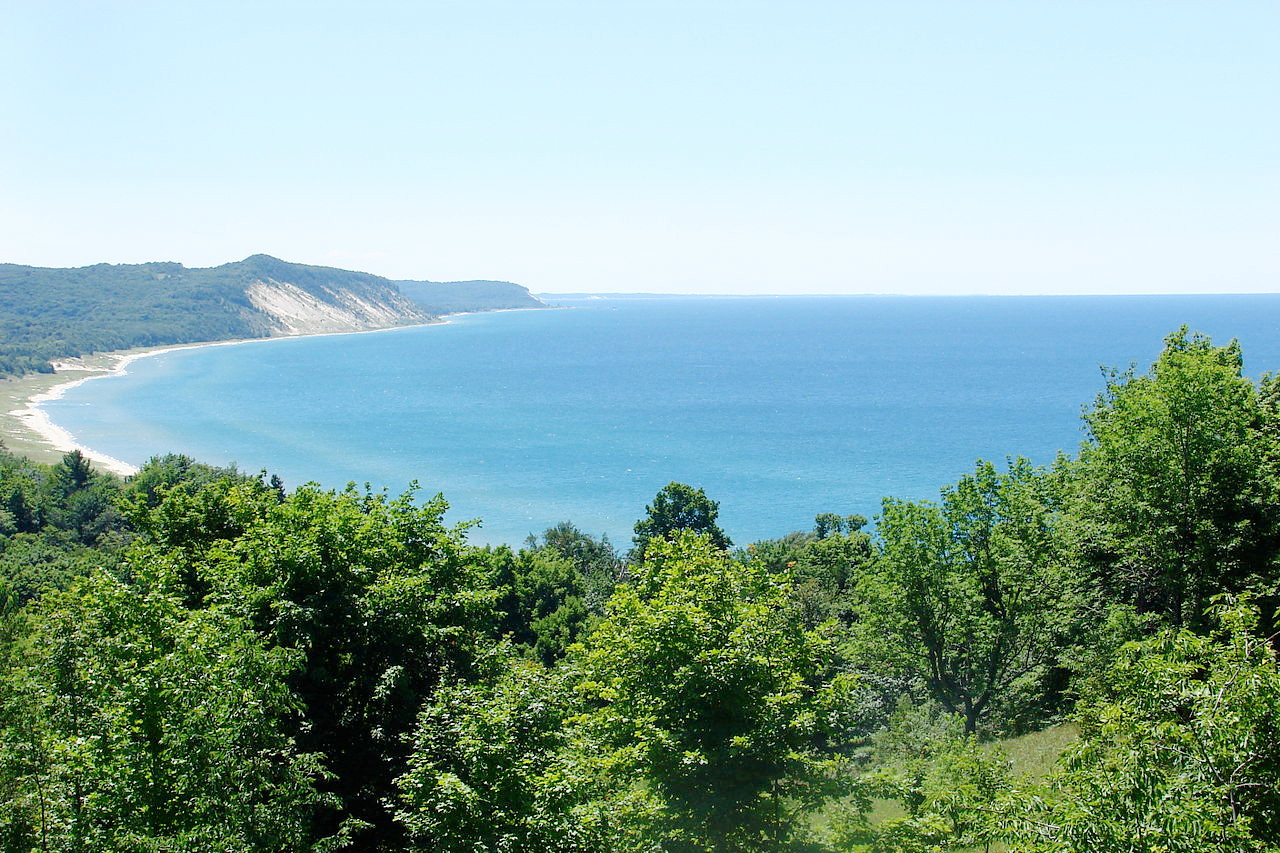
The surface of the upper peninsula is more irregular than that of the lower peninsula and the north-west part of the upper peninsula is rugged with hills and mountains. The famous Pictured Rocks on the lake shore of Lake Superior are a sandstone formation which extend for several miles along the coast; they rise almost vertically from the water's edge, and display a diversity of shapes as well as a great variety of tints and hues, especially of gray, blue, green and yellow. Tahquamenon Falls, in the eastern part of the upper peninsula, is the largest of the state’s more than 150 waterfalls.
The most rugged portion of the state is further west. South and southeast of Keweenaw Bay is an irregular area of mountains, hills, swamps and lakes. Some of the mountain peaks of the Huron Mountains rising to an elevation of 1,400 feet (425 m) or more above the lake. These are the highest hills in the state. The state's highest point, at 1,979 feet (603 m), is Mount Arvon.
Great Lakes
The two peninsulas of the State are nearly surrounded by the waters of the Great Lakes, providing a great length of shore line. Michigan's boundaries extend into four of the five Great Lakes, giving Michigan watch over parts of Lake Superior, Lake Michigan, Lake Huron, and Lake Erie.
Most of the many islands belonging to Michigan are located in northern Lake Michigan and in Lake Huron, although the largest, Isle Royale, about 44 miles (71 km) long, is found in northern Lake Superior. In northern Lake Michigan, Beaver Island is the largest, while Drummond Island, off the eastern tip of the upper peninsula, is the largest island in the northern Lake Huron area.
What is the nature of Michigan like?
Michigan is, to a considerable extent, a meeting place of the eastern deciduous hardwood forest and of the northern coniferous forest. Most of Michigan was once forest except in the southwest where there are small areas of prairie. The principal trees of the Upper Peninsula are maple, birch, hemlock, aspen, spruce, and fir; whereas maple, birch, aspen, pine, and beech predominate in the Lower Peninsula. Among forest shrubs are the willow, hazel, alder, shrub maple, birch, hawthorn, dogwood, elderberry, viburnum, and snowberry. Strawberries, raspberries, gooseberries, blueberries, and cranberries are among the fruit-bearing plants and shrubs that grow wild in many areas of the state.
What is the climate of Michigan like?
Michigan has a temperate climate with well-defined seasons. The warmest temperatures are found most generally in the southern part of the lower peninsula; cooler temperatures in the more northerly regions. July is invariably the warmest month, February the coldest, and heavy snows are recorded along the north shore of the Upper Peninsula. Michigan is cloudier than most states, in part because of the water vapor condensing from the Great Lakes.
| Climate data for Lansing, Michigan (1991−2020) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °F (°C) | 30.6 (−0.8) | 33.5 (0.8) | 44.4 (6.9) | 57.6 (14.2) | 69.4 (20.8) | 78.9 (26.1) | 82.8 (28.2) | 80.6 (27.0) | 73.6 (23.1) | 60.5 (15.8) | 47.0 (8.3) | 35.7 (2.1) | 57.9 (14.4) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 23.9 (−4.5) | 25.9 (−3.4) | 35.2 (1.8) | 47.0 (8.3) | 58.4 (14.7) | 68.0 (20.0) | 71.8 (22.1) | 70.0 (21.1) | 62.5 (16.9) | 50.8 (10.4) | 39.5 (4.2) | 29.5 (−1.4) | 48.5 (9.2) |
| Average low °F (°C) | 17.2 (−8.2) | 18.3 (−7.6) | 26.0 (−3.3) | 36.4 (2.4) | 47.5 (8.6) | 57.1 (13.9) | 60.9 (16.1) | 59.5 (15.3) | 51.5 (10.8) | 41.2 (5.1) | 31.9 (−0.1) | 23.3 (−4.8) | 39.2 (4.0) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 2.06 (52) | 1.71 (43) | 2.13 (54) | 3.26 (83) | 3.66 (93) | 3.76 (96) | 2.94 (75) | 3.48 (88) | 2.81 (71) | 3.16 (80) | 2.46 (62) | 1.90 (48) | 33.33 (847) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 14.3 (36) | 12.9 (33) | 5.9 (15) | 1.7 (4.3) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.2 (0.51) | 3.9 (9.9) | 11.3 (29) | 50.2 (128) |
| Source: NOAA | |||||||||||||
The official websites
Michigan
The Wolverine State
| Location: | Eastern north-central United States |
| Coordinates: | 44° 15′ N, 85° 30′ W |
| Size: | • 660 km N-S; 675 km E-W • 410 miles N-S; 420 miles E-W |
| Terrain: | Bordering the Great Lakes. Two peninsulas with generally level coastlands and hilly interiors |
| Climate: | Temperate climate with well-defined seasons. Warm summers and cold winters. |
| Highest point: | Mount Arvon 603 m / 1,979 ft |
| Forest: | 56% (2016) (source) |
| Population: | 9,883,635 (2019) |
| Population density: | Medium (67/km²) |
| Capital: | Lansing |
| Languages: | English (91%) |
| Human Development Index: | Very High (0.918) |


.jpg)
.jpg)


.jpg)