The Geography of
Minnesota
Why visit Minnesota?
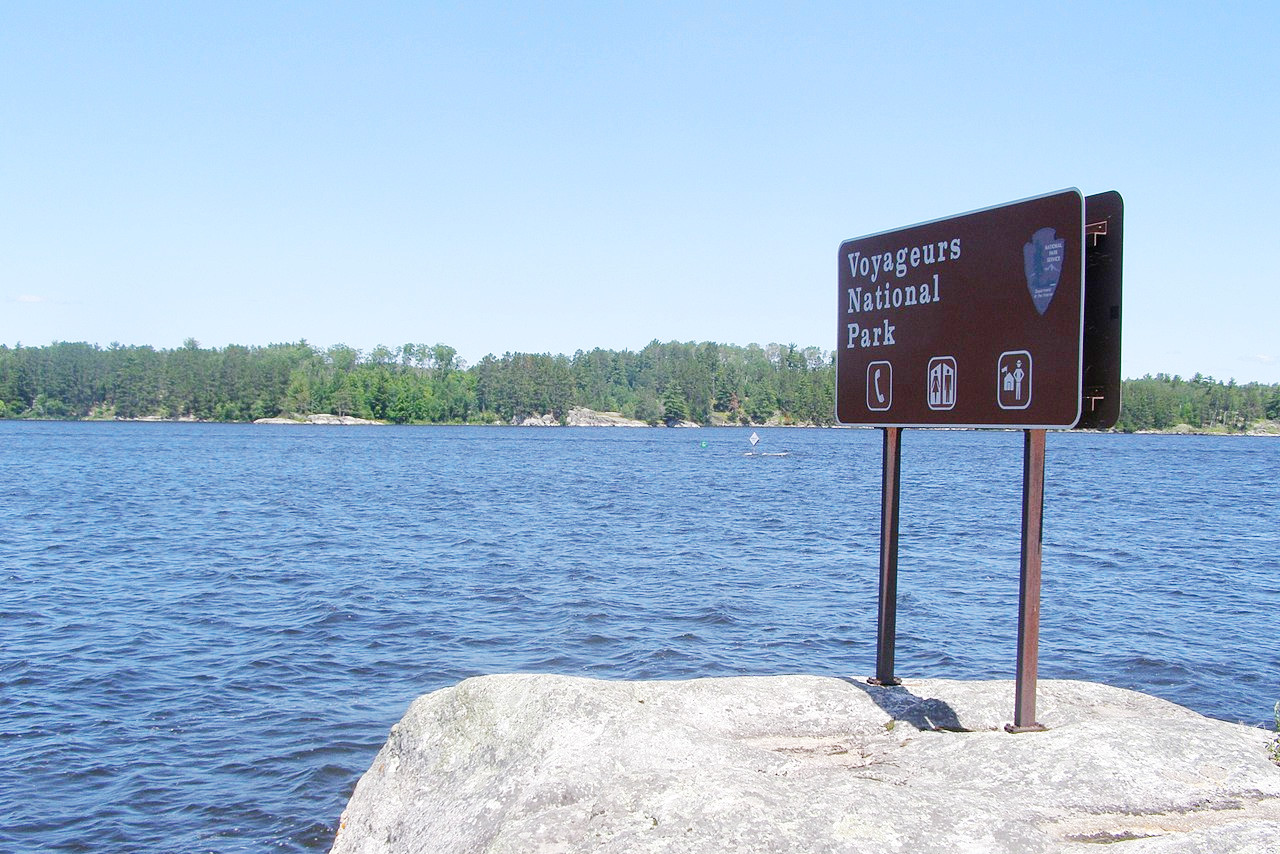
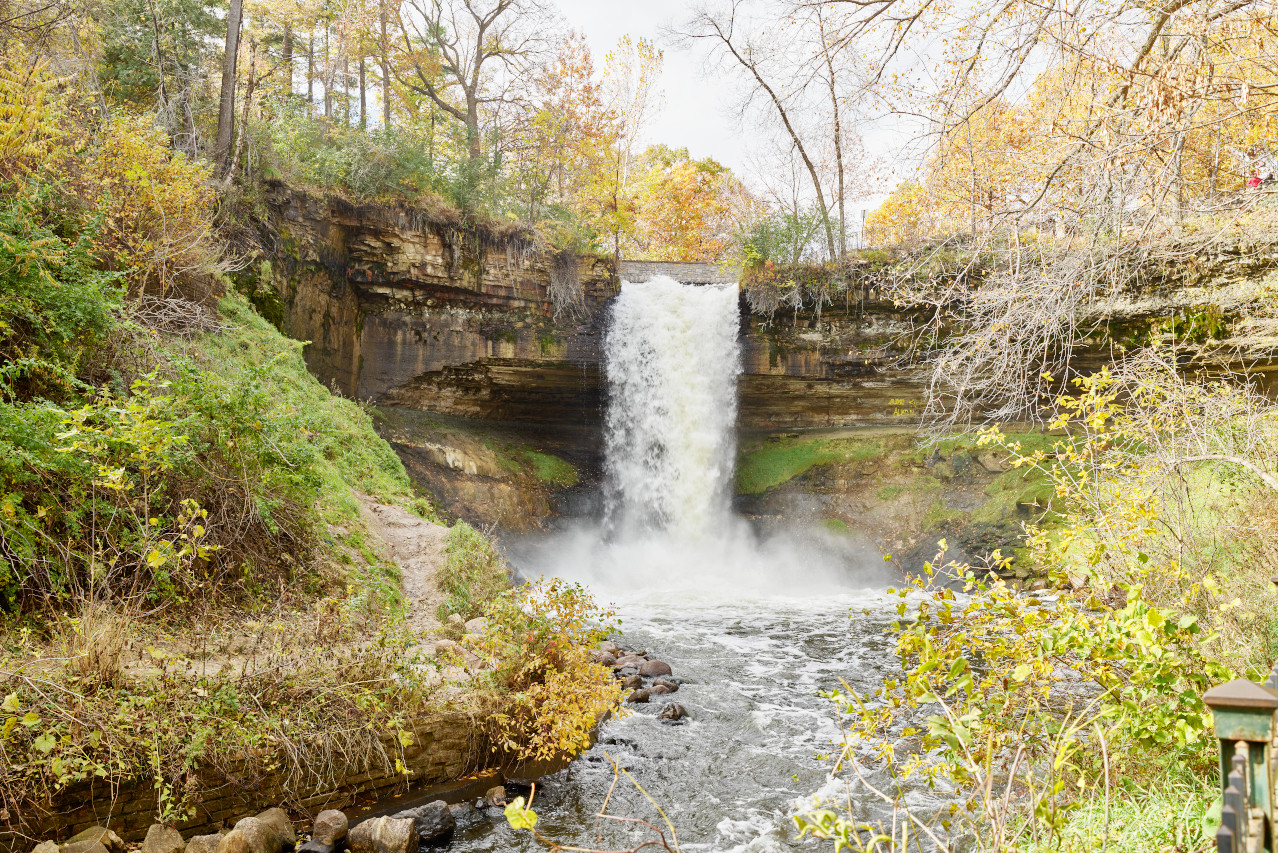
Minnesota is a great place to go out and explore. The lakes, the forests, and the rivers are all beautiful. Here can be found the sources of the Mississippi River and the Red River of the North; Voyageurs National Park near the Canadian border; Minnehaha Falls at Minneapolis; and more than 15,000 lakes.
Map
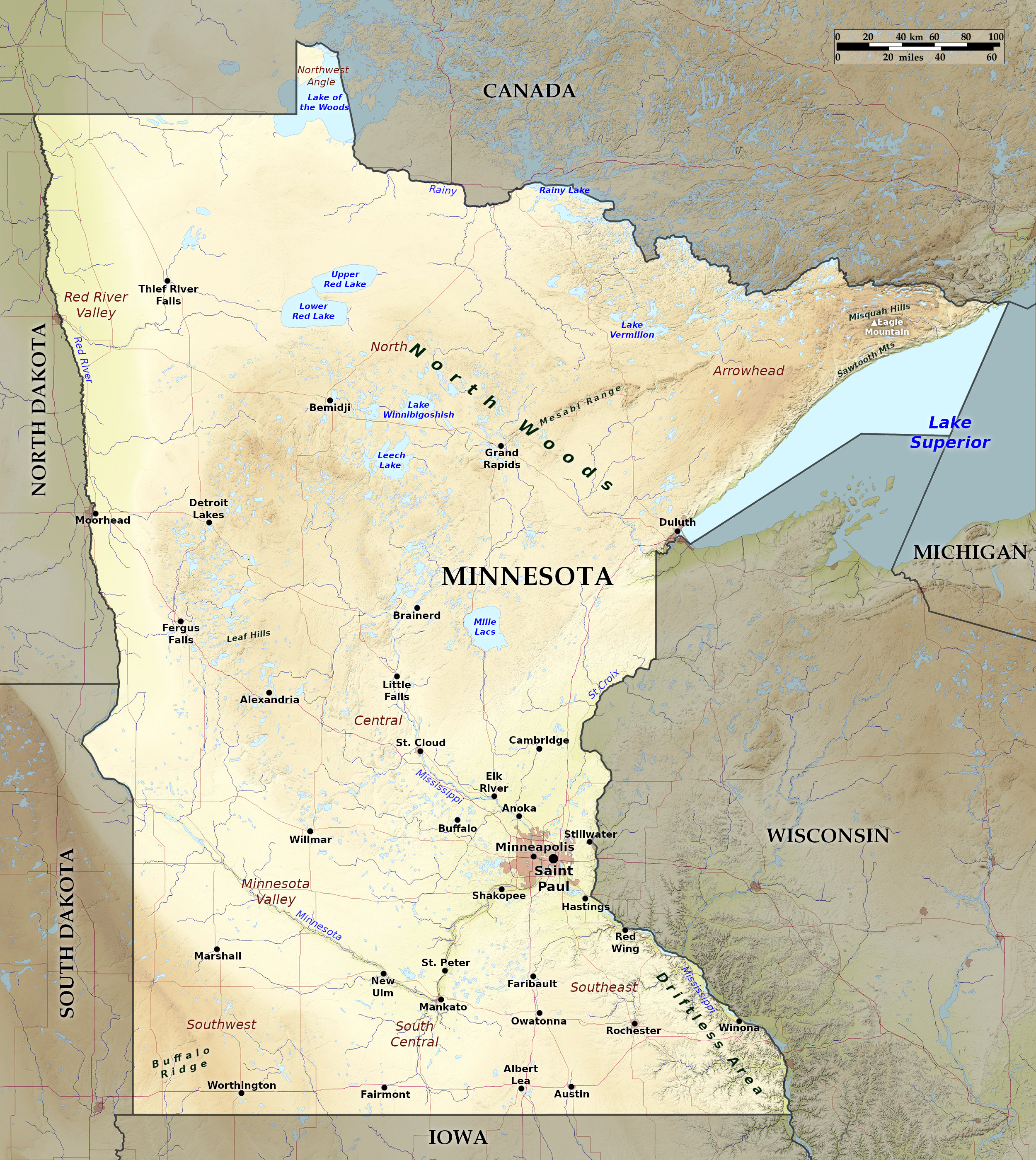 Relief map of Minnesota
Relief map of Minnesota
What is the landscape of Minnesota like?
Minnesota, lying at the northern rim of the Central Plains region lies around the head waters of the Mississippi River. It is largely prairie, with thousands of lakes; there are pine forests and rugged hills in the north.
North
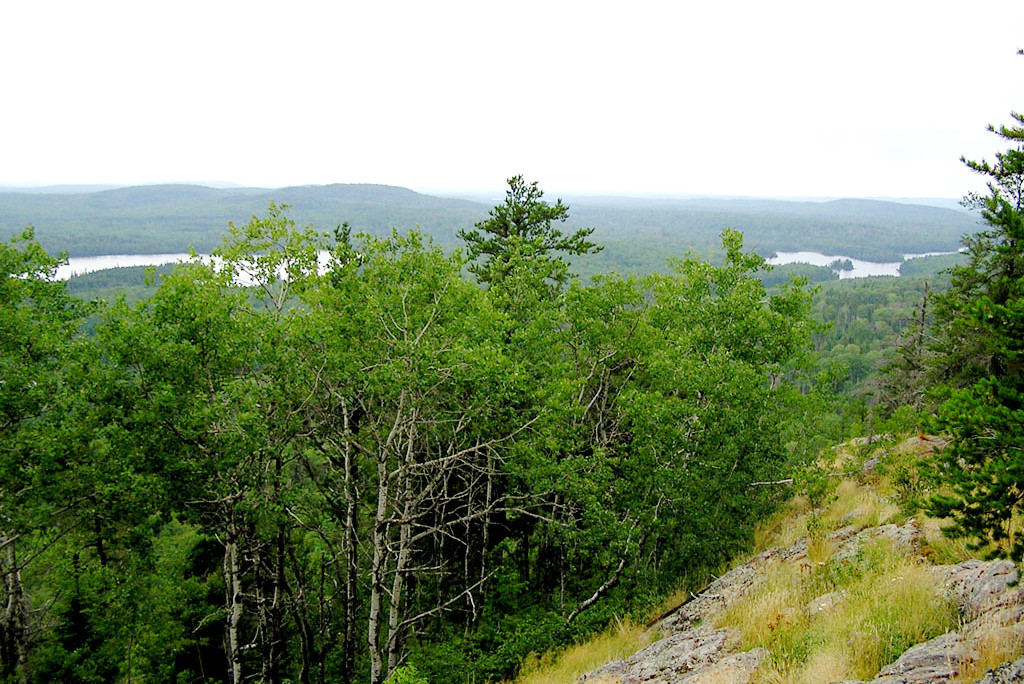
The north of the state is the great Minnesota pine belt which reaches from Lake Superior in the east all the way to the Red River valley on the western border. The northeast, known as Arrowhead Country, has the rugged hills of the Vermilion Range and the Mesabi Range, rising again in the extreme northeast corner, where the rugged granite uplift, known as the Misquah Hills, rises to a height of 2,301 ft (702 m) at Eagle Mountain, the highest point in the state. In the northwest part of Minnesota, embracing part of the Red River Valley of the North, the land is flat and even.
A very striking feature of the Minnesota landscape is the numerous glacial lakes estimated to number about 10,000 and ranging in size from a few acres in area to large bodies of water 15 to 35 miles in expanse. The lakes in the north differ from those of the south, being generally deep, with ragged rocky shores. On the northern boundary are two large lakes—the Lake of the Woods and Rainy Lake—both shared with Canada. In the northwest the ground slopes away to the level prairie reaches of the Red River valley. The Mississippi river, which flows for about 800 miles within or along the borders of the state, has its principal sources in and near Lake Itasca, a small glacial lake in north central Minnesota.
South
The southern and central portions of the State are chiefly rolling prairie. There are rolling hills and deep river valleys in the southeast, and a plateau in the southwest corner, where an altitude of 1,800 feet (550 m) is reached in the Coteau des Prairies. The southeast corner has a broken and hilly landscape where uplands alternate with numerous deeply eroded valleys running in various directions.
Most of Minnesota was covered by ice during the glacial ages. When the ice melted, it left behind a body of water known as Lake Agassiz, which extended into what we now call the Dakotas and Canada, leaving flat prairie in its wake. The glaciers also left behind the numerous shallow depressions that have developed into its modern-day lakes and streams.
The two principal tributaries of the Mississippi river are the St Croix and the Minnesota River. The St Croix, after having for about 135 miles formed the boundary between Wisconsin and Minnesota, enters the Mississippi at Hastings; the Minnesota, rising in Big Stone Lake on the western border, enters the Mississippi from the south-west between St Paul and Minneapolis after a course of about 450 miles.
What is the nature of Minnesota like?
Minnesota has two distinctive landscapes: the vast woodlands of its north and east give way to rolling prairie grasslands of the south and west. The northern part of the state was formerly covered with a dense growth of pine, and has supplied a large portion of the white pine utilized throughout the United States. Oak, maple, elm, birch, pine, ash, and poplar still grow in many places. Common shrubs include thimbleberry, sweetfern, and several varieties of honeysuckle. The pink and white (showy) lady slipper is the state flower. White and yellow water lilies cover the pond areas, with bulrushes and cattails on the shore.
What is the climate of Minnesota like?
Minnesota has a continental climate, with cold winters and warm summers. Nearly the whole state is usually covered with snow during the greater part of winter; although the dry atmosphere during the long winters considerably neutralizes the excessive cold.
Due to its higher latitude, Minnesota enjoys longer days in summer than states farther south; this fact, together with the abundant rainfall of early summer, accounts for the vigorous plant growth of Minnesota.
| Climate data for St. Paul, Minnesota (1991–2020) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °F (°C) | 23.9 (−4.5) | 28.7 (−1.8) | 41.7 (5.4) | 56.8 (13.8) | 68.9 (20.5) | 78.5 (25.8) | 82.6 (28.1) | 80.4 (26.9) | 72.4 (22.4) | 58.0 (14.4) | 42.1 (5.6) | 28.6 (−1.9) | 55.2 (12.9) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 16.3 (−8.7) | 20.8 (−6.2) | 33.1 (0.6) | 47.0 (8.3) | 58.9 (14.9) | 68.8 (20.4) | 73.3 (22.9) | 71.1 (21.7) | 62.9 (17.2) | 49.0 (9.4) | 34.6 (1.4) | 21.7 (−5.7) | 46.5 (8.1) |
| Average low °F (°C) | 8.6 (−13.0) | 12.9 (−10.6) | 24.6 (−4.1) | 37.2 (2.9) | 48.9 (9.4) | 59.2 (15.1) | 64.0 (17.8) | 61.7 (16.5) | 53.4 (11.9) | 40.0 (4.4) | 27.1 (−2.7) | 14.8 (−9.6) | 37.7 (3.2) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 0.48 (12) | 0.52 (13) | 1.43 (36) | 2.58 (66) | 3.97 (101) | 4.63 (118) | 3.97 (101) | 4.10 (104) | 3.08 (78) | 2.47 (63) | 1.32 (34) | 0.65 (17) | 29.20 (742) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 11.0 (28) | 9.5 (24) | 8.2 (21) | 3.5 (8.9) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.8 (2.0) | 6.8 (17) | 11.4 (29) | 51.2 (130) |
| Source: NOAA | |||||||||||||
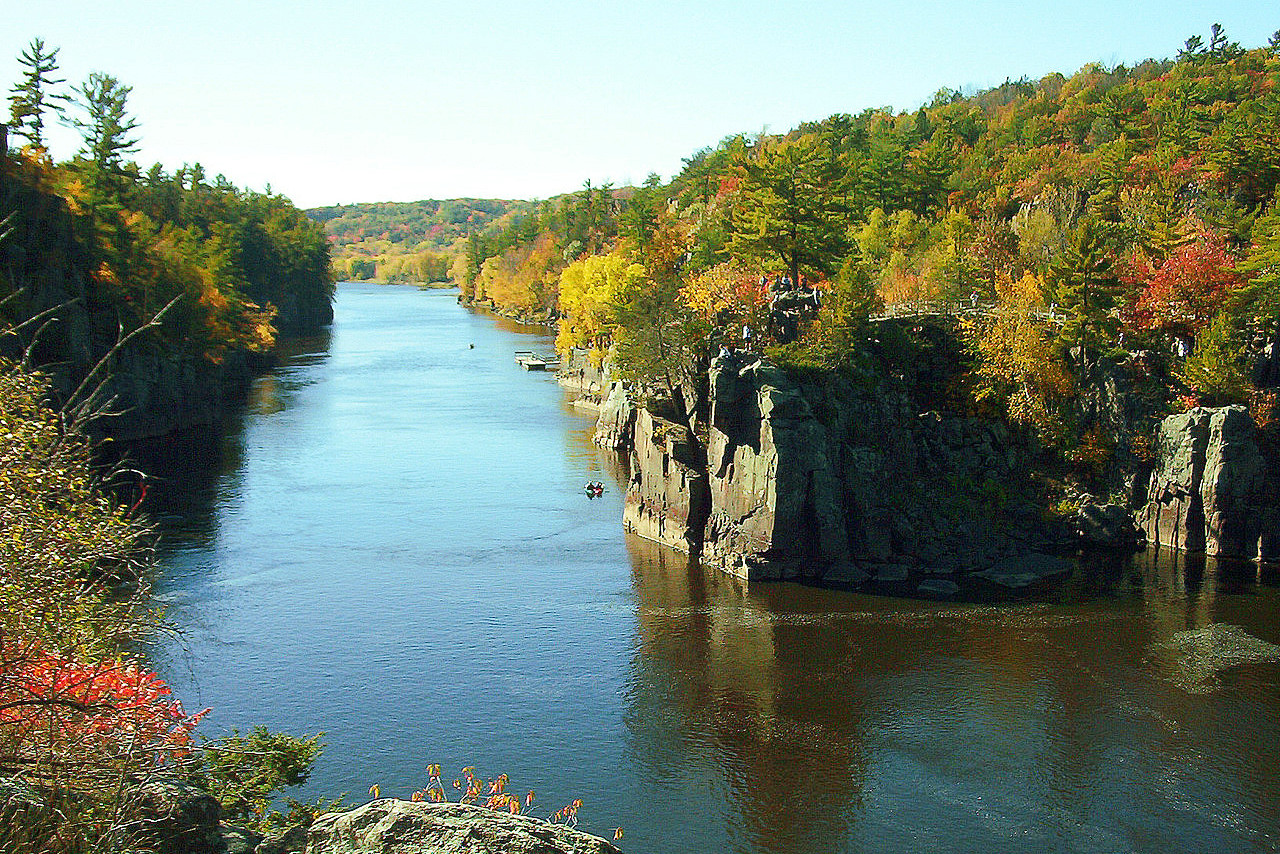
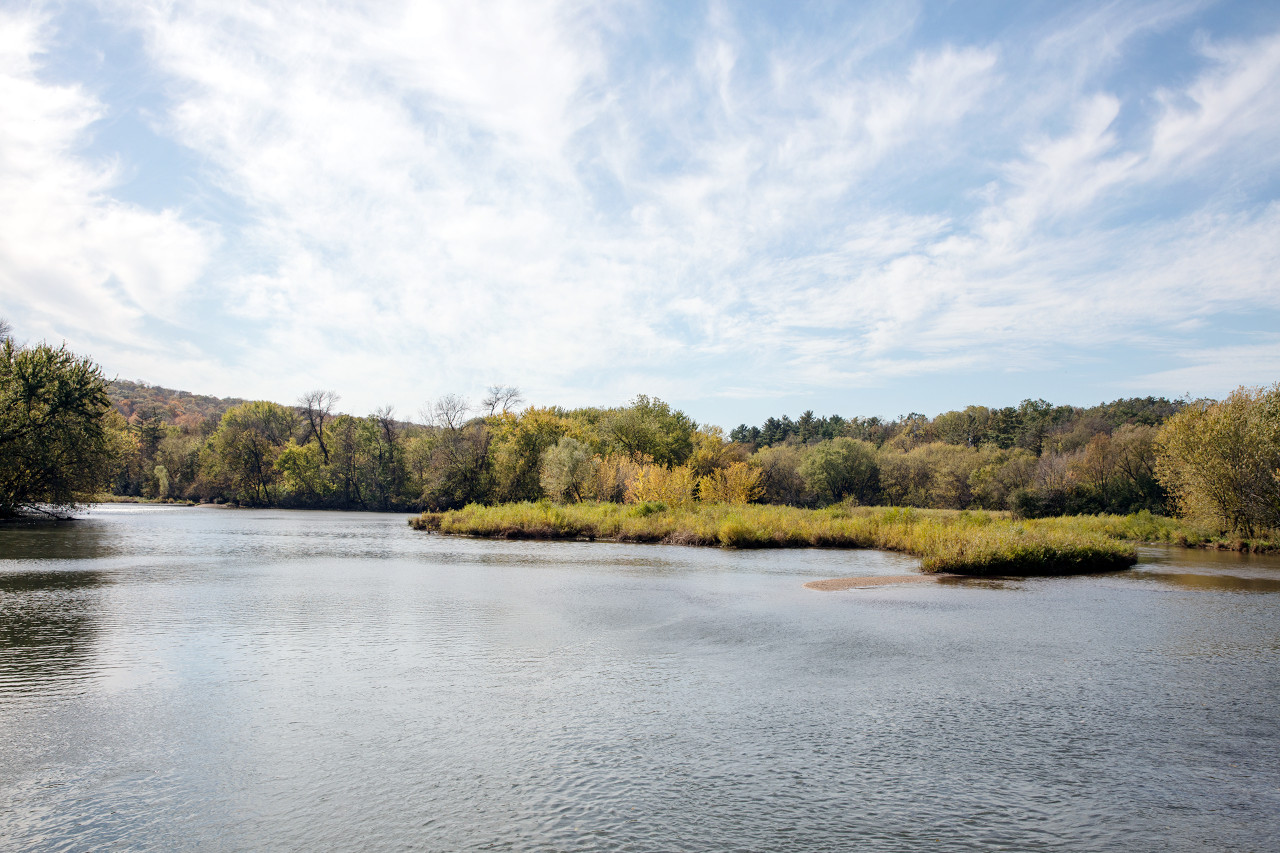 River view from Rochester, Minnesota
River view from Rochester, Minnesota
The official websites
Minnesota
The Gopher State
| Location: | Western north-central United States |
| Coordinates: | 46° 15′ N, 94° 15′ W |
| Size: | • 650 km N-S; 575 km E-W • 405 miles N-S; 360 miles E-W |
| Terrain: | Flat prairie and forest; rolling hills and valleys in parts of the south; rugged hills in the northeast |
| Climate: | Continental climate: warm summers and cold, snowy winters. |
| Highest point: | Eagle Mountain 701 m / 2,301 ft |
| Forest: | 34% (2016) (source) |
| Population: | 5,639,632 (2019) |
| Population density: | Low (27/km²) |
| Capital: | Saint Paul |
| Languages: | English (89%) |
| Human Development Index: | Very High (0.953) |

.jpg)
.jpg)

.jpg)



.jpg)

.jpg)